
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Purity of the ester: use the colour of the product and the information from the infrared spectrum to assess the purity of the ester.
The color of product was yellow.
Was orang Odour made with acetic acid on a 0.10 molar ratio and 1-Octanol 0.05 molar ratio.
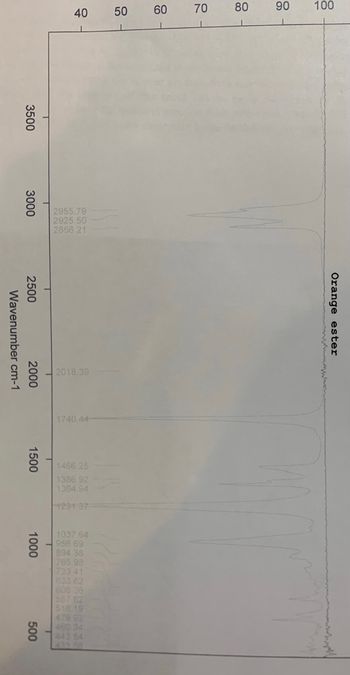
Transcribed Image Text:100
90
80
70
60
50
40
3500
3000
Orange ester
2018.39
2500
2000
Wavenumber cm-1
1466.25
1500
1000
500
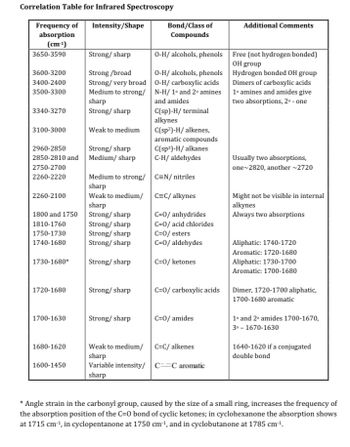
Transcribed Image Text:Correlation Table for Infrared Spectroscopy
Frequency of Intensity/Shape
absorption
(cm-1)
3650-3590
3600-3200
3400-2400
3500-3300
3340-3270
3100-3000
2960-2850
Strong/sharp
2850-2810 and Medium/ sharp
2750-2700
2260-2220
2260-2100
Medium to strong/
sharp
Weak to medium/
sharp
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
1730-1680* Strong/sharp
1800 and 1750
1810-1760
1750-1730
1740-1680
1720-1680
1700-1630
Strong/sharp
Strong/broad
Strong/ very broad
Medium to strong/
sharp
Strong/sharp
1680-1620
Weak to medium
1600-1450
Strong/sharp
Strong/sharp
Bond/Class of
Compounds
O-H/ alcohols, phenols
O-H/ alcohols, phenols
O-H/ carboxylic acids
N-H/ 1° and 2° amines
and amides
C(sp)-H/ terminal
alkynes
C(sp²)-H/alkenes,
aromatic compounds
C(sp³)-H/ alkanes
C-H/ aldehydes
C=N/nitriles
C=C/ alkynes
C=0/anhydrides
C=0/ acid chlorides
C=0/esters
C=0/ aldehydes
C=0/ ketones
C=0/amides
Additional Comments
Weak to medium/
C=C/ alkenes
sharp
Variable intensity/ C=C aromatic
sharp
Free (not hydrogen bonded)
OH group
Hydrogen bonded OH group
Dimers of carboxylic acids
1° amines and amides give
two absorptions, 2⁰ - one
Usually two absorptions,
one-2820, another -2720
Might not be visible in internal
alkynes
Always two absorptions
Aliphatic: 1740-1720
Aromatic: 1720-1680
C=0/ carboxylic acids Dimer, 1720-1700 aliphatic,
1700-1680 aromatic
Aliphatic: 1730-1700
Aromatic: 1700-1680
1° and 2° amides 1700-1670,
3⁰-1670-1630
1640-1620 if a conjugated
double bond
* Angle strain in the carbonyl group, caused by the size of a small ring, increases the frequency of
the absorption position of the C=0 bond of cyclic ketones; in cyclohexanone the absorption shows
at 1715 cm-¹, in cyclopentanone at 1750 cm-¹, and in cyclobutanone at 1785 cm-¹.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Why is part D only 0.2mol? Why can't 0.4mol be made?arrow_forward3arrow_forwardAlcohols A and B formed layers with Lucas reagent within 10 minutes. However, compound A formed brown precipitate with KMnO4 while compound B did not. Which are the possible identities of compounds A and B? a. isopropanol and tert-butanol b. ethanol and methanol c. propanol and tert-butanol d. isopentyl alcohol and isopropanolarrow_forward
- A student left some alkyl halides (RC1 and RBr) in an open container for several minutes. What happened to the composition of the halide mixture during that time? Assume that some liquid remains in the container.arrow_forward6. Make a table with the physical properties (molecular mass, b.p., m.p., density, solu- bility, flammability [for solvents only], and toxicity/hazards) of caffeine, methylene chloride, calcium carbonate, acetone, and petroleum ether.arrow_forward12. 1,2-dibromobutane + 2 eq NaNH, / THF then H,SO, / water with heating à a. 1-butene b. 2-butanol c. 2-butanone d. 2-bromo-1-butanol е. something else!! 13. ethene + Br, / H,O à a. ethanol b. 2-bromoethanol c. ethanediol d. 1-bromoethane е. something else!! For 2/3 of a point: arrange these in order of increasing basicity; be sure to show this on the back-side of your scantron!! HSO, , OH , NH, , sodium acetate, LICH, , sodium phenoxide, sodium ethoxidearrow_forward
- You are asked by your chemistry teacher to find: a) the solubility of different carboxylic acids in water and b) whether there is a connection between solubility and structure of different carboxylic acids. Follow the questions below to design and conduct an experiment to determine an answer to this question. a. From the paragraph above, write a question out that you will try and answer from conducting an experiment (C:2) b. Based upon your knowledge of the physical properties of organic compounds, hypothesize an order of solubility from lowest to highest: (1:3) Organic Compound Order of solubility (1=lowest, 3=highest) Pentanoic acid Hexanoic acid Ethanoic acid c. Provide an overall explanation for your hypothesis based upon your knowledge of physical properties. (A:3) d. Based upon the materials listed below, design a step by step experiment to test your hypothesis. Provide your individual steps. Include all the materials listed below. (1:3) Materials: CH,(CH,4COOH (), CH,COOH (),…arrow_forwardQuestion 4 (b). Chlorobenzene, also known as monochlorobenzene, benzene chloride, chlorobenzol, and phenyl chloride, is used in the production of chloronitrobenzene and diphenyl ether, in rubber intermediates; as a solvent in adhesives, paints, waxes, and polishes; and as an inert solvent. Ms Bontle Makgatho, a Bsc I student at Sefako Makgatho Health Sciences University is doing an internship at SKY PAINT, a company based in Gezina, Pretoria North. One of her duties involves the synthesis of Chlorobenzene using benzene as a starting material. (i). Draw a step wise mechanism for the synthesis of chlorobenzene using Benzene as the starting material (ii). Benzene is a well-known aromatic compound, what are the characteristic of an aromatic compound (list four) Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY