
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
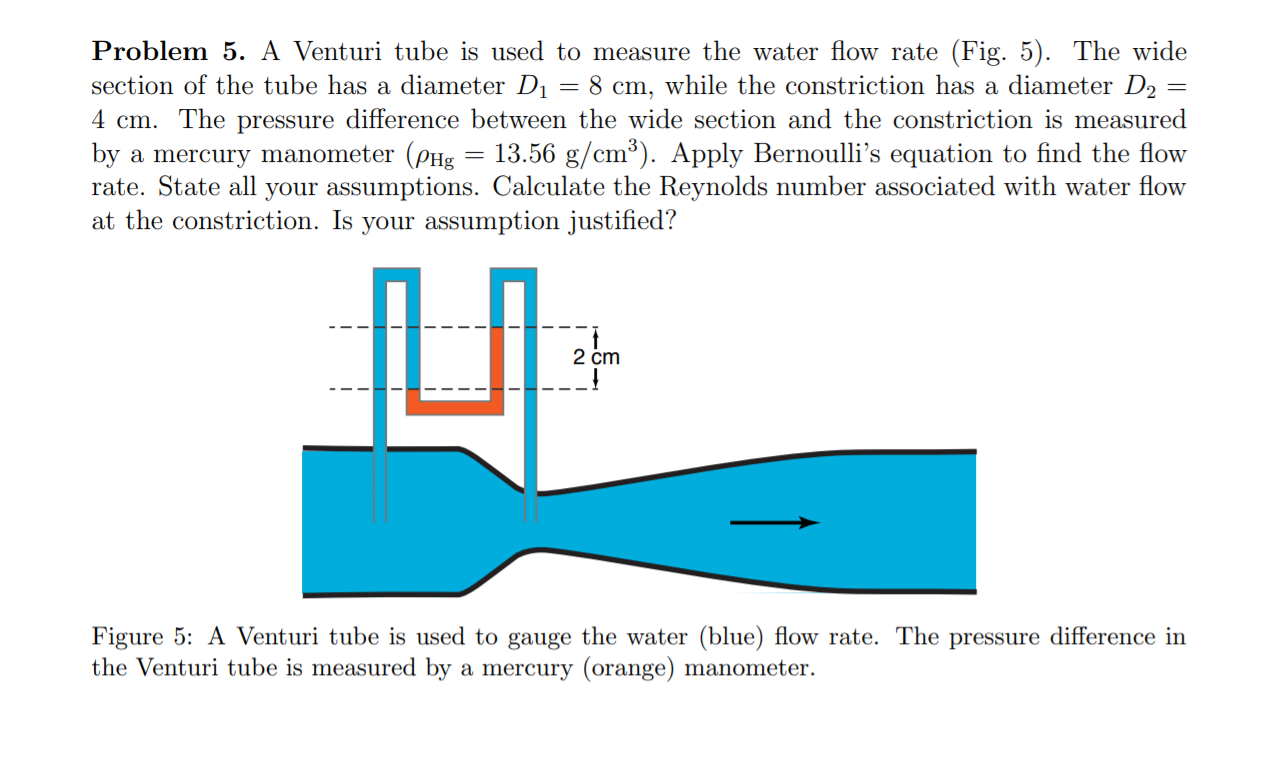
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 5. A Venturi tube is used to measure the water flow rate (Fig. 5). The wide
section of the tube has a diameter D1 = 8 cm, while the constriction has a diameter D2
4 cm. The pressure difference between the wide section and the constriction is measured
by a mercury manometer (PHg
rate. State all your assumptions. Calculate the Reynolds number associated with water flow
at the constriction. Is your assumption justified?
13.56 g/cm³). Apply Bernoulli's equation to find the flow
2 cm
Figure 5: A Venturi tube is used to gauge the water (blue) flow rate. The pressure difference in
the Venturi tube is measured by a mercury (orange) manometer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A differential "U"-tube manometer containing mercury of density 13000 kg/m³ is used to measure the pressure drop along a horizontal pipe. If the fluid in the pipe is water and the manometer reading is 0.65m, what is the pressure difference between the two tapping points? Fluid density Pw A B a b datum Manometric fluid density p Hg Figure of manometer setuparrow_forward1. A clean circular glass tube is to be selected in the design of a manometer to measure the pressure of Kerosene . Specific gravity of kerosene 0.82 and surface tension of kerosene = 0.025 N/m. If the capillary rise is to be limited to 1 mm, the smallest diameter (cm) of the galss tube should be most nearly ... a) 1.35 b) 1.5 c) 1.75 d) 2.00arrow_forwardA differential manometer is attached to a pipe shown. Calculate the pressure difference between points A and B.arrow_forward
- I need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forwardQuestion 1 b) The U-tube manometer can be used to detemine pressure difference between two systems. This type of manometer is called a differential U-tube manometer. Consider the differential manometer connected to a pipe, as shown in Figure 1. Explain step by step on how you can calculate the pressure difference between point A and B. P1 h, A Flow Test Section U-Tube Differential Manometerarrow_forwardPlease correct solutionarrow_forward
- 7) For the manometer setup shown, determine the difference in pressure between A and B. oll, s = 0.85 Water 680 mm Bo 1700 mm YWater 8) A differential manometer is attached to a pipe as shown. Calculate the pressure difference between points A and B. is h. 100 mm re A Mercury A B Oil, s = 0.90 %3!arrow_forwardc) The orifice flowmeter shown in Figure 4 is used to obtain the flowrate of oil inside a conduit. The diameter of the orice, d is one third of the pipe diameter, D with pressure difference recorded as 25 kPa. The pipe diameter D is 6 cm, discharge coefficient Ca, is 0.60, Bis the ratio of orifice diameter to pipe diameter and Oilspedific gravity, SG is 0.95. If the h is 7 cm, i. Calculațe the vollime flowrate of oil inside the conduit. ii. Determine the mass flowrate of oil inside the conduit. iii. Explain why the discharge coefficient Ca, for the orifice meter is higher compared to the venturi and nozzle meters. D=6 cm d Figure 4arrow_forwardA calibration test of a 12.5 mm diameter circular sharped-edged orifice in a vertical side of a large tank showed a discharge of 590 N of water in 81 seconds at a constant head of 4.70 m. Measurement of the jet showed that it traveled 2.35 m horizontally while dropping 300 mm a. Compute the coefficient of velocity. b. Compute the coefficient of discharge. c. Compute the coefficient of contraction. URGENT Please answer this problem in 30minutes. I need correct answers with complete and step by step solution. Box the final answers. Do not shortcut your solution. I will give an upvote if it satisfies. Thank you!arrow_forward
- 1. Water is flowing in a wide open channel as shown in the figure. Two pitot tubes are connected to a different manometer containing oil (sp.gr. = 0.82). Find the velocity at m point A and point B in - oil (op.gr.=0.82) 2 m wafer sarfecearrow_forwardEx.1 Ans. A glass tube 0.25 mm in diameter contains a mercury column with water above the mercury. The temperature is 20°C at which the surface tension of mercury in contact with water is 0.037 kg()/m. What will be the capillary depression of the mercury? Take angle of contact 0= 130°. 3.02 cmarrow_forwardI need the answer to the question in fluidsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning