
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
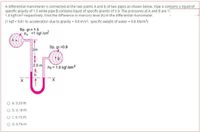
Transcribed Image Text:A differential manometer is connected at the two points A and B of two pipes as shown below. Pipe A contains a liquid of
specific gravity of 1.5 while pipe B contains liquid of specific gravity of 0.9. The pressures at A and B are 1
1.8 kgf/cm2 respectively. Find the difference in mercury level (h) in the differential manometer.
(1 kgf = 9.81 N; acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s; specific weight of water = 9.8 KN/m3)
Sp. gr.= 1.5
PA 1 kgf /cnf
3m
Sp. gr=0.9
2.0 m
Pe = 1.8 kgf /cm?
h
O a. 0.33 m
O b.0.18 m
O C. 0.15 m
O d. 0.74 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the meaning of Pre-History?arrow_forwardQ1 A U-tube manometer is used to measure the pressure of oil of specific gravity 0.85 flowing in a pipe line. Its left end is connected to the pipe and the right-limb is open to the atmosphere. The centre of the pipe is 100 mm below the level of mercury (specific gravity- 13.6) in the right limb. If the difference of mercury level in the two limbs is 160 mm, determine the absolute pressure of the oil in the pipe. Liquid (5,-ERS) Pipsarrow_forwardIn the inclined manometer shown in the figure below, the reservoir is large. Its surface may be assumed to remain at a fixed elevation. A is connected to a gas pipeline and the deflection noted on the inclined glass tube is 100 mm. Assuming q = 30° and the manometric fluid as oil with specific gravity of 0.86, the pressure at A is A 100 mm Ꮎ Barrow_forward
- Determine the gauge pressure at the center of pipe B in kilopascals. Mercury (S = 13.6) is the fluid in the manometer while oil (S = 0.93) is the fluid flowing in the pipe. Oil Mercury +B 0.2 m 0.02 marrow_forwardQ.23 Consider the flow of water through the frictionless pipe as shown in the figure. There is a sudden expansion at a section in the pipe. The flow velocity is 2.5 m/s and 1 m/s in AB and BC portion of the pipe respectively. The reading '' of the mercury- water differential manometer is: [Take specific gravity of mercury as 13.6] A O 50 cm Q B ↓ Water }arrow_forwardI need the answer to the question in fluidsarrow_forward
- Ans is 82.7 ,Show complete workarrow_forward5. Determine the new differential reading along the inclined leg of the mercury manometer of Fig. 3, if the pressure in pipe A is decreased 10 kPa and the pressure in pipe B remains unchanged. The fluid in A has a specific gravity of 0.9 and the fluid in B is water. -SG = 0.9 30⁰ Fig 3 100 mm 50 mm Water 80 mm Mercuryarrow_forwardmater 9arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning