
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
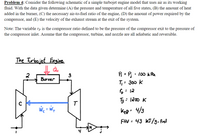
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 4: Consider the following schematic of a simple turbojet engine model that uses air as its working
fluid. With the data given determine (A) the pressure and temperature of all five states, (B) the amount of heat
added in the burner, (C) the necessary air-to-fuel ratio of the engine, (D) the amount of power required by the
compressor, and (E) the velocity of the exhaust stream at the exit of the system.
Note: The variable rp is the compressor ratio defined to be the pressure of the compressor exit to the pressure of
the compressor inlet. Assume that the compressor, turbine, and nozzle are all adiabatic and reversible.
The Turbojet Engine
2
P = Pj
: 100 kPa
Burner
T,: 300 k
6: 12
5= 1200 K
FHV = 43 KJ/g- frel
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 9 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- At the beginning of the compression process of an air-standard Diesel cycle operating with a compression ratio of 18, the temperature is 300 K, and the pressure is 0.1 MPa. The cutoff ratio for the cycle is 2. Calculate the followings, i) the temperature and pressure at the end of each process of the cycle, ii) the thermal efficiency, iii) the mean effective pressure, in MPa.arrow_forwardThermal systems problem: Assume that nitrogen is available in a storage tank at 2 MPa and 210 K. On the following chart, show the path for the following scenarios. a) An expansion valve is connected to this tank that drops the fluid (i.e., nitrogen) pressure at its outlet to one atmosphere. b) A compressor is connected to this tank that raises the fluid pressure at its outlet to 10 MPa. c) A turbine is connected to this tank that drops the fluid pressure at its outlet to one atmospheric pressure. d) A heat exchanger is connected to this tank that raises the fluid temperature to 330K at its outlet. e) A heat exchanger is connected to this tank that drops the fluid temperature to 135K at its outlet. f) Show the process for the fluid to change its state from 2 MPa and 210 K to 14 MPa and 240 K. Identify the required equipment. g) If a coolant at 150 K is available, is it possible to change the state of nitrogen from 2 MPa and 210 K to saturated liquid at atmospheric pressure? If…arrow_forwardA horizontal steam pipe (60 mm. OD) carries high pressure steam at 230℃ . Wind flows past this pipe at 1 m/s velocity. The ambient temperature is 32℃. Which mode(s) of convection should we consider here? Calculate the total rate of heat loss per m. length of the pipe.arrow_forward
- 1. A hole in the bottom of a large open tank discharges water to the atmosphere. If the exit velocity in the absence of losses is Ve, find the loss coefficient for the hole if the actual velocity is Ve/2. Assume turbulent flow. 2. Air enters a duct at a speed of 100 m/s and leaves it at 200 m/s. If no heat is added to the air and no work is done by the air, what is the change in temperature of the air as it passes through the duct?arrow_forwardplease show how to derive h using nusselt equation and solve for qheatlossarrow_forwardDetermine the efficiency for the cycle (standard air used as the working fluid) indicated in the sketch. Assume the pressures and temperatures are known quantities at each state. 1-2 constant volume process and 2-3 constant pressure process.arrow_forward
- Separate streams of air and water flow through the compressor and heat exchanger arrangement shown below. Steady-state operating data is provided in the figure. Heat transfer with the environment can be neglected, as can all potential and kinetic energy effects. Air is modeled as an ideal gas. Determine: (a) the total power required by both compressors, in kW. (b) the mass flow rate of the water, in kg / s.arrow_forwardQ.3 A converging-diverging nozzle is supplied by a huge air reservoir. The nozzle has a throat area of 10 cm? and an exit area of 20 cm?. The reservoir conditions are P. = 300 kPa and To = 30 °C. Determine the range of the back pressure over which (a) shocks appear in the nozzle, (b) oblique shocks form at the exit, and (c) expansion waves form. (d) Calculate the mass flow rate through the nozzle for the case in which a normal shock appears at the exit plane.arrow_forwardA gas turbine power plant with the following specifications: two axial compressor stages, the pressure ratio is 6/1 for each compressor. The inlet and exit angles of both moving and fixed blades are 40° and 20° respectively, the work done factor is 0.82, six stages for each compressor. intercooling between stages. A high pressure turbine is used to drive the compressors, and a low pressure turbine drives the generator. The temperature of the gases at entry to the high pressure turbine is 600°C and the gases are reheated to 700°C after expansion in the first turbine. The exhaust gases leaving the low pressure turbine are passed through a heat exchanger to heat the air leaving the high pressure stage compressor. The air inlet temperature to the unit is 20°C. The isentropic efficiency of each turbine stage is 0.95; the heat exchanger thermal ratio is 0.7. A mechanical loss is 5% for both the generator- turbine shaft and the compressor- turbine shaft. Assume any missed values to Calculate…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The