Question
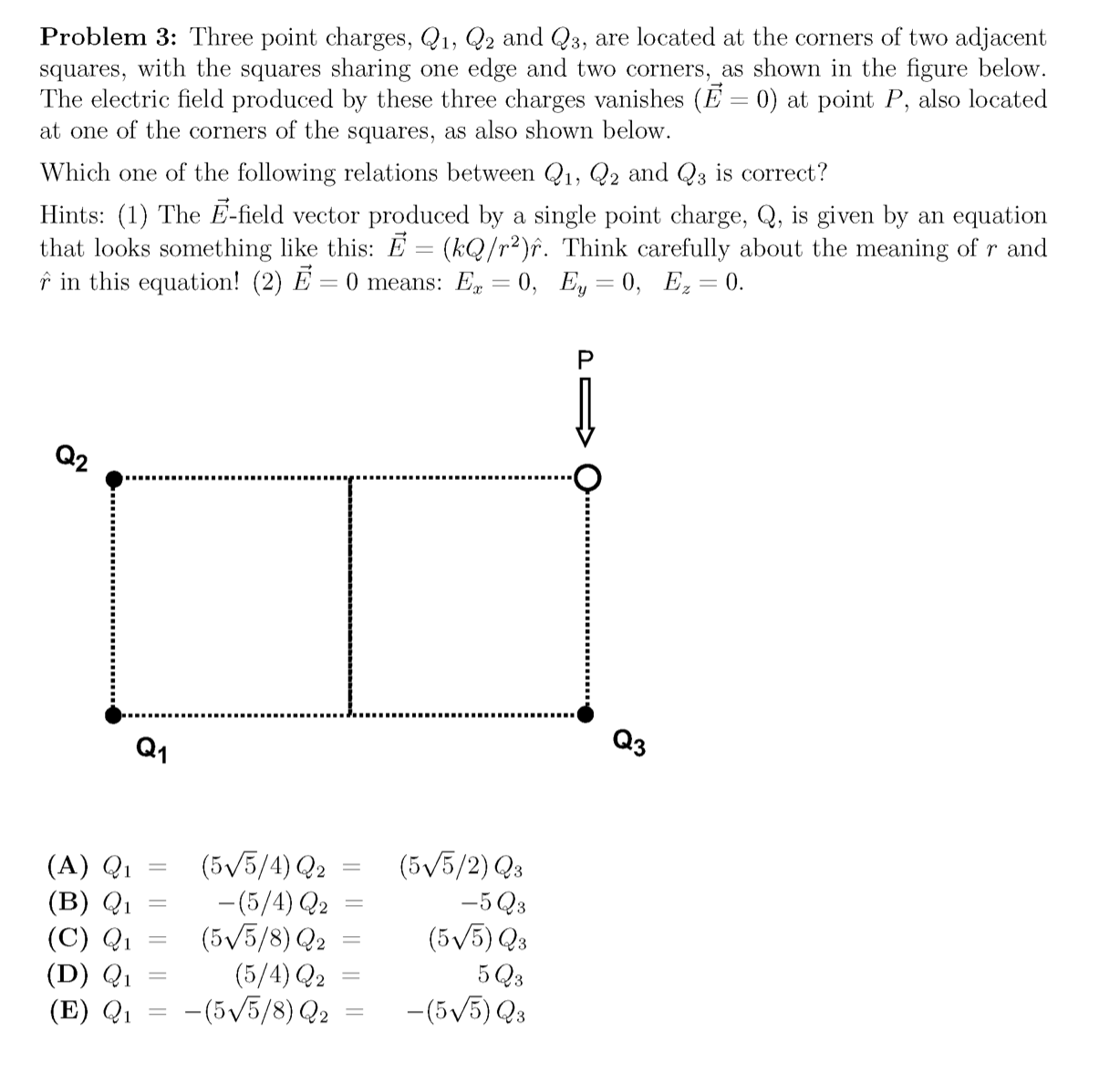
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 3: Three point charges, Q1, Q2 and Q3, are located at the corners of two adjacent
squares, with the squares sharing one edge and two corners, as shown in the figure below.
The electric field produced by these three charges vanishes (E = 0) at point P, also located
at one of the corners of the squares, as also shown below.
Which one of the following relations between Q1, Q2 and Q3 is correct?
Hints: (1) The E-field vector produced by a single point charge, Q, is given by an equation
that looks something like this: E = (kQ/r²)f. Think carefully about the meaning of r and
î in this equation! (2) E = 0 means: E = 0, Ey = 0, E, = 0.
Q2
Q1
Qз
(5V5/4) Q2
-(5/4) Q2
(5/5/8) Q2
(5/4) Q2
-(5/5/8) Q2
(5/5/2) Q3
(A) Q1
(B) Q1
(C) Q1
(D) Q1
(E) Q1
-5 Q3
(5V5) Q3
5 Q3
-(5/5) Q3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Chapter 37, Problem 012 The length of a spaceship is measured to be exactly 1/2 its rest length. (a) What is the speed parameter ß of the spaceship relative to the observer's frame? (b) By what integer factor do the spaceship's clocks run slow, compared to clocks in the observer's frame? (a) Number Units (b) Number Unitsarrow_forwardTwo identical metal blocks resting on a smooth horizontal surface are connected by a lightweight spring having a spring constant k = 0.2 N/m, as shown in the figure. The length of the spring before it is stretched is L0 = 10 cm. A total charge Q is carefully applied to the block, which is assumed to be a point charge. Because the blocks are given an electric charge, the spring is stretched so that its length becomes L = 10.2 cm. Find Q!arrow_forwardTwo charges Q1= -48 µC and Q2= -21 µC are placed on the two corners of a square as shown in the figure below. If the side length of the square is a=48 mm, how much work is required to bring a third charge, Q3= -28 µC from infinitely far away to the empty bottom-right corner of the square? Please take k = 9.0 x 109 N.m2/c2 and express your answer using one decimal place in units of J or N.m. Please do not forget to type the minus sign if you got a negative value. Q1 а а а Q2 аarrow_forward
- = A particle with charge 9₁ = +4.7 μC is located at (x=0,y=0). A second particle with charge 92 is located at (x=0,y=4.00 cm), and a third charge 93 = +5.4 µC is located at (x=3.00 cm,y=0). (a) In your notebook, draw a diagram of the three-charge system showing the location of the charges. (b) Calculate the potential energy of this three-charge system. PE = J -8 μCarrow_forwardHow to solve this questionarrow_forwardHello! I need some help on this! Consider the arrangement of two fixed point charges, equal in magnitude, shown in the figure. Which of the following statements are correct for the initial motion of a third charge if it is released from rest in the vicinity of the two charges shown?arrow_forward
- Here are two charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by a distance s. What is the direction (a – j) of the electric field at location 1 (marked with an X), and what is the direction (a – j) of the electric field at location 2 (marked with an X)?arrow_forwardThree charged metal disks are arranged as shown (cutaway view). The disks are held apart by insulating supports not shown in the diagram. Each disk has an area of 2.2 m² (this is the area of one flat surface of the disk). Use the value 8.8 12 C2/(N•m²) for €o.The charge Q1 = 4e-8 coulombs, and the charge Q2 = 2e-7 coulombs. 0.02 0.02 0.02 mm 1.7 mm ----- mm 4 mm mm F-- -+--| + A +. + В G + + + + +Qi -Q1 -Q2 +Q2 Disk 1 Disk 2 Disk 3 What is the magnitude of the electric field in the region between disks 1 and 2? = 1.07e-8 X V/m What is the direction of the electric field between disks 1 and 2? +x Which of the following statements are true? Choose all that apply. 3 mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios