
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:(b)
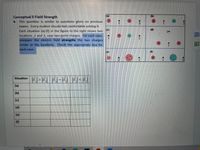
Conceptual E-Field Strength
4. This question is similar to questions given on previous
exams. Every student should feel comfortable solving it.
Each situation (a)-(f) in the figure to the right shows two
locations ,1 and 2, near two point charges. For each case,
compare the electric field strengths the two charges
create at the locations. Check the appropriate box for
(c)
(d)
20
each case.
Situation
E E
E
E.
2
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Three balls, with charges of +4g, -2q, and -q, are equally spaced along a line. The spacing between neighboring balls is r. We can arrange the balls in three different ways, as shown in the figure. In each case, the balls are in an isolated region of space very far from anything else. Treat the balls as point charges. +4g -29 -2g 2 || 1 +4q -g +4q (a) Rank the arrangements according to their potential energy, from most positive to most negative. See if you can do this without explicitly calculating the potential energy in each case. (Use only ">" or "=" symbols. Do not include any parentheses around the letters or symbols.) (b) Using q = 3.40 x 10-6 C and r = 35.0 cm, calculate the electrostatic potential energy in each of the cases above. 1: 2: 3:arrow_forwardCharge q, = 2.50 nC is at x, = 0 and charge q, = 6.00 nC is at x, = 4.00 m. At what point between the two charges is the electric field equal to zero? (Enter the x coordinate in m.) HINT Write an expression for the net electric field as a function of position, x, in the region between the two charges. (Don't forget that the electric field is a vector, so direction is important!) Set this expression equal to zero and solve for the variable x using the quadratic equation. Click the hint button again to remove this hint. marrow_forwardCould some one please explain the best way to solve this problem and show all workarrow_forward
- You are given three pith balls. When balls A and B are brought close together (far away from C), the two repel. When A and C are brought close together (far away from B), the two attract. When B and C are brought close together (far away from A), the two attract. Find four solutions for how A, B, and C could be charged (+, - or neutral) relative to one another.arrow_forwardLevitation: The largest electric field strength you can create in air before dielectric breakdown (a spark) occurs is about 3.0 x 10°V/m. Suppose you created an electric field with this strength – pointing directly upward – between a set of parallel plates that are 9.9cm apart. You want to use this system to levitate water droplets with a mass of 1.8g. (a) How much charge would you have to put on a droplet to make it levitate? (b) Suppose that 43 charged droplets are levitating and the field strength suddenly drops by 24 percent, to about 2.3 x 106 V/m, how quickly would the droplets accelerate? Earrow_forwardThe electric dipole in the figure consists of two charges, +Q and -Q, that are a distance, d, apart, where Q = 65.4 nC and d = 39.3 cm. Point A, which lies along the vertical (dotted) line midway between the two dipole charges, is an unknown distance, r, from the +Q charge. SYMBOLIC INPUT. Use the variables from the problem: Q, d, r, and Coulomb's constant, k, as needed. Electric Potential (1 of 2) The electric potential at point A will be zero The electric potential at point B will be zero zero zero This tells you that the electric field is perpendicular to perpendicular to the middle line.. Udipole 11 +Q Potential Energy (2 of 2) Write a symbolic expression for the electric potential energy of the system, then calculate its numeric value. HJ Barrow_forward
- How to solve this questionarrow_forwardA very long insulating cylindrical shell of radius 6.70 cm cames charge of linear density 8.70 μC/m spread uniformly over its outer surface. You may want to review (Pages 765-769) For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of An infinite line charge or charged conducting cylinder What would a voltmeter read if it were connected between the surface of the cylinder and a point 4.80 cm above the surface? 195] ΑΣΦ AV= Submit Request Answer Part B AV- What would a voltmeter read if it were connected between the surface and a point 1.00 cm from the central axis of the cylinder? 1Η ΑΣΦΑ Submit ? Request Answer V ? Varrow_forwardThree charged metal disks are arranged as shown (cutaway view). The disks are held apart by insulating supports not shown in the diagram. Each disk has an area of 2.2 m² (this is the area of one flat surface of the disk). Use the value 8.8 12 C2/(N•m²) for €o.The charge Q1 = 4e-8 coulombs, and the charge Q2 = 2e-7 coulombs. 0.02 0.02 0.02 mm 1.7 mm ----- mm 4 mm mm F-- -+--| + A +. + В G + + + + +Qi -Q1 -Q2 +Q2 Disk 1 Disk 2 Disk 3 What is the magnitude of the electric field in the region between disks 1 and 2? = 1.07e-8 X V/m What is the direction of the electric field between disks 1 and 2? +x Which of the following statements are true? Choose all that apply. 3 mmarrow_forward
- Charges X (+5 microCoulombs), Y (+5 microCoulombs), and Z (-5 microCoulombs) are located in a straight line with point Y midway between charges X and Z. Charge X is on the left, Y in the middle, and Z on the right. Where along the line that passes through the three points could the Electric Field Strength be Zero? (Include all possible locations.)arrow_forward9:09 docs.google.com 4. Applying Conservation of Charge: A researcher is analyzing a particle decay process. The data for one experiment shows a particle of charge -3e, decaying to form two new particles. One of the new particles has a charge of - e. -3e Choose -1 e +3 e n -2 e +2 e e with the correct words in the following Conservation of Charge Review: a) Charge is neither created nor destroyed, it can only be (siphoned/ transferred added) from one 10 points Q? -e * 25 pointsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON