
University Physics Volume 2
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168161
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
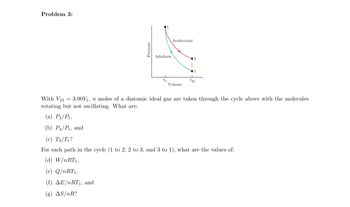
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 3:
Pressure
Adiabatic
Isothermal
Volume
3
V₂3
With V233.00V₁, n moles of a diatomic ideal gas are taken through the cycle above with the molecules
rotating but not oscillating. What are:
(a) P₂/P₁,
(b) P3/P₁, and
(c) T3/T₁?
For each path in the cycle (1 to 2, 2 to 3, and 3 to 1), what are the values of:
(d) W/nRT1,
(e) Q/nRT1,
(f) AE/nRT₁, and
(g) AS/nR?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two monatomic ideal gases A and B are at the same temperature. If 1.0 g of gas A has the same internal energy as 0.10 g of gas B, what are (a) the ratio of the number of moles of each gas and (b) the ration of the atomic masses of the two gases?arrow_forwardAn ideal gas has a pressure of 0.50 atm and a volume of 10 L. It is compressed adiabatically and quasi-statically until its pressure is 3.0 atm and its volume is 2.8 L. Is the monatomic, diatomic, or polyatomic?arrow_forwardFind (a) the most probable speed, (b) the average speed, and (c) the rms speed for nitrogen molecules at 295 K.arrow_forward
- The product of the pressure and volume of a sample of hydrogen gas at 0.00 is 80.0 J. (a) How many moles of hydrogen are present? (b) What is the average translational kinetic energy of the hydrogen molecules? (c) What is the value of the product of pressure and volume at 200 ?arrow_forwardA mole of gas has isobaric expansion coefficient dV/dT=R/p and isochoric pressure-temperature coefficient dp/dT=p/T . Find the equation of state of the gas.arrow_forwardThe temperature of an ideal monatomic gas rises by 8.0 K. What is the change in the internal energy of 1 mol of the gas at constant volume?arrow_forward
- An ideal gas expands quasi-statically and isothermally from a state with pressure p and volume V to a state with volume 4V. Show that the work done by the gas in the expansion is pV(ln 4).arrow_forwardA monatomic ideal gas undergoes a quasi-static process that is described by the function pV=p1+3(vv1) , where the stating state is (p1,v1) and the final state (p2,v2) . Assume the system consists of n moles of the gas in a container that can exchange heat with the environment and whose volume can change freely. (a) Evaluate the work done by the gas during the change in the state. (b) Find the change in internal energy of the gas. (c) Find the heat input to the gas during the change. (d) What ale initial and final temperatures?arrow_forwardUnreasonable results. (a) Find the temperature of 0.360 kg of water, modeled as an ideal gas, at a pressure of 1.01105 Pa if it has a volume of 0.615 m3. (b) What is unreasonable about this answer? How could you get a better answer?arrow_forward
- In the text, it was shown that N/V=2.681025m3 for gas at STP. (a) Show that this quantity is equivalent to N/V=2.681019cm3, as stated. (b) About how many atoms are mere in one m3 (a cubic micrometer) at STP? (c) What does your answer to part (b) imply about the separation of Mama and molecules?arrow_forwardTwo moles of a monatomic ideal gas such as helium is compressed adiabatically and reversibly from a state (3 atm, 5 L) to a state with pressure 4 atm. (a) Find the volume and temperature of the final state. (b) Find the temperature of the initial state of the gas. (c) Find the work done by the gas in the process. (d) Find the change in internal energy of the gas in the process.arrow_forwardA sample of a monatomic ideal gas occupies 5.00 L at atmospheric pressure and 300 K (point A in Fig. P17.68). It is warmed at constant volume to 3.00 atm (point B). Then it is allowed to expand isothermally to 1.00 atm (point C) and at last compressed isobarically to its original state. (a) Find the number of moles in the sample. Find (b) the temperature at point B, (c) the temperature at point C, and (d) the volume at point C. (e) Now consider the processes A B, B C, and C A. Describe how to carry out each process experimentally. (f) Find Q, W, and Eint for each of the processes. (g) For the whole cycle A B C A, find Q, W, and Eint. Figure P17.68arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning