
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider the following AD/AS diagram of the macroeconomy, with LRAS shown as the vertical curve, AD as the downward sloping curve, and SRAS as the upward sloping curve.
First, place a point at the current equilibrium. Then, suppose the government wants to stimulate the economy to restore it to long-run equilibrium by cutting taxes. Draw a new curve that shows the impact of this policy change. (You'll have to determine which, but draw it so that it reflects a parallel, vertical shift in one of the existing curves. Make sure that it's the same size as the ones shown here using the segment tool.) Finally, place a point at the new equilibrium using the point tool.
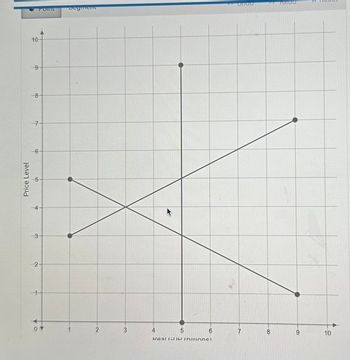
Transcribed Image Text:Price Level
10
9
00
Tonn
7
5
3
2
4
40
Segment
2
11
6
Real GDP Thillionsl
Unido
00
nedo
10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 1 Consider the aggregate supply-aggregate demand (AD-AS) model that we saw in class. Assume that prices are fixed in the short run and are fully flexible in the long run. The initial full-employment level of output is Y=900 and the initial price level is P=100: The aggregate demand curve is given by Y= 1500 - 6P: Scenario 1, short run: A reduction in personal income taxes shifts the demand curve to Y=1530 - 6P. In the short run, the output is and the price level is Note: Type in your answer rounded to two decimal places, i.e., your answer must be of the form "999.99". I will not be able to fix correct answers that were entered incorrectly, such as "999.999" or "999,99" or "999". In case the last digit in the correct answer is zero, e.g., "999.90" or "999.00", Blackboard may automatically delete it and you should not do anything about it. In case of percentages, do not type in the percentage symbol "%".arrow_forwardAssuming that there is no government spending or trade, an economy’s GDP is the sum of domestic consumption C and investment I, i.e. Y = C+ I Assume that I is unaffected by GDP Assume the consumption function is C = c0 + c1Y In any equilibrium aggregate demand, AD must be equal to Y, GDP. Given this model, which FIVE of the following statements are correct? Select one or more: A. If the economy above is a demand-driven economy, then the equilibrium solution for Y is given by Y = m(c0 + I), where m = 1/(1 - c1) is the multiplier. B. if c1 = 0.8 the multiplier is equal to 1/0.8= 1.25 C. if c1 = 0.75 the multiplier is equal to 4 D. assume c0 =100, I=50, c1=0.6. The equilibrium value of Y in a demand-driven economy is 300. E. Assume that Y is initially 400, I is initially 100, and the multiplier is 2.5. I increases by 10%. The multiplier implies that in equilibrium Y will increase by 25%. F. The higher is c1 the larger is the multiplier G. If consumers…arrow_forwardPrice Level AD1 AD₂ AD2 Real Domestic Output, GDP Refer to the accompanying graph. What combination would most likely cause a shift from AD1 to AD2? Multiple Choice О an increase in taxes and no change in government spending О a decrease in taxes and a decrease in government spending О a decrease in taxes and an increase in government spendingarrow_forward
- Hello Can you help me out. Use the AD/AS model to illustrate the following. Draw 6 graphs by hand. Show how the AD or the AS curve shift and in what direction (left or right). Also state what happens to equilibrium real GDP (Y), employment, and the equilibrium price level. [Note: Use the SRAS curve, not the LRAS.] A. an increase in government spending and/or transfer payments B. restrictive fiscal policy C. expansive monetary policy D. increase in investment according to Keynesians E. increase in investment according to supply-side economists F. a stock market crasharrow_forwardNotice the major differences between our Keynesian Cross (in your chapter 9 appendix) and the Macro Equilibrium (AS and AD) diagram? Which model has more to offer in which situations?arrow_forwardPhilip's Curve and AD-AS Model: Use assumptions below to set up an initial point denoted as the point A for a and b. For each of the following draw an AD/AS diagram and a corresponding Philip's curve assuming the following: 1) Natural unemployment is 5% 2) Unemployment is 4% 3) Actual GDP is 20,000 4) Full employment GDP is 10,000 a)show in both diagrams the effect of a surprise increase in inflation. b)Show in both diagrams the effect of Friedman and the Natural rate Theory(Hint:using monetary policy in the short run, but self-correction in the long run) c) Show in both diagrams the effects of a decrease in income tax on price level, output,unemployment and inflation.(Hint: Fiscal Policy) d)show in both diagrams the effect of a decrease in expected inflation.arrow_forward
- Draw and carefully describe a graph that utilizes the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply model that would illustrate the state of the aggregate economy in the United States at the very beginning of 2020 before the start of the pandemic and the 2020 recession. Make sure that you explain your graph in your own words. You should draw your own AD/AS graph which you can then embed into your post. Your graph needs to be clearly labeled and explained in some detail. Make sure that your graph includes an aggregate demand (AD) curve, a short run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve, and a long run aggregate supply curve (LRAS, Potential GDP) curve. You should clearly label both axes of the graph.arrow_forwardWhich of the following is a major difference between the AD-AS model and the dynamic AD-AS model? The dynamic AD-AS model assumes OA. AD only includes consumption, investment, and government purchases, while the AD-AS model assumes AD includes consumption, investment, government purchases and net exports. B. the SRAS is stable and will not shift, while the AD-AS model assumes the SRAS can only change with an exogenous event such as oil price changes. OC. the economy does not experience long-run growth, while the AD-AS model assumes there is constant inflation in the economy. OD. potential GDP increases continually, while the AD-AS model assumes the LRAS does not change.arrow_forwardlet's consider the AS/AD model. furthermore, assume two events happen at the same time: government conducts contractionary fiscal policy and the global price of energy (oil) falls. show the effects of these two events in a graph and explain what will happen to the GDP and price level?arrow_forward
- What would the LM curve look like in a classical world? If this really were the LM curve that we thought best characterized the economy, would we lean toward the use of fiscal policy or monetary policy? (You may assume your goal is to affect output.arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer questions 8 through 11: The graph below shows the AD-AS diagram for Spain. Suppose that the economy experiences a negative aggregate demand shock denoted by the move from AD1 to AD2. Note that the new curve is shown in gray. 1200+ 1100 ALN 1000+ 900 Al 800 - 700- 600 500 400 - 309AS 200 100+ LRAS 200 Real GDP 300. 400 100 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 120 8. What has happened to the cyclical unemployment in Spain (select one)? a. Cyclical unemployment remains the same. b. Cyclical unemployment decreased. c. Cyclical unemployment increased. Price Levelarrow_forwardUse the graph below to answer questions #4-5. This graph depicts the AD-AS model, which involves the Aggregate Demand curve (AD), Aggregate Supply curve (AS) and Long Run Aggregate Supply curve (LRAS). Our assumptions with this model match those from class. LRAS AS AD Assume in the multiple choice questions below that our starting point is pt A. Assume that in the months leading up to a major election, the Federal government enacts legislation that significantly increases government spending. Assume further that government pays for this spending by increasing the money supply. Based on our discussion of the self-correcting mechanism, how would this policy affect the graph in the short run and long run? Itranscript Oa. in the short run, AD will increase, but over the long run, AS will eventually shift upward as workers begin to ask for cost of living increases from their employers Ob. in the short run, AD will increase, but over the long run. AS will eventually shift leftward as workers…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education