
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:PRICE (Dollars per pound)
100
90
80
70
60
50
中
Supply (20 firms)
Supply (30 firms)
40
Supply (40 firms)
Demand
30
20
10
0
0
125
250 375 500 625 750 875 1000 1125 1250
QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds)
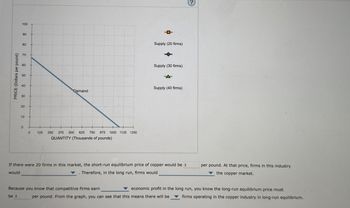
If there were 20 firms in this market, the short-run equilibrium price of copper would be s
would
Therefore, in the long run, firms would
per pound. At that price, firms in this industry
the copper market.
economic profit in the long run, you know the long-run equilibrium price must
firms operating in the copper industry in long-run equilibrium.
Because you know that competitive firms earn
be $
per pound. From the graph, you can see that this means there will be
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 8. Short-run and long-run effects of a shift in demand Suppose that the seitan industry is initially operating in long-run equilibrium at a price level of $5 per pound of seitan and quantity of 50 million pounds per year. Suppose that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reports that compounds naturally occurring in seitan are linked to chronic illness. The FDA's research is expected to cause consumers to demand seitan at every price. In the short run, firms will respond by Shift the demand curve, the supply curve, or both on the following graph to illustrate these short-run effects of the FDA's research. PRICE (Dollars per pod 0 10 20 Supply In the long run, some firms will respond by Demand TO QUANTITY (Mons of pounds) 20 100 Demand Supply until Shift the demand curve, the supply curve, or both on the following graph to illustrate both the short-run effects of the FDA's research and the new long-run equilibrium after firms and consumers finish adjusting to the news.arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the short-run supply curve for pears. Place the orange line (square symbol) on the following graph to show the most likely long-run supply curve for pears. (Note: Place the points of the line either on K and T or on K and C.) (?) 48 Long-Run Supply K Short-Run Supply 2 4 6 8 10 QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds of pears) PRICE (Dollars per pound) 40 32 24 16 8 0 12arrow_forwardP $35 $30 $25 $20 $15 $10 $5 $0 5 10 (FIRM) 17 18 20 ATC JAVC F 9 $35 $30 $25 $20 $15 $10 $5 $0 (MARKET) X Consider the perfectly competitive market depicted in the graphs. Assuming the market is in equilibrium, what should this firm do? lay off workers temporarily in the short run keep producing in the short run leave the market permanently in the long run shut down temporarily in the short runarrow_forward
- 6. Deriving the short-run supply curve The following graph plots the marginal cost (MC) curve, average total cost (ATC) curve, and average variable cost (AVC) curve for a firm operating in the competitive market for sun lamps. COSTS (Dollars) 100 20 80 TO 0 □ 5 D MC-D Price (Dollars per lamp) 10 20 32 40 50 60 ATC AVC Quantity (Lamps) DO 15 QUANTITY (Thousands of lamps) 50 For every price level given in the following table, use the graph to determine the profit-maximizing quantity of lamps for the firm. Further, select whether the firm will choose to produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. (Assume that when price exactly equals average variable cost, the firm is indifferent between producing zero lamps and the profit-maximizing quantity of lamps.) Lastly, determine whether the firm will earn a profit, incur a loss, or break even at each price. ? Produce or Shut Down? Profit or Loss?arrow_forward(Figure: Profit-Maximization for Fabulous Finn's Flower Firm in the Short Run) Use Figure: Profit-Maximization for Fabulous Finn's Flower Firm in the Short Run. If the market price is Pa: Price, ATC, AVC, and MC (per unit) P2 91 92 9 Quantity (per perlod) firms will leave the industry, and the price will fall in the long run. there will be economic profits, and firms will enter the industry in the long run. the market supply curve will shift to the left, and price will fall in the long run. O the firm will produce q4 O Oarrow_forwardPlace the orange line (square symbol) on the graph to show the most likely long-run supply curve for pears. (Note: Place the points of the line ei an W and R or on W and M.) PRICE (Dollars per pound) 48 40 2 Z L 0 W 04 6 4 Short-Run Supply 2 8 10 QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds of pears) 12 0 Long-Run Supplyarrow_forward
- 7. Short-run supply and long-run equilibrium Consider the competitive market for copper. Assume that, regardless of how many firms are in the industry, every firm in the industry is identical and faces the marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves shown on the following graph.arrow_forward8. Short-run and long-run effects of a shift in demand Suppose that the seitan industry is initially operating in long-run equilibrium at a price level of $5 per pound of seitan and quantity of 125 million pounds per year. Suppose a top medical journal publishes research that animal-alternative protein sources such as seitan could increase your expected lifespan by 3 years. The publication is expected to cause consumers to demand Shift the demand curve, the supply curve, or both on the following graph to illustrate these short-run effects of the publication. PRICE (Dollars per pound) 10 9 8 7 6 2 1 0 0 Supply In the long run, some firms will respond by Demand 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 QUANTITY (Millions of pounds) seitan at every price. In the short run, firms will respond by 中喜中重 Demand Supply ? untilarrow_forwardAssume that the cost data in the following table are for a purely competitive producer: Average Average Average Total Variable Marginal Cost Total Fixed Product Cost Cost Cost 1 $60.00 $45.00 $105.00 $ 45.00 30.00 42.50 72.50 40.00 3 20.00 40.00 60.00 35.00 4 15.00 37.50 52.50 30.00 12.00 37.00 49.00 35.00 6. 10.00 37.50 47.50 40.00 7 8.57 38.57 47.14 45.00 7.50 40.63 48.13 55.00 9. 6.67 43.33 50.00 65.00 10 6.00 46.50 52.50 75.00 Instructions: If you are entering any negative numbers be sure to include a negative sign (-) in front of those numbers. Select "Not applicable" and enter a value of "0" for output if the firm does not produce. a. At a product price of $57.00 (i) Will this firm produce in the short run? (Click to select) V (ii) If it is preferable to produce, what will be the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing output? |(Click to select V output = units per firm (iii) What economic profit or loss will the firm realize per unit of output? |(Click to select v per unit = $ b.…arrow_forward
- please also do the graph and the choices for the first blank is 2000, 7500, 8000, 10000 and the choices for the second blank is profit or economic loss thank you!!!arrow_forwardSuppose that the perfectly competitive turkey industry is in long-run equilibrium at a price of $3 per pound of turkey and a quantity of 600 million pounds per year. Suppose the Surgeon General issues a report saying that eating turkey is bad for your health. The Surgeon General's report will cause consumers to demand v turkey at every price. In the short run, firms will respond by Shift the supply curve, the demand curve, or both on the following diagram to illustrate these short-run effects of the Surgeon General's announcement. Note: Select and drag one or both of the curves to the desired position. Curves will snap into position, so if you try to move curve and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it a little farther. (?) Supply 5 Demand Supply Demand 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 QUANTITY (Millions of pounds) PRICE (Dollars per pound)arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education