
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
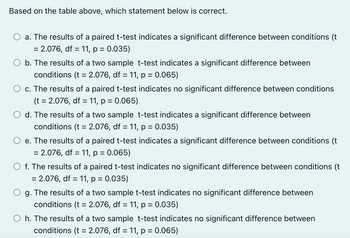
Transcribed Image Text:Based on the table above, which statement below is correct.
a. The results of a paired t-test indicates a significant difference between conditions (t
= 2.076, df = 11, p = 0.035)
b. The results of a two sample t-test indicates a significant difference between
conditions (t = 2.076, df = 11, p = 0.065)
c. The results of a paired t-test indicates no significant difference between conditions
(t = 2.076, df = 11, p = 0.065)
d. The results of a two sample t-test indicates a significant difference between
conditions (t = 2.076, df = 11, p = 0.035)
e. The results of a paired t-test indicates a significant difference between conditions (t
= 2.076, df = 11, p = 0.065)
○ f. The results of a paired t-test indicates no significant difference between conditions (t
= 2.076, df = 11, p = 0.035)
g. The results of a two sample t-test indicates no significant difference between
conditions (t = 2.076, df = 11, p = 0.035)
h. The results of a two sample t-test indicates no significant difference between
conditions (t = 2.076, df = 11, p = 0.065)
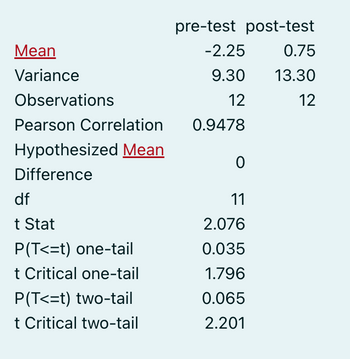
Transcribed Image Text:pre-test post-test
Mean
Variance
-2.25
0.75
9.30
13.30
Observations
12
12
Pearson Correlation
0.9478
Hypothesized Mean
0
Difference
df
11
t Stat
2.076
P(T<=t) one-tail
0.035
t Critical one-tail
1.796
P(T<=t) two-tail
0.065
t Critical two-tail
2.201
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- help asap. i will rate positive.arrow_forwardQ18. Why do we conduct post hoc analysis in ANOVA? a. To make a comparison on individual adjusted R-squares B. To make a comparison of the individual group meansC. To make a comparison of the individual group scatter plots D. None of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the test statistic? What is the p-value? Can we conclude that the mean travel times of the two routes are different? Yes or No?arrow_forward
- Choose the correct answer.If the P-value of a test of significance is 0.999 then:A. the null hypothesis should be rejected.B. the null hypothesis should not be rejected.C. the alternative hypothesis provides a plausible explanation of the data.D. Both A and C are true.arrow_forwardListed in the accompanying table are heights (in.) of mothers and their first daughters. The data pairs are from a journal kept by Francis Galton. Use the listed paired sample data, and assume that the samples are simple random samples and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that there is no difference in heights between mothers and their first daughters. Mother 64.0 66.0 63.0 62.0 66.5 66.0 65.0 60.0 67.0 63.0 Daughter 67.0 66.5 70.5 66.0 61.0 66.0 65.5 65.0 67.0 65.0 In this example, Hd is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual difference d is defined as the daughter's height minus the mother's height. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? Ho: Ha = 0 in. H₁ Hd 0 in. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Identify the test statistic. t= (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardKenneth, a competitor in cup stacking, claims that his average stacking time is 8.2 seconds. During a practice session, Kenneth has a sample stacking time mean of 7.8 seconds based on 11 trials. At the 4% significance level, does the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that Kenneth's mean stacking time is less than 8.2 seconds? Accept or reject the hypothesis given the sample data below. H0:μ=8.2 seconds; Ha:μ<8.2 seconds α=0.04 (significance level) z0=−1.75 p=0.0401 Select the correct answer below: a. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the p-value 0.0401 is greater than the significance level α=0.04. b. Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value 0.0401 is greater than the significance level α=0.04. c. Reject the null hypothesis because the value of z is negative. d. Reject the null hypothesis because |−1.75|>0.04. e. Do not reject the null hypothesis because |−1.75|>0.04.arrow_forward
- A dietitian wishes to see if a person's cholesterol level will change if the diet is supplemented by a certain mineral. Seven subjects were pretested and then took the mineral supplement for a six-week period. The results are shown below in the table. Use a paired samples t-chart at a = 0.01 significance level to see difference (Before - After) between the cholesterol levels. State the hypotheses and conclusion. Also, conduct a 99% confidence interval. Subject 1 Before 210 After 190 2 205 170 3 208 210 4 192 188 5 178 173 6 244 228 7 211 198arrow_forwardWhat does the t test for the difference between the means of 2 independent populations assume? A. The sample sizes are equal. B. The sample variances are equal. C. The populations are approximately normal. D. All of the abovearrow_forwardThe claim is that for a smartphone carrier's data speeds at airports, the mean is μ=11.00 Mbps. The sample size is n=12 and the test statistic is t=−1.683. what is the pvaluearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning