
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
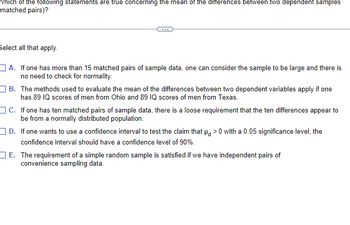
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following statements are true concerning the mean of the differences between two dependent samples
matched pairs)?
Select all that apply.
A. If one has more than 15 matched pairs of sample data, one can consider the sample to be large and there is
no need to check for normality.
B. The methods used to evaluate the mean of the differences between two dependent variables apply if one
has 89 IQ scores of men from Ohio and 89 IQ scores of men from Texas.
C. If one has ten matched pairs of sample data, there is a loose requirement that the ten differences appear to
be from a normally distributed population.
D.
If one wants to use a confidence interval to test the claim that μ>0 with a 0.05 significance level, the
confidence interval should have a confidence level of 90%.
E. The requirement of a simple random sample is satisfied if we have independent pairs of
convenience sampling data.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 6. Which of the following statements are true? A. The population mean u and population median ũ will not generally be equal to one another. B. There are four quartiles; they divide the data set into four equal parts. C. A 10% trimmed mean would be computed by eliminating the smallest 5% and the largest 5% of the sample values and then averaging what is leftover. D. All of the above. В. С.arrow_forwarda. A researcher is interested in determining if there is a relationship between handedness and penmanship. To study this question, the researcher submitted samples from 100 students to penmanship experts. The samples were rated to be of low, medium or high penmanship quality. The observed frequencies were totaled according to left verses right handedness. Penmanship Handedness low medium high Left 8 29 6 right 9 37 11 Which test is appropriate for this data? ANOVA F-testtwo sample z-testchi-square testtwo sample t-testone sample t-testone sample z-test b. What is the difference between a Type I and Type II error? c. What is the main idea behind conducting the Chi-square test?arrow_forwardSuppose we wanted to see if there was a correlation between suspension and ethnicity. We have the following summary of data below. What statistical test would we use? Suspended Note Suspended Black 17 17 White 65 878 Group of answer choices No answer text provided. Chi-squared Z-test T-testarrow_forward
- The average house has 11 paintings on its walls. Is the mean larger for houses owned by teachers? The data show the results of a survey of 14 teachers who were asked how many paintings they have in their houses. Assume that the distribution of the population is normal. 12, 13, 12, 12, 12, 11, 13, 12, 13, 11, 10, 12, 11, 13 What can be concluded at the a = 0.05 level of significance? a. For this study, we should use Select an answer b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Но: Select an answer H1: Select an answer c. The test statistic ? ▼ (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) d. The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) e. The p-value is (? v f. Based on this, we should | Select an answer the null hypothesis. g. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... The data suggest the population mean is not significantly more than 11 at a = 0.05, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the population mean number of paintings that are in teachers' houses…arrow_forwardSubject : Basic Statistics 11. I've posted an image of the question.arrow_forwardListed in the accompanying table are heights (in.) of mothers and their first daughters. The data pairs are from a journal kept by Francis Galton. Use the listed paired sample data, and assume that the samples are simple random samples and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that there is no difference in heights between mothers and their first daughters. Mother 61.0 69.0 60.0 66.0 65.5 64.0 63.5 63.0 68.5 69.0 D Daughter 63.5 68.0 62.0 67.0 65.2 69.0 63.5 63.0 66.0 70.0 In this example, Ha is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual difference d is defined as the daughter's height minus the mother's height. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? Ho: Hd in. H1: Hd in. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Identify the test statistic. t= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value. P-value =…arrow_forward
- MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY AND VARIABILITY.1. Suppose two classes achieved the following grades on a math test,Class A: 64, 70, 73, 77, 85, 90, 94Class B: 74, 75, 75, 76, 79, 80, 94 In each class, find the mean, median, mode, range, interquartile range, Variance,Standard Deviation, coefficient of variance Which class is better?arrow_forwardWhich of the following accurately describes the effect of increasing the sample size? O Increases the standard error and has no effect on the risk of a Type l er Decreases the risk of a Type l error and has no effect on the standard error O Decreases the standard error and has no offect on the risk of a Type l error O Increases the risk of a Type l error and has no effect an the standard erroarrow_forwardListed in the accompanying table are heights (in.) of mothers and their first daughters. The data pairs are from a journal kept by Francis Galton. Use the listed paired sample data, and assume that the samples are simple random samples and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that there is no difference in heights between mothers and their first daughters. ... Question content area top right Part 1 Mother 62.0 65.0 64.7 65.5 65.0 67.0 66.0 66.5 63.0 58.5 Daughter 68.0 69.0 66.5 63.0 68.0 62.0 66.5 66.7 63.5 66.5 Question content area bottom Part 1 In this example, μd is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual difference d is defined as the daughter's height minus the mother's height. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? H0:…arrow_forward
- Which of these would not make you question the results of a study? A. Anonymous answers B. A small sample C. Assuming causation from correlation D. A large margin of errorarrow_forwardMm3arrow_forwardQ.19 Urgent question! I will thumbs up! In the final answer that you circle, please also include the brief approach / formula you used under "Answer". Thanks!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman