
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please refer to part (b) of Figure 1 included with this quiz. Here, theta (the angle the incident ray makes with respect to the vertical) is 40.0 degrees. What is d (the distance between the ray emerging from the bottom of the glass and where the ray would have been if it had continued straight on with no glass to refract it)?
1.78 m
1.11 m
0.56 m
1.33 m
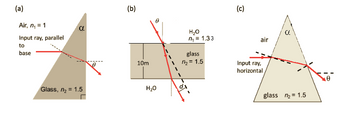
Transcribed Image Text:(a)
Air, n₁ = 1
Input ray, parallel
to
base
a
Glass, n₂ = 1.5
(b)
10m
H₂O
H₂O
n₁ = 1.33
glass
n₂ = 1.5
(c)
air
Input ray,
horizontal,
a
glass n₂ = 1.5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A beam of light is directed toward the surface of a block of zircon at an angle of 29.0° with respect to the normal (a line perpendicular to the surface at the spot where the ray hits the block). Part of the light is reflected and the rest refracted. What is the angle (in degrees) between the reflected and refracted beams?arrow_forwardA scuba diver training in a pool looks at his instructor as shown in the figure on the next page. The index of refraction of water is 1.33.a. What angle does the ray from the instructor’s face make with the perpendicular to the water surface at the point where the ray enters? The angle between the ray in the water and the perpendicular to the water surface is 25.0°. b. Find the height of the instructor’s head above the water. c. How much time does it take light to travel from the scuba diver to the instructor’s head? d. Find the apparent depth of the diver’s head below water as seen by the instructor.arrow_forwardA ray of light is incident on the surface of a block of diamond at an angle of 43.0° with respect to the normal (a line perpendicular to the surface at the spot where the ray hits the block). A fraction of the light is reflected and the rest refracted. What is the angle (in degrees) between the reflected and refracted rays? in degrees °arrow_forward
- As shown below, light from a vacuum is incident on a shard of Shawtonium (a newly discovered compound). The backside of the shard is up against an unknown material. When the light strikes the backside of the shard, total internal reflection occurs. The light then emerges from the side of the shard and resumes traveling through a vacuum. The index of refraction of Shawtonium is 1.8. Determine 0₁ & 0₂. vacuum 0₁ = 0₂ = unknown 8₂ shard 71° 36° 01...arrow_forwardThe index of refraction of water is 1.33 and the index of refraction of crown glass is 1.52. Whichstatement about the speed of light in these materials is true?a) The speed of light is the same in water and crown glass.b) The speed of light in water is faster than the speed of light in crown glass.c) The speed of light in crown glass is faster than the speed of light in water.d) More information is needed to compare the speed of light in the materials.arrow_forwardLight enters a container of liquid at an angle of 49° to the normal; the refracted beam makes an angle of 29° with the normal. Calculate the index of refraction of this liquid. Group of answer choices 1.96 1.44 1.56 1.78arrow_forward
- In the above figure, theta (the angle the incident ray makes with respect to the vertical) is 26.0 degrees. What is d (the distance between the ray emerging from the bottom of the glass and where the ray would have been if it had continued straight on with no glass to refract it)?arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a light ray traveling in a slab of sodium chloride surrounded by air. The ray is incident on the right surface at an angle of 55° with the normal and then reflects from points A, B, and C. (Select all that apply.) A ray travels within a rectangular slab that is surrounded by air. The ray starts at the top of the slab and is incident on the right side of the slab at point A, and makes an angle of 55° to the normal. The ray reflects internally down and to the left and is incident on the bottom of the slab at point B, whereupon it reflects internally up and to the left until it is incident on the left side of the slab at point C, where it again reflects internally, up and to the right. (a) At which of these points does part of the ray enter the air? (Select all that apply.) A B C (b) If the sodium chloride slab is surrounded by diamond, at which point does part of the ray enter the diamond? (Select all that apply.) A B Carrow_forwardA ray of light is passed through a ruby and it hits a surface in contact with air (n = 1.000) at an angle of 45° with respect to the normal. Use the table below to determine happens when it hits the surface? What is the critical angle? The ray refracts into the air at an angle of 45° with respect to the normal. The ray reflects back into the ruby at an angle of 45° with respect to the normal. The ray refracts at an angle of 90° with respect to the normal, along the surface. The ray is absorbed in the air. None of the above.arrow_forward
- Q1. A ray of light (ray a) in air (index of refraction=1) strikes a flat piece of glass at an angle of p0 = 84° with respect to the normal, as shown in the figure. The index of refraction of the glass is 1.5. What is the angle 0 between the reflected ray (ray b) and refracted ray (ray c) rays? (based on this question, answer from i to v) doi a 1 91 air glass 0. |02 C Fig. 1 nd thearrow_forwardThe figure below shows the path of a light beam through several slabs with different indices of refraction. (n4 = 1.01) 10% = n = 1.60 n = 1.40 n = 1.20 14 (a) If 01 35.0°, what is the angle 02 of the emerging beam? 63.12 X Your response is within 10% of the correct value. This may be due to roundoff error, or you could have a mistake in your calculation. Carry out all intermediate results to at least four-digit accuracy to minimize roundoff error.ºarrow_forwardray of light strikes a flat block of glass at an incidence angle of ?1 = 38.6°. The glass is 2.00 cm thick and has an index of refraction that equals ng = 1.52. a.)What is the angle of refraction, ?2, that describes the light ray after it enters the glass from above? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 2 decimal places.) b.) With what angle of incidence, ?3, does the ray approach the interface at the bottom of the glass? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 2 decimal places.) c.) With what angle of refraction, ?4, does the ray emerge from the bottom of the glass? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 1 decimal place.) d.) The distance d separates the twice-bent ray from the path it would have taken without the glass in the way. What is this distance (in cm)? e.) At what speed (in m/s) does the light travel within the glass? f.) How many nanoseconds does the light take to pass through the glass along the angled path shown here?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON