
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
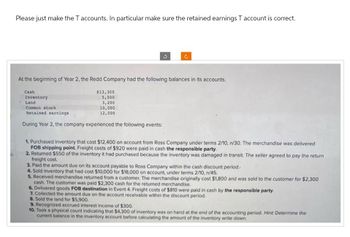
Transcribed Image Text:Please just make the T accounts. In particular make sure the retained earnings T account is correct.
At the beginning of Year 2, the Redd Company had the following balances in its accounts.
Cash
Inventory
Land
Common stock
Retained earnings
$13,300
5,500
3,200
10,000
12,000
During Year 2, the company experienced the following events:
1. Purchased inventory that cost $12,400 on account from Ross Company under terms 2/10, n/30. The merchandise was delivered
FOB shipping point. Freight costs of $920 were paid in cash the responsible party.
2. Returned $550 of the inventory it had purchased because the inventory was damaged in transit. The seller agreed to pay the return
freight cost.
3. Paid the amount due on its account payable to Ross Company within the cash discount period.
4. Sold inventory that had cost $10,000 for $18,000 on account, under terms 2/10, n/45.
5. Received merchandise returned from a customer. The merchandise originally cost $1,800 and was sold to the customer for $2,300
cash. The customer was paid $2,300 cash for the returned merchandise.
6. Delivered goods FOB destination in Event 4. Freight costs of $810 were paid in cash by the responsible party.
7. Collected the amount due on the account receivable within the discount period.
8. Sold the land for $5,900.
9. Recognized accrued interest income of $300.
10. Took a physical count indicating that $4,300 of inventory was on hand at the end of the accounting period. Hint: Determine the
current balance in the inventory account before calculating the amount of the inventory write down.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help me with all answers I will give upvote thankuarrow_forwardFisher Corporation uses the perpetual FIFO inventory method and has the following information regarding its inventory: Date Inventory Events Amount June 1 Beginning balance 60 units at $6 $360 June 3 Purchased 510 units at $10.00 5,100 June 25 Purchased 370 units at $12.00 4,440 If the company sold 350 units of inventory for $12 each what would be the effect of the sale? Record the effect on the following accounts: Assets Liabilities Stockholders' Equity Revenues and Expenses (Income Statement) Net Income Cash - Decrease $4200; Inventory - Decrease $3500 Cash - Decrease $4200; Inventory - Increase $4200 Cash - Decrease $4200; Inventory - No Change Cash - Increase $4200; Inventory - Decrease $3260 Cash - Increase $4200; Inventory - Increase $3500 Cash - Increase $4200; Inventory - No Change Cash - No Change; Inventory - Decrease $3260 Cash - No Change; Inventory - Increase $3260 Cash - No Change; Inventory - No Changearrow_forwardnces Blooming Flower Company was started in Year 1 when it acquired $60,500 cash from the issue of common stock. The following data summarize the company's first three years' operating activities. Assume that all transactions were cash transactions. Purchases of inventory Sales Cost of goods sold Selling and administrative expenses Income Statements Required: Prepare an income statement (use multistep format) and balance sheet for each fiscal year. (Hint: Record the transaction data for each accounting period in the accounting equation before preparing the statements for that year.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Balance Sheets Assets Cash Merchandise inventory Prepare a balance sheet for each fiscal year. (Hint: Record the transaction data for each accounting period in the accounting equation before preparing the statements for that year.) Total assets Liabilities Stockholders' equity Common stock Retained earnings Year 1 $ 22,200 26,400 12,500…arrow_forward
- The management of Zigby Manufacturing prepared the following balance sheet for March 31. ZIGBY MANUFACTURING Balance Sheet March 31 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Raw materials inventory Finished goods inventory Equipment Less: Accumulated depreciation $ 2,160,000 540,000 $ 144,000 1,239, 840 354,600 1,171,944 1,620,000 Liabilities Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Loan payable Long-term note payable Equity Common stock Retained earnings $ 723,600 12,000 1,800,000 1,206,000 788,784 $ 2,535,600 1,994,784 $4,530,384 Total assets $4,530,384 Total liabilities and equity To prepare a master budget April, May, and June, management gathers the following information. a. Sales for March total 73,800 units. Budgeted sales in units follow: April, 73,800; May, 70,200; June, 72,000; and July, 73,800. The product's selling price is $24.00 per unit and its total product cost is $19.85 per unit. b. Raw materials inventory consists solely of direct materials that cost $20 per pound. Company…arrow_forward* Question Completion Status: 1. 4 6 7 8 10 11 12 Presented below are selected account balances for DEF Corporation as of December 31, 2021. (All accounts have their normal balances) Inventory 12/31/21 $65,000 Cost of Goods Sold $230,000 Sales Revenue 450,000 Selling Expenses 26,000 Interest Revenue 10,000 Administrative Expenses 28,000 Dividends 20,000 Income Tax Expense 20,000 Common Stock 70,000 Retained Earnings 48,000 Rent Revenue 13,000 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 11,000 Accounts Receivables 88,000 Rent Expense 16,000 Instructions: Prepare the necessary closing entries for DEF Corporation on December 31, 2021. Select and copy the table below to answer in the space provided. Account Description Debit Credit Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers. Save All Answers Close Window Save and Submitarrow_forwardPresented below are selected account balances for Skysong Co. as of December 31, 20X1. Inventory 12/31/X1 Common Stock Retained Earnings Dividends Sales Returns and Allowances $60,380 73,910 44,880 18,039 Cost of Goods Sold Selling Expenses Administrative Expenses Income Tax Expense $224,260 16,250 37,419 29,860 11,879 Sales Discounts 15,240 Sales Revenue 417,310 Prepare closing entries for Skysong Co. on December 31, 20X1.arrow_forward
- The accounting records of Wall's China Shop reflected the following balances as of January 1, Year 2 Cash Beginning inventory Common stock Retained earnings $ 17,600 14,260 (155 units @ $92) 14,700 17,160 The following five transactions occurred in Year 2 1. First purchase (cash): 120 units @ $94 2. Second purchase (cash): 205 units @ $102 3. Sales (all cash): 425 units @ $197 4. Paid $15,000 cash for salaries expenses 5. Paid cash for income tax at the rate of 40 percent of income before taxes Required a. Compute the cost of goods sold and ending inventory, assuming (1) FIFO cost flow. (2) LIFO cost flow, and (3) weighted-average cost flow. Compute the income tax expense for each method. b. Record the above transactions in general journal form and post to T-accounts assuming each of the cost flows listed. Assume perpetual inventory system is used. 1. FIFO 2 LIFO 3. Weighted Average c. Use a vertical model to show the Year 2 income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows…arrow_forwardĮThe following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, Year 1, the general ledger of a company includes the following account balances: Accounts Debit Credit Cash Accounts Receivable Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts $ 25,600 47,200 $ 4,700 Inventory Land 20,500 51,000 17,500 Equipment Accumulated Depreciation Accounts Payable Notes Payable (6%, due April 1, Year 2) Common Stock 2,000 29,000 55,000 40,000 31,100 $161,800 $161,800 Retained Earnings Totals During January Year 1, the following transactions occur: January 2 Sold gift cards totaling $9,000. The cards are redeemable for merchandise within one year of the purchase date. January 6 Purchase additional inventory on account, $152,000. January 15 The comapany sales for the first half of the month total $140,000. All of these sales are on account. The cost of the units sold is $76,300. January 23 Receive $125,900 from customers on accounts receivable. January 25 Pay $95,000 to inventory suppliers on…arrow_forwardA business had an opening inventory of $180,000 and a closing inventory of $220,000 in its financial statements for the year ended 31 December 20X5. Which of the following entries for these opening and closing inventory figures are made when completing the financial records of the business? Debit Credit $ Inventory account Statement of P/L A 180,000 180,000 Statement P/L 220,000 Inventory account 220,000 В Statement of P/L 180,000 Inventory account 180,000 Inventory account Statement of P/L 220,000 220,000 Inventory account 40,000 Purchases account 40,000 D Purchases account 40,000 Inventory account 40,000arrow_forward
- Why i'm i getting this question wrong ?arrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forwardA company uses periodic system for stock/inventory valuation. At the beginning of the period there was opening inventory amounted to N$30 000. During the year, a firm bought goods costing N$190 000. The value of closing inventory was N$25 000. What was the amount of the cost of sales? Answer:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education