
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
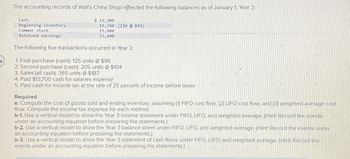
Transcribed Image Text:The accounting records of Wall's China Shop reflected the following balances as of January 1, Year 3:
Cash
Beginning inventory
Common stock
Retained earnings
$ 19,300
19,740 (210 @ $94)
15,600
23,440
The following five transactions occurred in Year 3:
4
1. First purchase (cash): 125 units @ $96
2. Second purchase (cash): 205 units @ $104
3. Sales (all cash): 365 units @ $187
4. Paid $13,700 cash for salaries expense
5. Paid cash for income tax at the rate of 25 percent of income before taxes
Required
a. Compute the cost of goods sold and ending inventory, assuming (1) FIFO cost flow. (2) LIFO cost flow, and (3) weighted-average cost
flow. Compute the income tax expense for each method.
b-1. Use a vertical model to show the Year 3 income statement under FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average. (Hint Record the events
under an accounting equation before preparing the statements.)
b-2. Use a vertical model to show the Year 3 balance sheet under FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average. (Hint Record the events under
an accounting equation before preparing the statements.)
b-3. Use a vertical model to show the Year 3 statement of cash flows under FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average. (Hint Record the
events under an accounting equation before preparing the statements.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Fisher Corporation uses the perpetual FIFO inventory method and has the following information regarding its inventory: Date Inventory Events Amount June 1 Beginning balance 60 units at $6 $360 June 3 Purchased 510 units at $10.00 5,100 June 25 Purchased 370 units at $12.00 4,440 If the company sold 350 units of inventory for $12 each what would be the effect of the sale? Record the effect on the following accounts: Assets Liabilities Stockholders' Equity Revenues and Expenses (Income Statement) Net Income Cash - Decrease $4200; Inventory - Decrease $3500 Cash - Decrease $4200; Inventory - Increase $4200 Cash - Decrease $4200; Inventory - No Change Cash - Increase $4200; Inventory - Decrease $3260 Cash - Increase $4200; Inventory - Increase $3500 Cash - Increase $4200; Inventory - No Change Cash - No Change; Inventory - Decrease $3260 Cash - No Change; Inventory - Increase $3260 Cash - No Change; Inventory - No Changearrow_forwardA record of transactions for the month of May was as follows: Purchases Sales May 1 (balance) 480 @ $5.50 May 3 240@ $8.00 4 1,390 @ $5.40 6 1,080 @ $8.00 8 800 @ $5.60 12 900 @ $8.50 14 700 @ $5.70 18 450 @ $8.50 22 1,250 @ $5.80 25 1,400 @ $9.00 29 560 @ $5.85 Assuming that perpetual inventory records are kept in dollars, determine the ending inventory using LIFO. Ending inventory +A $arrow_forward3A company with an accounting date of 31 October carried out a physical check of inventory on 4 November 20X3, leading to an inventory value at cost at this date of $483,700. Between 1 November 20X3 and 4 November 20X3 the following transactions took place: (1) Goods costing $38, 400 were received from suppliers. (2) Goods that had cost $ 14,800 were sold for $20,000. (3) A customer returned, in good condition, some goods which had been sold to him in Octoberfor $600 and which had cost $400. (4) The company returned goods that had cost $1,800 in October to the supplier, and received a credit note for them.REQUIRED: Please calculate the figure should be appeared in the company's financial statements at 31 October 20X3 for closing inventory, based on this information.arrow_forward
- The accounting records of Wall's China Shop reflected the following balances as of January 1, Year 2 Cash Beginning inventory Common stock Retained earnings $ 17,600 14,260 (155 units @ $92) 14,700 17,160 The following five transactions occurred in Year 2 1. First purchase (cash): 120 units @ $94 2. Second purchase (cash): 205 units @ $102 3. Sales (all cash): 425 units @ $197 4. Paid $15,000 cash for salaries expenses 5. Paid cash for income tax at the rate of 40 percent of income before taxes Required a. Compute the cost of goods sold and ending inventory, assuming (1) FIFO cost flow. (2) LIFO cost flow, and (3) weighted-average cost flow. Compute the income tax expense for each method. b. Record the above transactions in general journal form and post to T-accounts assuming each of the cost flows listed. Assume perpetual inventory system is used. 1. FIFO 2 LIFO 3. Weighted Average c. Use a vertical model to show the Year 2 income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows…arrow_forwardInventory purchased on credit in the periodic system, select one?arrow_forwardanswer step by steparrow_forward
- A company reported the following balances in some selected accounts: Inventory, 1 March $4,000, Transportation-in $200, Inventory, 31 March $6,000, Purchases $16,000, Purchase Returns and Allowances $500, Purchase discounts $700, Sales $35,000, Sales discounts $1,500. The Cost of Goods Sold for the period is: Group of answer choices $13,000 $16,000 $12,600 $13,400arrow_forwardThe records of Heese Stores provided the following data for the year: Cost Retail (Base inventory) Inventory, January 1 $150,000 $ 250,000 Net purchases 830,800 1,318,000arrow_forwardCarr Corporation has provided the following information for its most recent month of operation: sales $8,300; beginning inventory $1,150; ending inventory $2,150 and gross profit $5,450. How much were Carr's inventory purchases during the period? Multiple Choice O $9,450. $5,450. $3,850. $6,150.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education