
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please do question 4 for the reaction mechanism
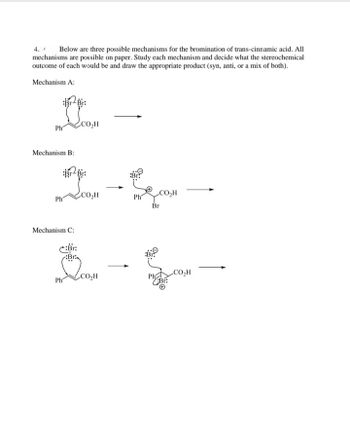
Transcribed Image Text:The document outlines three potential mechanisms for the bromination of trans-cinnamic acid. Each mechanism illustrates a different approach to the reaction, and all are feasible on paper. The task is to analyze each mechanism, determine the stereochemical outcome (syn, anti, or a mix), and draw the expected product.
**Mechanism A:**
- The diagram shows the trans-cinnamic acid molecule with a Br-Br bond approaching it.
- There are no specific stereochemical details or further reaction steps provided in the diagram, suggesting that this is a simplified representation.
**Mechanism B:**
- The trans-cinnamic acid reacts with Br-Br.
- A cyclic bromonium ion intermediate is formed.
- The bromide ion attacks from the side opposite the existing bond, indicating an anti-addition.
- This mechanism highlights the formation of a trans product due to the anti-attack.
**Mechanism C:**
- The first step shows the approach of Br-Br to trans-cinnamic acid, forming a bromonium ion with a positive charge on the bromine.
- The bromide ion subsequently attacks from the side opposite the formed bromonium ion.
- This results in the formation of the anti product, similar to Mechanism B, with the bromine atoms added on opposite sides of the molecule.
In summary, each mechanism details a potential stereochemical pathway for the bromination of trans-cinnamic acid, with Mechanism B and C both resulting in anti-addition due to the bridging bromonium intermediate and subsequent attack by the bromide ion from the opposite side.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pls help ASAP.arrow_forward4.arrow_forward5. The collision theory of reaction rates states that the rate of a reaction depends on the number of collisions between mol- ecules, the average energy of the collisions, and the effectiveness of the collisions. (a) How does temperature affect each of these factors in collision theory? (b) Does the effect of temperature on the reaction rate support the collision theory of reaction rates? Explain.arrow_forward
- ス3 45 Mass of Cu(NO,),.3H;O 2.3366 Volume of Deionized H,0 57.0 Concentration of Cu* Solution Moles Cu* TRIAL # Initial Temperature Final Temperature qreaction reaction- 23.25 AH. .14 24.96 24.14 24.96 とL'Sで 25.72 25.70 ○L'Sで 24.99 24.98 24.98 25.14 .14 24.98 8. 9. 10 Average Bond Energy Coordination Number of Cu²*arrow_forwardArrange the reactions in increasing order of rate. What type of reactions are these?arrow_forwardQuestion: What is the fundamental difference between kinetic stability and thermodynamic stability in chemical reactions, and how do they influence reaction rates?arrow_forward
- All catalysts have the same rate of effectiveness for all reactions. O True O Falsearrow_forwardThe half-life of a chemical reaction is the time it takes for half the present reactants to be used up when a reaction has reached the half-way point when only half of the reactant is used the time passed when a reaction is half overarrow_forwardfastest reaction rate and why using the collision theory. Use examples from the data to support your response. Use the diagram below to explain which letter choice would have the A B ZER ELIZER D SELTZERarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY