
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please consider the following phases of jumping:
C. Falling back down toward the trampoline
D. Pushing down into the trampoline and slowing down after falling
please draw free body diagram for the above cases. The diagram needs to have all relevant forces labeled, scalded poportionstelt, and there to be a coordinate axis present. Indicate the net force if it is non-zero.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
C. FBD of falling back down toward the trampoline.
Remember the person is in air, so the forces acting on him/her will depend on mass of the person(m) times acceleration due to gravity(g).
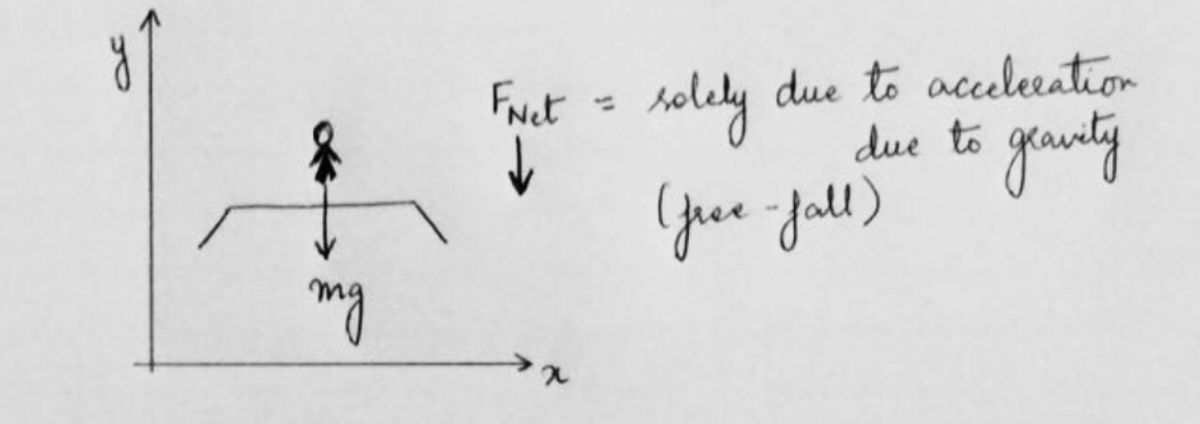
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The question below refer to a large truck which breaks down out on the road and receives a push back to town by a small compact car. Pick one of the choices A through J below which correctly describes the forces between the car and the truck in the description below: The car, still pushing the truck, is at cruising speed and continues to travel at the same speed. A. The force of the car pushing against the truck is equal to that of the truck pushing back against the car. B. The force of the car pushing against the truck is less than that of the truck pushing back against the car. C. The force of the car pushing against the truck is greater than that of the truck pushing back against the car. D. The car's engine is running so it applies a force as it pushes against the truck, but the truck's engine isn't running so it can't push back with a force against the car. E. Neither the car nor the truck exert any force on each other. The truck is pushed forward simply because it is in the way…arrow_forwardProblem 5 Push a Push The three boxes shown are at rest when we pull the right- hand box to the right with a force Fo. (a) Draw free-body diagrams for all three boxes. Draw a fourth free-body dia- gram for the entire system. (b) What is the acceleration of the 3m box? (c) What is the magnitude of the force on the m box due to the rope? What is the magnitude of the force on the 3m due to the m box? m 3m 2marrow_forwardPlease solvearrow_forward
- Draw the free body diagram for the block shown below and determine if sliding would occur if the block is sitting on an icy surface. Warrow_forwardTwo Men and a Truck Movers need to lower a piano out a third story balcony doors onto the ground below. They rig up a dolly system to safely lower the piano. Each of the cables holding up the piano has a tension force of 2285 N. The angle at which the cables are attached to the piano is 69 degrees. Calculate the mass of the piano.arrow_forward$4.. YouTube to MP3 Co. phone cover for mo... AGARWAL-PHY-166 N3 Part A What force is needed to accelerate a sled (total mass = 60 kg ) at 1.8 m/s on horizontal frictionless ice? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Value Units Submit Request Answer rovide Feedbackarrow_forward
- Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. A flying squirrel is gliding (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Diagram the forces acting on the squirrel.arrow_forwardProblem 4: A crate sits on a rough surface. Using a rope, a man applies a force to the crate, as shown in the figure. The force is not enough to move the crate, however, and it remains stationary. Use f to represent the force of friction. Please use the interactive area below to draw the Free Body Diagram for the crate. L. y 1 Add Force S Reset All Ftotal,x: Ftotal.y:arrow_forwardA horizontal force, F1, and a force F2 acting at an angle of 0 to the horizontal, are applied to a block of mass m. The block is moving to the right at a constant velocity across a rough surface. y F, Use Fk to denote the force of kinetic friction. m Please use the interactive area below to draw the Free Body Diagram for the block. 1 Add Force S Reset All Fn v 90 vx Fg v 270 vx F1 v0 Fk v 180 vx Fn Fk F1 Fg Ftotal,x:0 Ftotal,y: 0 Submit I give up! Hint Feedbackarrow_forward
- A. Free-body Diagram. Directions: In each of the following situations, represents the object with a dot. Draw and label all the forces using the standard force symbols learned in the class in the space provided. 1. Object is motionless on the surface. 3. Object slows down due to friction on an incline plane. 3. Object slows down due to friction on an incline 2. Object is motionless plane. on the surface.arrow_forwardA sports car with a mass of 1,385 kg is at rest on a flat, horizontal road. 5.4 s later, that car is moving forward at a speed of 90 mph. Calculate the acceleration of the car and the average net force acting on the car.For this problem: Draw a diagram of the motion Draw a free body diagram.Write your N2 Law equationList your kinematics variablesSolve the algebraic equation using variables.Plug in your information and solve.arrow_forwardFor each object below, draw a clear Free Body Force Diagram. Label all forces that act on the object such as mg, T, n, etc. Label appropriate axes such as x, y, and z. Include friction in all cases where an object slides against another. All pulleys are massless and frictionless.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON