
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
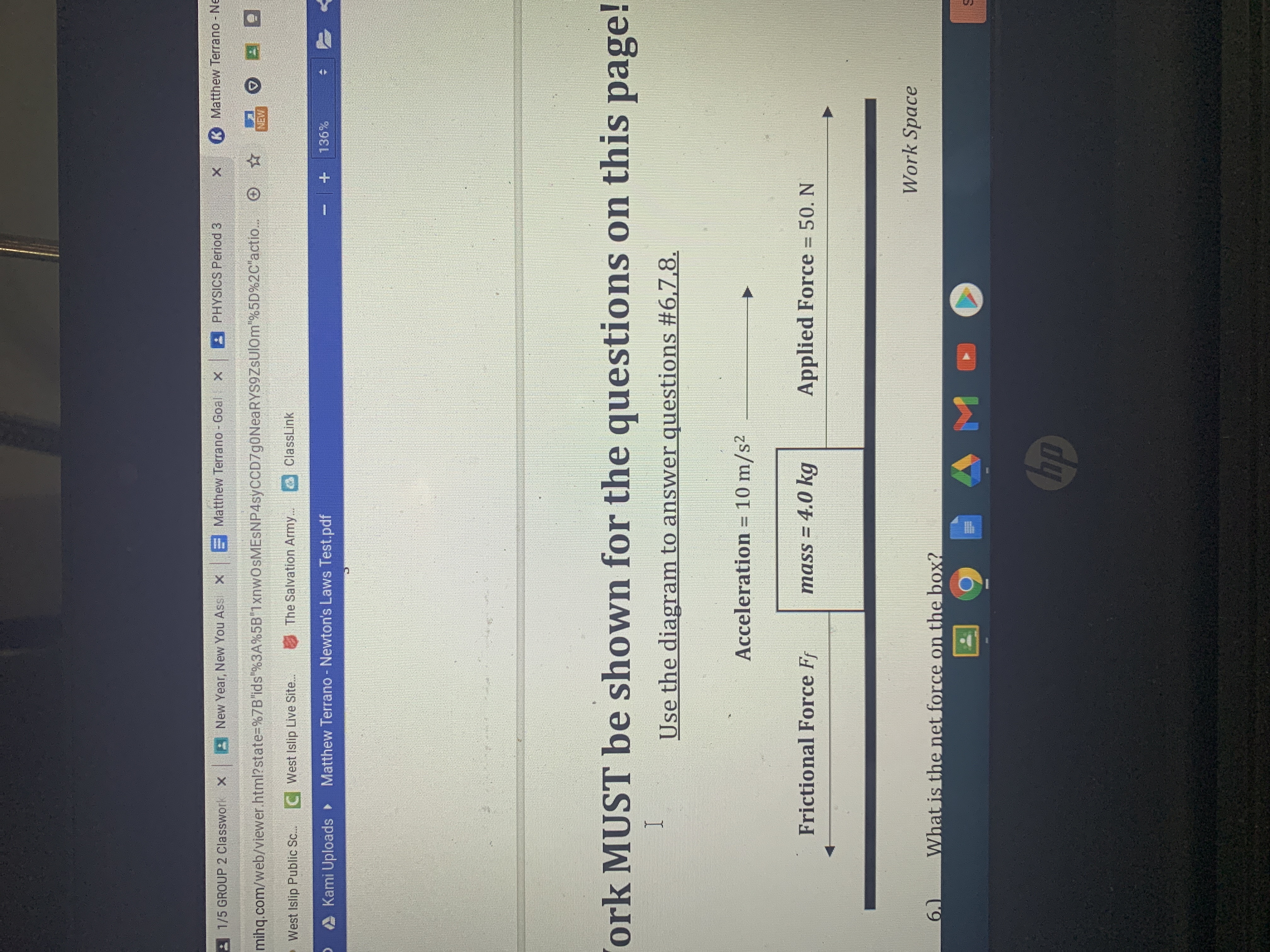
using the diagram in the picture what is the magnitude of the frictional force (Ff) on the box?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the System Diagram and Free Body Diagram shown below. If you were to add up the force of tension and the force of gravity, what would you get? Question options: The normal force - - The force of kinetic friction -0 - The centripetal force - The force of static friction - The centrifugal force Consider the System Diagram and Free Body Diagram shown below. System Diagram Free Body Diagram the system the environment FT tension Non-contact forces Gravityarrow_forwardA circular loop of wire lies in a plane perpendicular to a magnetic field. The magnetic field has a magnitude of 1.3 T and points out of the page as shown in the figure. The radius of the loop is 18 cm and it has a resistance of 3.2 Ω. Find the induced emf in the loop of wire if the magnetic field doubles in magnitude in 1 seconds. What is the induced current in the loop? In which direction is the induced current?arrow_forwardPlease draw the free diagram clear and also indicate if we need to add forcearrow_forward
- A person pushes a box along the ground. The box has the force diagram shown below. Examine the force diagram to answer the following questions: a. Is the box in equilibrium? If so explain how you can tell. If not, explain why not. b. If the person wants the box to move at constant velocity, should they adjust their pushing on the block? If so, explain how they should change their push. If not, explain why they should change nothing about their pusharrow_forwardTo find the resultant of multiple forces using Cartesian components and to determine the direction of this resultant from its components. Part B- Resultant of adding F, and F2 and Fa As shown, three forces act on the tip of a pole. F1 and forms the following angles with the x, y, and z axes, respectively: a = 56.2, 8 = 66.6°, and 136.9. F- 110 lb, forms the angle 28 with the z axis, and forms the angle 8 = 15' between the x axis and the projection of F, in the zy plane. 50 i + 145 j + 25 k Ib. F = 150 lb Find the resultant of adding Fi. Fa, and F. Express your answer in component form. Express your answers, separated by commas, to three significant figures. > View Available Hìnt(s) Vo AEo tvec R1s = i lb, j lb, k Ib Submit Part C- Direction of a resultant For the given forces, Fi. F. and Fs. find the three direction angles ag. BR. and ya betwoen the resuitant force Rn found in Part B and the x. y, and z axes, respectively. Express your answers, separated by commas, in degrees to three…arrow_forwardangle of inclination is 30 degreesarrow_forward
- A 4.8-m-long rope of mass 1.8 kg hangs from a ceiling.arrow_forwardA weight hangs on a frictionless pulley as shown in the figure.a.) What is the tension on the pulley strut?b.) What is the value of angle B?arrow_forward(Newton's laws and their applications) A block with mass m1 slides down an inclined plane whose angle is 22 °, the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane is 0,250. The block is attached to an ideal rope that passes through two ideal pulleys until it is attached to a fixed support, as shown in figure 3. A rope leaves the axis of the movable pulley up to a block of mass m2 3 m2 m1 Figure 3. Diagram of exercise 3 A. Discuss what difference the exercise will make if one more pulley is placed on the ceiling that makes the rope connect to the rod of the movable pulley.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON