
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
In the network shown below, all resistors are 2 Ω and all batteries are 5
Volts. What are the magnitude and direction (up or down) of the current labelled i
in the figure? Hint: You might be tempted to set up mesh equations for this, which
is obviously ridiculous (although it would work if you spent the time to do it).
Instead, try to find a path that includes the branch with i but no other branches that
have resistors. Then you can use KVL. Draw the path on the circuit diagram.
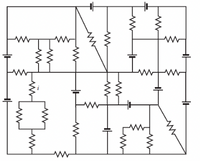
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts an intricate electrical circuit diagram consisting of multiple components, including resistors and capacitors. The circuit is connected in various configurations, such as series and parallel connections.
Key features of the circuit:
1. **Resistors**: Multiple resistors are placed throughout the circuit, identifiable by the zigzag line symbols. They are arranged in various configurations involving parallel and series connections, contributing to the overall resistance of the circuit.
2. **Capacitors**: There are several capacitors denoted by two parallel lines, one of which is curved. These components are positioned at various points in the circuit, affecting the circuit's ability to store charge.
3. **Complex Configurations**: The circuit includes complex networks where resistors and capacitors are interlinked in multiple loops and branches. This complexity may represent a challenge for analysis in educational settings, often requiring the application of Kirchhoff's laws or other circuit analysis techniques.
4. **Current 'i'**: A current notation 'i' is present in one of the branches, indicating a flow of electric current through that part of the circuit, which may be a point of analysis for calculating current distribution or other electrical properties.
This diagram can be used for educational purposes, such as teaching circuit analysis, examining the combination of series and parallel circuits, and understanding the role of different electrical components.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the voltage drops across and current through each resistor in the following circuit. Use Kirchhoff s rules showing your direction for current, voltage drops across the resistors, your work to evaluate the circuit and your checks that the values you have are correct. R1 10 R2 10 V 22 V R3 20arrow_forwardFor the circuit shown in the figure above, what is the equivalent resistance Req as seen from the a-b terminals? Assume R1 = 83 , R2 = 55 , and R3 = 91arrow_forwardParallel Circuits: Find the Unknown Resistor value R1 and Currents 1, 12 & 13 on the circuit below. 1.0 k 0.5 A R3 R2 680 0 100 V: R1 (c)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,