
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Find the minimum height h1 that will allow the cart in the figure to make it around the loop at h2 if h2 = 12.5 m. Approximate the cart as a point mass and treat the surface as frictionless.
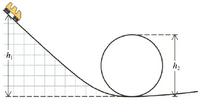
Transcribed Image Text:h2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 2.0kg ball moves counterclockwise in a 0.75 m radius Vertical Circle. The Vt at the bottom is measured to be 7.0 m/s. What is the tension in the string at A, B, C, D? (See attachment)arrow_forwardA small block, initially at rest at point A, slides down a curve leading to a half-circle of radius R 6.75 m. The surface is frictionless, with the exception of a horizontal segment BC of length s=22.5 m, which has the coefficient of friction equal u=0.145. A. What is the minimal height (h) for which the block reaches the top of the semicircle, point D? B. For the minimal height calculated in Part (a), what is the speed at point C? Please answer both A and B.arrow_forwardA 0.2-kg ball is attached to a rope and is swung in a horizontal surface that has negligible friction. The circular path is moves in has a radius of 0.6 m. If the ball makes 150 revolutions per minute, the tension force of the string is:arrow_forward
- A roller coaster has a vertical loop with radius 27.2 m. With what minimum speed should the roller-coaster car be moving at the top of the loop so that the passengers do not lose contact with the seats?arrow_forwardA metallic box begins at rest at point 1 at a height of 5R, where R is the radius of the circular part of the track. The box slides down the frictionless track and around the loop. If the box has a gravitational weight of 80 N, what is the magnitude of the normal force acting on the box at point 2?arrow_forwardA robe can hold a maximum F₁ = 100M. On a frictionless horizontal surface, a 0.75kg object attached to the This object goes rope. around a circle with 1.5m radius. lalhat is the Vmax the object can have ? 7 e it canarrow_forward
- Consider a roller-coaster car on a track that has a loop of known radius R. If there is no friction between the rollercoaster car and the track, then determine (a) the minimum speed at the top of the loop for the rollercoaster car to still be in contact with the track and (b) the minimum height h the rollercoaster car must start from in order to go all the way around the loop without losing contact with the track (assuming the rollercoaster starts from rest). The only knowns here are R and g, so your symbolic answers need to be in terms of these. Part (a) can be treated using newton's second law and uniform circular motion (even though it's not really uniform). Start with a free-body diagram of a coaster car at the top of the loop. What does it mean for the rollercoaster car to still be "in contact" with the track? Part (b) can be treated using conservation of mechanical energy. You'll need your result from part (a). How high above the ground are you when you're at the top…arrow_forwardA roller coaster of mass 380.0 kg is moving with a speed of 2.50 m/s at point A, at a height of h= 60.0m from the ground (see the figure). The radius of the circular loop is 22.0 m. Neglect friction. 1. Find the speed of the roller coaster at point C. 2. Compute the normal force on the cart at point C.arrow_forwardConsider the pendulum shown in the figure. The pendulum is released at point A, swings through its lowest point at point C, and reaches its turning point at point D. You may ignore the effects of air resistance. Answer the following questions: A В D C (a) Draw the free body diagram when the object is located at point B. (b) On your free-body diagram, draw a circle around the force components that contribute to the centripetal acceleration and draw a square around the force components that contribute to the tangential acceleration. (c) Draw the direction of the total acceleration vector when the object is located at point B.arrow_forward
- Experimental Ezra ties a 59.4 g tennis ball to a string and swings it in a vertical circle. Ezra swings the ball so that it always has constant speed of v = 4.82 m/s. The radius of the swing is r = 0.787 m and Ezra's hand is H = 1.40 m above the ground as shown. y Harrow_forwardA 35.0 kg child is on a swing following a circular path with a radius of 3.25 m. As the swing passes through the lowest point of the circular path, the seat exerts a force of 480 N [up] on the child, what is the speed of the swing at that point?arrow_forwardwhat if the track is frictionless, find the speed at the top of the point D loop with a radius of 20. meters?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON