
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
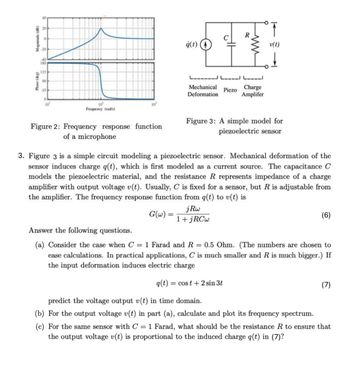
Transcribed Image Text:Phase (deg)
Magnitude (dB)
20
20
40
180
135
90
45
10'
0
ġ(t)
하
R
www
Mechanical
Deformation
Piezo
Charge
Amplifer
10
10
Frequency (rad's)
v(t)
Figure 2: Frequency response function
of a microphone
Figure 3: A simple model for
piezoelectric sensor
3. Figure 3 is a simple circuit modeling a piezoelectric sensor. Mechanical deformation of the
sensor induces charge q(t), which is first modeled as a current source. The capacitance C
models the piezoelectric material, and the resistance R represents impedance of a charge
amplifier with output voltage v(t). Usually, C is fixed for a sensor, but R is adjustable from
the amplifier. The frequency response function from q(t) to v(t) is
Answer the following questions.
G(w)=
=
jRw
1+jRCw
(6)
(a) Consider the case when C = 1 Farad and R = 0.5 Ohm. (The numbers are chosen to
ease calculations. In practical applications, C is much smaller and R is much bigger.) If
the input deformation induces electric charge
=
q(t) cost+2 sin 3t
(7)
predict the voltage output v(t) in time domain.
(b) For the output voltage v(t) in part (a), calculate and plot its frequency spectrum.
(c) For the same sensor with C = 1 Farad, what should be the resistance R to ensure that
the output voltage v(t) is proportional to the induced charge q(t) in (7)?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A test was undertaken to find the dynamic properties of a SDOF system. The measured transient response recorded is shown in Figure QA2a. If the stiffness of the system is 1,000 N/m estimate: i) the damping ratio, ii) the undamped natural frequency, and iii) the mass of the system. Displacement (m) 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 O -0.02 -0.04 -0.06 -0.08 Figure QA2a 0.5 Time (s) 1.5 2arrow_forwardIt's not a graded assignement, but a question in past paper.arrow_forwardDo not answer in image formatarrow_forward
- please help me with my homework. please provide brief explination , many thanks for your timearrow_forwardThe problem is in the photoarrow_forwardQUESTION 4 Consider a system model given by d²x (t) dx (t) +3. dt² dt x (0) = 0 dx (1) dt O O t=0 What is the impulse response? -21 e -t - e 2e-¹ -e = 1 - e 1 --e 2 1 + -e 2 -2¹ +e-¹ +1 -1 ¹+e-21 + 2x(t) =f(t) 2 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY