
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
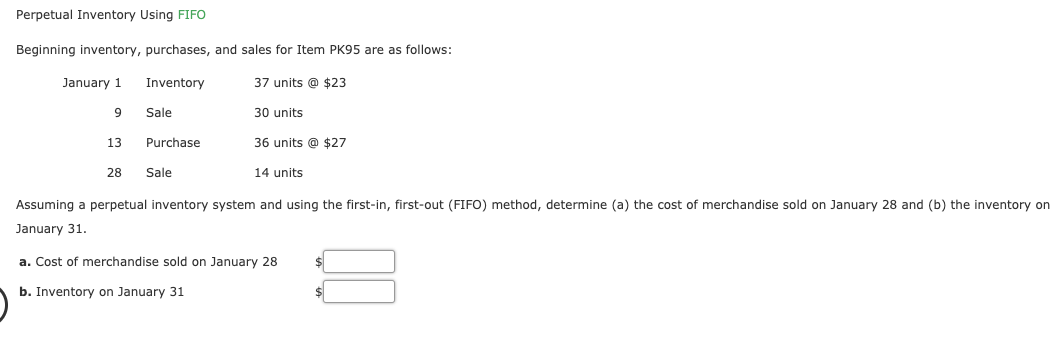
Transcribed Image Text:Perpetual Inventory Using FIFO
Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item PK95 are as follows:
37 units @ $23
30 units
36 units @ $27
January 1
Inventory
Sale
13
Purchase
28
Sale
14 units
Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on January 28 and (b) the inventory on
January 31.
a. Cost of merchandise sold on January 28
b. Inventory on January 31
$4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item 88-HX are as follows: Jan. 1 Inventory 92 units @ $18 8. Sale 74 units 15 Purchase 102 units @ $21 27 Sale 86 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of goods sold on Jan. 27 and (b) the inventory on Jan. 31. a. Cost of goods sold on Jan. 27 b. Inventory on Jan. 31arrow_forwardPerpetual Inventory Using LIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item PK95 are as follows: October 1 Inventory 108 units @ $20 5 Sale 86 units 11 Purchase 120 units @ $24 21 Sale 101 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on October 21 and (b) the inventory on October 31. a. Cost of merchandise sold on October 21 $fill in the blank 1 b. Inventory on October 31 $fill in the blank 2arrow_forwardPerpetual Inventory Using LIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item 88-HX are as follows: July 1 Inventory 80 units @ $23 8 Sale 64 units 15 Purchase 89 units @ $27 27 Sale 75 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of goods sold on July 27 and (b) the inventory on July 31.arrow_forward
- Perpetual Inventory Using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Zeta9 are as follows: Oct. 1 Inventory 73 units @ $18 7 Sale 47 units 15 Purchase 54 units @ $20 24 Sale 33 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of goods sold on October 24 and (b) inventory on October 31arrow_forwardPerpetual inventory using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Zeta9 are as follows: Date Line Item Description Value Oct. 1 Inventory 39 units @ $15 Oct. 7 Sale 31 units Oct. 15 Purchase 39 units @ $17 Oct. 24 Sale 13 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of goods sold on October 24 and (b) the inventory on October 31.a. Cost of goods sold on October 24 fill in the blank 1 of 2b. Inventory on October 31 fill in the blank 2 of 2arrow_forwardPerpetual inventory using LIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item 88-HX are as follows: July 1 Inventory 82 units @ $20 July 8 Sale 66 units July 15 Purchase 91 units @ $24 July 27 Sale 76 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of goods sold on July 27 and (b) the inventory on July 31. a. Cost of goods sold on July 27 b. Inventory on July 31arrow_forward
- Perpetual Inventory Using FIFO Beginning Inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Zeta9 are as follows: Oct. 1 Inventory 47 units @ $20 7 Sale 31 units 15 Purchase 35 units @ $23 24 Sale 20 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, determine, (a) the cost of goods sold on October 24 and (b) the inventory on October 31. a. Cost of goods sold on October 24 - $412 b. Inventory on October 31 - $ ??????arrow_forwardPerpetual Inventory Using LIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item CZ83 are as follows: March 1 82 units @ $34 5 66 units 91 units @ $37 76 units 11 21 Inventory Sale Purchase Sale Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on March 21 and (b) the inventory on March 31. a. Cost of merchandise sold on March 21 b. Inventory on March 31arrow_forwardPerpetual Inventory Using LIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item PK95 are as follows: July 1 5 Inventory Sale 104 units @ $22 83 units 11 Purchase 115 units @ $24 21 Sale 97 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, determine (a) the cost of merchandise sold on July 21 and (b) the inventory on July 31. a. Cost of merchandise sold on July 21 b. Inventory on July 31arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education