
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) has the chemical formula C2H3NO5 and is an important lung irritant in photochemical smog. An experiment to determine the decomposition kinetics of PAN gave the data below. Determine the order of reaction and calculate the rate constant for the decomposition of PAN.(base the table below):
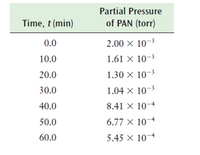
Transcribed Image Text:Partial Pressure
Time, t (min)
of PAN (torr)
0.0
2.00 × 10-3
10.0
1.61 × 10-3
20.0
1.30 × 10-3
30.0
1.04 × 10-3
40.0
8.41 × 10-4
50.0
6.77 × 10¬+
60.0
5.45 × 10-4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Scientists working in Lake Tohopekaliga calculating half-lives of pollutants called volatile organic compounds, often measure a transport rate constant. In one study conducted in the fall of 2010, researchers from the University of South Florida found the half-life of a particular pollutant in the lake when the concentration measured 0.640 M was 13.0 days. Assuming that the process is first order, calculate the rate constant of this process. a) 0.0246 b) 0.0123 c) 0.120 d) 0.160 e) 0.0533arrow_forwardHydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a common and troublesome pollutant in industrial wastewaters. One way to remove H2S is to treat the water with chlorine, in which case the following reaction occurs: H2S(aq)+Cl2(aq)→S(s)+2H+(aq)+2Cl−(aq) The rate of this reaction is first order in each reactant. The rate constant for the disappearance of H2SH2S at 28 ∘C is 3.5×10−2 M−1s−1 If at a given time the concentration of H2S is 2.2×10−4M and that of Cl2 is 0.029 M, what is the rate of formation of Cl-? Express the rate in molarity per second to two significant figures.arrow_forwardHydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a common and troublesome pollutant in industrial wastewaters. One way to remove H2S is to treat the water with chlorine, in which case the following reaction occurs: H2S(aq) + Cl2(aq)---->S(s) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl - (aq) The rate of this reaction is first order in each reactant. The rate constant for the disappearance of H2S at 28 °C is 3.5 x 10-2 M-1 s-1. If at a given time the concentration of H2S is 2.0 x 10 - 4 M and that of Cl2 is 0.025 M, what is the rate of formation of Cl - ?arrow_forward
- The decomposition of hydrogen 2 peroxide is catalyzed by iodide ion. The reaction mechanism is thought to be H,O2(aq) + I(aq) → H,0(I) + 10(aq) 10(aq) + H,O2(aq) → H,O(I) + O2(g) + I(aq) At 25°C, the first step is slow relative to the second step. What is the rate law predicted by the reaction mechanism? Is there a reaction intermediate? 13 | 106arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction:2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3 (g)Write the relative rate expressions for all products and reactants in the order they appear in the written reaction. If the rate of consumption of O2 is 0.90 mM/sec at some time in the reaction, what is the rate of formation of the SO3 at the same time in the reaction?arrow_forward22.6a At 518°C, the half-life for the decomposition of a sample of gaseous acetaldehyde (ethanal) initially at 363 Torr was 410 s. When the pressure was 169 Torr, the half-life was 880 s. Determine the order of the reactionarrow_forward
- Suppose the formation of nitrosyl chloride proceeds by the following mechanism: elementary reaction NO (g) + Cl₂(g) → NOC1₂ (g) k₁ k₂ 2 NOCI₂(g) + NO (g) 2NOCI (g) Suppose also k₁ « k₂. That is, the first step is much slower than the second. step 1 Write the balanced chemical equation for the overall chemical reaction. Write the experimentally- observable rate law for the overall chemical reaction. Note: your answer should not contain the concentrations of any intermediates. 0 rate = k rate constant ロ→ロ 00 × Sarrow_forwardConsider the reaction : 3A + 2B → 4C Initially, and at some fixed temperature, the reaction proceeds at such a rate that 2.3 millimoles of A are consumed in 1 minute and 12 secondes. The reaction takes place in 1 L. The following table contains the experimental data for the reaction. (Taken from Ball. Physical Chemistry, 2nd edition, 2006) Rate (M/s) [A], M [B], M 1.081 x 10-5 0.660 1.23 6.577 x 10-5 4.01 1.23 6.568 x 10-5 4.01 2.25 d. What is the order of the reaction. e. Express the rate law and the integrated form equation. Is the reaction elementary? f. If the rate constant k = 1.61x10-5s-1 and [A0] = 4M, find the period of time between the 12th and 13th half-life. *g. If, for the same reaction, at the same temperature, we were to add a catalyst, would Ea, A, k and v be larger, smaller or equal? Explain.arrow_forwardThe thermal decomposition of phosphine (PH3) into phosphorus and molecular hydrogen is a first-order reaction: 4PH3(g) - P4(g) + 6H2(g) The half-life of the reaction is 35.0 s at 680°C. The first-order rate constant for the reaction is 0.0198/s. Calculate the time (in seconds) required for 95 percent of the phosphine to decompose.arrow_forward
- The reaction between nitric oxide and bromine is described by the following chemical equation: 2NO (g) + Br, (g) – 2NOB (g) Suppose a two-step mechanism is proposed for this reaction, beginning with this elementary reaction: NO (g) + Br, (g) NOB12 (g) Suppose also that the second step of the mechanism should be bimolecular. Suggest a reasonable second step. That is, write the balanced chemical equation of a bimolecular elementary reaction that would complete the proposed mechanism.arrow_forwardIn a study of the decomposition of nitrous oxide at 565 °CN2O(g)N2(g) + ½ O2(g)the following data were obtained: [N2O], M 2.10 1.05 0.525 0.263 seconds 0 602 1.81×103 4.21×103 Hint: It is not necessary to graph these data.(1)The observed half life for this reaction when the starting concentration is 2.10 M is s and when the starting concentration is 1.05 M is s.(2)The average (1/[N2O]) / t from t = 0 s to t = 602 s is M-1 s-1.The average (1/[N2O]) / t from t = 602 s to t = 1.81×103 s is M-1 s-1.(3)Based on these data, the rate constant for this order reaction is M-1 s-1.arrow_forwardThe formation of nitrosyl chloride is described by the following chemical equation: 2NO (g) + Cl₂ (g) → 2NOCI (g) Suppose a two-step mechanism is proposed for this reaction, beginning with this elementary reaction: NO (g) +Cl₂ (g) NOCI₂ (g) Suppose also that the second step of the mechanism should be bimolecular. Suggest a reasonable second step. That is, write the balanced chemical equation of a bimolecular elementary reaction that would complete the proposed mechanism. 11 × Śarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY