
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305387102
Author: Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
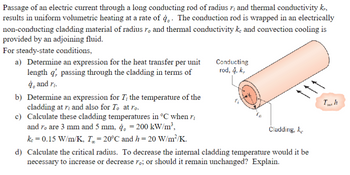
Transcribed Image Text:Passage of an electric current through a long conducting rod of radius r; and thermal conductivity kr,
results in uniform volumetric heating at a rate of q. The conduction rod is wrapped in an electrically
non-conducting cladding material of radius ro and thermal conductivity ke and convection cooling is
provided by an adjoining fluid.
For steady-state conditions,
a) Determine an expression for the heat transfer per unit
length q', passing through the cladding in terms of
à, and ri.
b) Determine an expression for T, the temperature of the
cladding at ri and also for To at ro.
c)
Calculate these cladding temperatures in °C when ri
and ro are 3 mm and 5 mm, q, = 200 kW/m³,
kc = 0.15 W/m/K, T = 20°C and h= 20 W/m²/K.
Conducting
rod, å, k,
Cladding, k
d) Calculate the critical radius. To decrease the internal cladding temperature would it be
necessary to increase or decrease ro; or should it remain unchanged? Explain.
To, h
201
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 15 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- i need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forwardQ1 Passage of an electric current through a long conducting rod of radius r; and thermal conductivity k, results in uniform volumetric heating at a rate of ġ. The conduct- ing rod is wrapped in an electrically nonconducting cladding material of outer radius r, and thermal conduc- tivity k, and convection cooling is provided by an adjoining fluid. Conducting rod, ġ, k, 11 To Čladding, ke For steady-state conditions, write appropriate forms of the heat equations for the rod and cladding. Express ap- propriate boundary conditions for the solution of these equations.arrow_forward
- Please show solution clearlyarrow_forward1.1 Consider the fireclay brick wall of Example 1.1 that is operating under different thermal conditions. The tem- perature distribution, at an instant in time, is T(x) = a+ bx where a 1400 K and b = -1000 K/m. Determine the heat fluxes, q", and heat rates, q, at x = 0 and x = L. Do steady-state conditions exist?arrow_forwardPls handwritearrow_forward
- Please show all work for this mechnical measure problem. Not Ai generated the answers have been wrong I need to understand.arrow_forwardGive True or False for the following: 1.In liquids and gases, heat transmission is caused by conduction and convection 2.The surface geometry is the important factor in convection heat transfer 3. The heat transfer by conduction from heated surface to the adjacent layer of fluid, 4. The heat transfer is increased in the fin when &> 1 5.The unit of the thermal diffusivity is m²/s 6. Temperature change between the materials interfaces is attributed to the thermal contact resistance 7. A material that has a low heat capacity will have a large thermal diffusivity. 8. Heat conduction flowing from one side to other depends directly on thickness 9.Fin efficiency is the ratio of the fin heat dissipation with that of no fin 10.The critical radius is represented the ratio of the convicted heat transfer to the thermal conductivityarrow_forward3.37 Measurements show that steady-state conduction through a plane wall without heat generation produced a convex temperature distribution such that the mid- point temperature was AT, higher than expected for a linear temperature distribution. Tuz AT. T(x) Assuming that the thermal conductivity has a linear dependence on temperature, k = k,(1 + aT), where a is a constant, develop a relationship to evaluate a in terms of AT, T, and T,.arrow_forward
- Derive a formula for the thermal resistance, R₁, for a spherical shell assuming one- dimensional heat flux in the radial direction. The inside and outside radii of the spherical shell are r; and r., respectively, and the shell is made of a material having thermal conductivity k. Assume the temperatures at the inside and outside surfaces of the shell are T and T., respectively. The thermal resistance formula assumes the rate of heat transfer through the spherical shell, Q, is constant. The heat flux is in the radial direction for this one-dimensional case, and the dT heat flux is given by Fourier's law: q, = -k The rate of heat transfer through a dr spherical surface is Q =q₁A where A = 4лr². Derive the formula for the thermal 1 ++)) r = resistance for a spherical shell answer: R₁ 1 1 4лk riarrow_forwardPlease show all work for this mechnical measure problem. Not Ai generated the answers have been wrong I need to understand.arrow_forwardPlease help, asap. Will provide helpful ratings for correct solution. Thank uarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning