
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Part C, D and E please, Thank You!
D) What is the null hypothesis?
E) Reject the null hypothesis because the P-value is greater than the significant level, a
Reject the null hypthosesis because the P-value is less than or equal to the significant level, a
Fail to reject the null hypothesis because the P-value is greater than or equal to the significant level, a
Fail to reject the null hypothesis because the P-Value is greater than the significant level, a
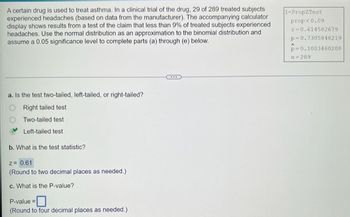
Transcribed Image Text:A certain drug is used to treat asthma. In a clinical trial of the drug, 29 of 289 treated subjects
experienced headaches (based on data from the manufacturer). The accompanying calculator
display shows results from a test of the claim that less than 9% of treated subjects experienced
headaches. Use the normal distribution as an approximation to the binomial distribution and
assume a 0.05 significance level to complete parts (a) through (e) below.
a. Is the test two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed?
Right tailed test
Two-tailed test
Left-tailed test
b. What is the test statistic?
Z= 0.61
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
c. What is the P-value?
P-value=
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
1-PropZTest
prop<0.09
z-0.614582679
p=0.7305848219
p-0.1003460208
n=289
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Part C is incorrect, please help! So, that will probably
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Part C is incorrect, please help! So, that will probably
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Provide an appropriate response. If we fail to reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false, then we have made a Type B error Type I error Correct decision Type II errorarrow_forwardA scientist has read that the mean birth weight, u, of babies born at full term is 7.5 pounds. The scientist, believing that u is different from this value, plans to perform a statistical test. She selects a random sample of birth weights of babies born at full term and finds the mean of the sample to be 7.9 pounds and the standard deviation to be 1.6 pounds. Based on this information, answer the questions below.arrow_forwardResearchers conducted an experiment to test the effects of alcohol. Errors were recorded in a test of visual and motor skills for a treatment group of 23 people who drank ethanol and another group of 23 people given a placebo. The errors for the treatment group have a standard deviation of 2.40, and the errors for the placebo group have a standard deviation of 0.78. Assume that the two populations are normally distributed. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that both groups have the same amount of variation among the errors. Let sample 1 be the sample with the larger sample variance, and let sample 2 be the sample with the smaller sample variance. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? OA. H₂:0² = 0²/2 OB. H₂:0² = 0²/2 H₁: 0²/12 #02/22 H₁:0² > 0²/2 ỌC Họỏi cơ OD. Ho: 0²/02/2 H₁:0² <0² H₁:0² = 0²/2 Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Use technology to identify the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- A high p-value, such as 0.8, provides evidence to say the null hypothesis is true. This statement is true. O This statement is false.arrow_forwardAll test of hypothesis are based on the assumptions that A. The null hypothesis is true B. The observed difference is important c. The null hypothesis is false and should be rejected D. Type l errors are more serious than type ll errors E. None of the abovearrow_forwardSeveral recent studies have suggested that people who suffer from abnormally high blood pressure can benefit from regular exercise. She conducts a small sample of 3 random patients with high blood pressure and measures blood pressure before and after the exercise program. Subject Before After 1 155 133 2 160 140 3 145 120 Conduct a test to see if the claim is supportive. State the hypotheses from the previous problem. (high blood pressure problem)arrow_forward
- In this case, p-value is greater. So null hypothesis should not be rejected, correct?arrow_forwardWhen asked what it means for the result of a hypothesis test to be practically significant (or practically important), Tatum says this means that the P-value is small and the null hypothesis has been rejected. what is wrong about this? i can't read this handwritingarrow_forwardWhich of these is true regarding hypothesis tests? If the P-value is less than the specified alpha level, the null is accepted If the P-value is less than the specified alpha level, the null is rejected in favor of the alternative If the P-value is greater than the specified alpha level, the alternative is accepted none of these statements is true If the P-value is greater than the specified alpha level, the null is rejected in favor of the alternativearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman