
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:ter
11 of 12
I Review | Constants | Periodic Table
Part A
of
eo
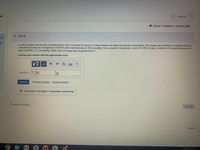
In order to determine the rate of photosynthesis (the conversion by plants of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen), the oxygen gas emitted by an aquatic plant is
collected over water at a temperature of 293 K and a total pressure of 756.4 mmHg. Over a specific time-period, a total of 1.40 L of gas is collected. The partial pressure of
water at 293 K is 17.55 mmHg. What mass of oxygen gas (in grams) forms?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
m(02) = 7.29
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
Provide Feedback
Next >
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- atm 1.50 1.00 0.50 0 5 10 Is NO₂ being created or destroyed by t reaction? 15 seconds Be Careful If NO2 is being created or destroyed, w which it is being created or destroyed 11 seconds after the reaction starts? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. If NO₂ is being created or destroyed, what is the average rate at which it is being created or destroyed during the first 11 seconds of the reaction? 20 Please make sure to use the correct unit symbol. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. 25 created 30 ОК 1.0 atms 1.3 atms - 1 - 1 x10 010 X Sarrow_forward2C4H6(g) → C8H12(g) At high temperatures, the compound C4H6 (1,3-butadiene) reacts according to the equation above. The rate of the reaction was studied at 625 K in a rigid reaction vessel. Two different trials, each shown with a different starting concentration, were carried out. The data were plotted in three different ways, as shown below. (a) For trial 1, calculate the initial pressure, in atm, in the vessel at 625 K. Assume that initially all the gas present in the vessel is C4H6. (Hint-this is a gas law problem from chemistry last year) (b) Use the data plotted in the graphs to determine the order of the reaction with respect to C4H6. (c) The initial rate of the reaction in trial 1 is 0.0010 mol/(L *s). Calculate the rate constant, k, for the reaction at 625 K.arrow_forwardConsider the following general reaction for which gases A and B are mixed in a constant volume container: A(g) + B(g) -> C(g) + D(g) Match what happens to the rate of the reaction under the following changes: (consider each change separately) v all of gas B is removed from the container more gas A is added to the container the temperature of the container is increased there is no change to the reaction rate ya catalyst is added to the container I. the reaction proceeds at a faster rate v gas D is also added to the container the reaction proceeds at a slower rate II. some of gas B is removed from the container Iy the reaction does not proceed at all the volume of the container is increasedarrow_forward
- In a hot combustion chamber, oxygen diffuses through air to a flat carbon surface where it reacts to produce CO and/or CO2. Reduce the general differential equation for mass transfer to write a specific differential equation for oxygen that will describe the steady-state mass transfer process. The concentration of oxygen at z=δ is 21 mole percent. The reaction at the surface may be assumed to occur instantaneously. No reaction occurs in the gas film. What would be the form of the equation providing the flux of oxygen if (a) only carbon monoxide is produced on the carbon surface; (b) only carbon dioxide is produced on the carbon surface; (c) the following instantaneous reaction occurs on the surface, 4C+3O2→2CO+2CO2.arrow_forward= O Kinetics and Equilibrium Calculating average and instantaneous reaction rate from a graph of... Here is a graph of the pressure of boron trifluoride (BF, in a reaction vessel during a certain chemical reaction. Use this graph to answer the questions in the table below. Explanation Check atm y 30+ 25.724 20- 15 10- 5 0 50 100 150 seconds Is BF3 being created or destroyed by the chemical reaction? If BF is being created or destroyed, what is the rate at which it is being created or destroyed 110 seconds after the reaction starts? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. in beine If BF is being created or destroyed, what is the 200 250 created destroyed 300 x neither created nor destroyed 0 x10 010 X 0/5 Ś Izabella ? olo 18 Ar 8. © 2024 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardConsider the reaction 2AB(g) → A2(g) + B2(g). If [AB] at 96 minutes was 0.71OM and dropped to 0.520M by 320.minutes, calculate the rate of consumption during this time frame.arrow_forward
- In the nuclear industry, workers use a rule of thumb that the radioactivity from any sample will be harmless after 10 half-lives. What fraction of a radioactive sample remains after this time? (Radioactive decay obeys first-order kinetics.)arrow_forwardHere is a graph of the pressure of ozone (03) in a reaction vessel during a certain chemical reaction. Use this graph to answer the questions in the table below. atm 3.00- 2.50- 200- 1.950 1.50- 1.00- 0.50- > 0 500 1000 1500 seconds 2000 2500 3000 3arrow_forwardThe impact of CFCs on the ozone layer is amplified by the fact that the decomposition of a single CFC molecule can result in the destruction of thousands of ozone molecules. CFCs react with oxygen to produce many reactive intermediates. O CFCs replicate in the stratosphere. O CFCs decompose before reaching the stratosphere.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY