
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
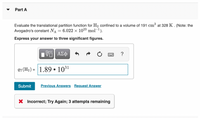
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Evaluate the translational partition function for H2 confined to a volume of 191 cm³ at 328 K . (Note: the
Avogadro's constant NA
6.022 x 1023 mol-1).
Express your answer to three significant figures.
ΑΣφ
?
qT(H2) = 1.89 • 1031
%3D
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining
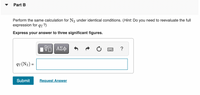
Transcribed Image Text:Part B
Perform the same calculation for N2 under identical conditions. (Hint: Do you need to reevaluate the full
expression for qT ?)
Express your answer to three significant figures.
?
qT (N2) =
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 5. The rotational constant of 127135Cl is 0.1142 cm-1. (a) What is the most highly populated rotational level for the 127135CI molecules at 25 °C? (b) Calculate the bond length in the molecule. (c) Draw the rotational spectrum showing all absorptions in the region from 0 cm 1 to 10 cm 1.arrow_forwardHelp please..arrow_forwardThe lowest triplet state in naphthalene (C10H8) is about 11,000 cm-1 below the lowest excited singlet electronic level at 77 K. Calculate the ratio of populations in these two states at equilibrium. [Hint: The Boltzmann equation is given by N2/N1 = (92/91)exp(-AE/KBT), where g₁ and 92 are the degeneracies for levels 1 and 2.] N₂ N1arrow_forward
- The rotational constant for the molecule 1H35Cl is B = 10.60 cm-1. Using Boltzmann statistics, determine the most likely rotational state J that such a molecule would be expected to have at a temperature of 300 K.arrow_forwardPlease prove the statementarrow_forward25. Calculate the values of the rotational and vibrational partition functions of CO2 at 300 K, given that the rotational constant is B = 0.391 cm' and the vibrational constants are w1 = and w3 = 2284 cm'. [Ans: qvib = 1.09] 1388 cm', w2 = 667 cm',arrow_forward
- (4) For a rotational-vibrational spectrum of H8'Br (B = 8.46 cm-1) taken at 520 K, determine the R-branch transition that is expected to be the most intense.arrow_forwardPlot the molar heat capacity of a collection of harmonic oscillators as a function of T/θV, and predict the vibrational heat capacity of ethyne at (i) 298 K, (ii) 500 K. The normal modes (and their degeneracies in parentheses) occur at wavenumbers 612(2), 729(2), 1974, 3287, and 3374 cm–1.arrow_forward5. For carbon monoxide at 298K, determine the fraction of molecules in the rotational levels for J=0, 5, 10, 15, and 20. The rotational constant (B) is 3.83x10^-23 Joules.arrow_forward
- P31.17 Calculate the rotational partition function for CINO at 500. K where BA 2.84 cm ¹, BB = 0.187 cm¯¹, and Bc 0.175 cm ¹. =arrow_forwardPart A Determine the total molecular partition function for gaseous H2O at 1000. K confined to a volume of 2.20 cm³ . rotational constants for water are BA = 27.8 cm-1, BB = 14.5 cm-1, and Bc = 9.95 cm-1. The vibrational frequencies are 1615, 3694, and 3802 cm-. The ground electronic state is nondegenerate. (Note: the Avogadro's constant NA The 6.022 x 1023 mol-1). Express your answer to three significant figures. Ην ΑΣφ ? 1.29 • 1029 Itotal = Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remainingarrow_forwardConsider the rotational temperatures of the following hetero diatomic molecules: θr(CO) = 2.1 K, θr(HF) = 30.2 K. In which case would the classical approximation be accurate? Justify your answer.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY