
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Part 2 only

Transcribed Image Text:Part 2:
Note: A starter code is provided called A4_starter.py, use this as the template and fill
out the necessary bits in the code to implement the required functionality. The code also
contains comments that complement instructions in this document, so read both.
Imagine that you are writing a Python program that will be used by a few geologica
researchers. Each researcher has a set of unknown crystals and wants to determine
what they are, and how they bend light. Each researcher has done a series of
experiments to determine the refractive indices of a set of unknown materials.
Unfortunately, their experiment does not produce exact values, but they are within
+0.02 of known refractive indices of materials. They wish to know what the materials
are, and what the angle of refraction would be if they stacked these materials together
in various orders. You should create a Python program that takes in a set of comma
separated values corresponding to the refractive indices of each layer in the stack. Your
program must:
1. Determine the material corresponding to the given refractive index
2. Print out line-by-line the material name and the angle of refraction at that layer (2
decimal places).
3. Loop back until the user decides to quit.
The following table lists some materials and their refractive indices:
Material
Diamond
Sapphire
Emerald
Opal
Pearl
This table is given to you as a list-of-lists in the Python code. Each element of the outer
list is a list of two items: the name and the refractive index. You must ONLY USE THE
LIST-OF-LISTS to determine the most likely material corresponding to the user input.
You will need to iterate over the list-of-lists and check for which of the materials has a
refractive index that is within ±0.02 of a given layer.
Assumptions:
●
Refractive Index
2.42
1.78
1.58
1.45
1.52
User will always enter values that are reasonable.
● User may enter any number of values but will enter at least one value.
Hints:
Look at the .split() method covered in class to figure out how to separate the
values.
You can use a nested for loop to get the refractive index of each item, then
decide if it is within +0.02 of known values.
O Look at the abs() function covered in the class, can that be used here?
Don't forget degrees to radians conversion, as necessary!
Sample Input and Output (match exactly):
Note: Contains 3 sets of inputs
Enter the angle of incidence (in degrees):22.5
Enter the refractive indices as comma separated values:1.569,1.539,1.770,1.456,2.437
Layer 1 is made of Emerald. Angle of refraction is 14.12 degrees.
Layer 2 is made of Pearl. Angle of refraction is 14.40 degrees.
Layer 3 is made of Sapphire. Angle of refraction is 12.49 degrees.
Layer 4 is made of Opal. Angle of refraction is 15.24 degrees.
Layer 5 is made of Diamond. Angle of refraction is 9.03 degrees.
Do you want to enter more values? Enter 'y' or 'yes' to continue, or anything else to quit:y
Enter the angle of incidence (in degrees):66.6
Enter the refractive indices as comma separated values:1.469,1.799,2.402,1.561
Layer 1 is made of Opal. Angle of refraction is 38.66 degrees.
Layer 2 is made of Sapphire. Angle of refraction is 30.67 degrees.
Layer 3 is made of Diamond. Angle of refraction is 22.46 degrees.
Layer 4 is made of Emerald. Angle of refraction is 36.01 degrees.
Do you want to enter more values? Enter 'y' or 'yes' to continue, or anything else to quit:YES
Enter the angle of incidence (in degrees):39
Enter the refractive indices as comma separated values:1.786,1.580
Layer 1 is made of Sapphire. Angle of refraction is 20.63 degrees.
Layer 2 is made of Emerald. Angle of refraction is 23.47 degrees.
Do you want to enter more values? Enter 'y' or 'yes' to continue, or anything else to quit:no
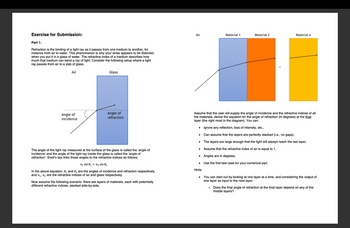
Transcribed Image Text:Exercise for Submission:
Part 1:
Refraction is the binding of a light ray as it passes from one medium to another, for
instance from air to water. This phenomenon is why your straw appears to be distorted
when you put it in a glass of water. The refractive index of a medium describes how
much that medium can bend a ray of light. Consider the following setup where a light
ray passes from air to a slab of glass.
Air
Angle of
incidence
Glass
Angle of
refraction
The angle of the light ray measured at the surface of the glass is called the 'angle of
incidence' and the angle of the light ray inside the glass is called the 'angle of
refraction'. Snell's law links these angles to the refractive indices as follows:
n₁ sin 0₁ = n₂ sin 0₂
In the above equation, 0₁ and 0₂ are the angles of incidence and refraction respectively,
and n₁, n₂ are the refractive indices of air and glass respectively.
Now assume the following scenario: there are layers of materials, each with potentially
different refractive indices, stacked side-by-side.
Air
●
●
Material 1
Assume that the user will supply the angle of incidence and the refractive indices of all
the materials, derive the equation for the angle of refraction (in degrees) at the final
layer (the right most in the diagram). You can:
•
ignore any reflection, loss of intensity, etc.,
Can assume that the layers are perfectly stacked (i.e., no gaps),
● The layers are large enough that the light will always reach the last layer,
Assume that the refractive index of air is equal to 1,
• Angles are in degrees,
Use the first test case for your numerical part.
Hints:
Material 2
Material n
You can start out by looking at one layer at a time, and considering the output of
one layer as input to the next layer.
O Does the final angle of refraction at the final layer depend on any of the
middle layers?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The Sieve of Eratosthenes is used to separate different types of things.arrow_forwardThe Science of Computing Mystery Mania Six men: Bill Fox, Tom Smith, Robert Stevenson, Fred Edison, Larry Davis, and John Harrison were in a library together. Suddenly, the lights went out. When the lights came back on, Bill Fox was found shot. The other detectives have investigated; questioned the suspects, the witnesses, and people who know the suspects; and have collected physical evidence from the crime scene. They have collected 14 clues but have not been able to solve the crime. It's now up to you. Note that no two suspects have the same height, color car, color umbrella, color shirt, or color shoes. The clues: • John Harrison owns a purple car Tom Smith is 5'3" tall • The suspect who was wearing a yellow shirt owns a red car The suspect who is 5'6" tall was wearing a blue shirt • The suspect who owns a red car is 6'3" tall • The suspect who was carrying a yellow umbrella is not the one who owns a green car • The suspect who is 6' tall is not the one who was wearing a black shirt…arrow_forwardCould you briefly list the numerous computer parts?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education