Question
Transcribed Image Text:B
AAN EE
Tamat Parme
Solving problems by relaung sinusordal wave and vector functions to their related
engineering applications. You also must solve the problems of differential and integral
calculus for your related works.
Fart
AaBb AaB AaE AD Cet Accide
1 Amg 1 Coe 1 Cor. 1
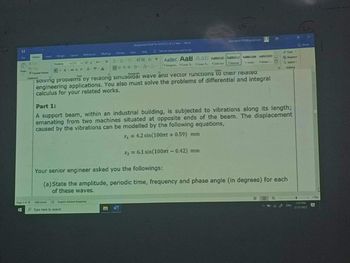
Part 1:
A support beam, within an industrial building, is subjected to vibrations along its length;
emanating from two machines situated at opposite ends of the bear. The displacement
caused by the vibrations can be modelled by the following equations,
x₁ = 4.2 sin(100nt +0.59) mm
x₂ = 6.1 sin(100m - 0.42) mm
O fype here to search
Your senior engineer asked you the followings:
(a) State the amplitude, periodic time, frequency and phase angle (in degrees) for each
of these waves.
Q Engah Sandad Complung
IMG
Transcribed Image Text:Home
IN
Help
AaBb AaB AaB DbCct Acco
1 Aug Cover 1.Cor. 1 Link Gad
1 Numa
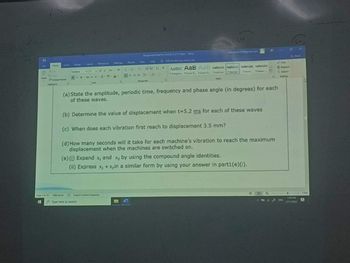
(a) State the amplitude, periodic time, frequency and phase angle (in degrees) for each
of these waves.
(b) Determine the value of displacement when t-5.2 ms for each of these waves
(c) When does each vibration first reach to displacement 3.5 mm?
(d) How many seconds will it take for each machine's vibration to reach the maximum
displacement when the machines are switched on.
Pfype here to search
(e) (i) Expand x, and x₂ by using the compound angle identities.
(ii) Express x₁ + x₂in a similar form by using your answer in parti(e) (i).
IMG
1:04 PM
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The pendulum shown below consists of a uniform disk with radius r = 2.35 cm and a mass of 410 grams. The disk is supported in a vertical plane by a pivot located d = 1.75 cm from the center of the disk. Pivot• d R. a. What is the frequency of oscillation if the disk is displaced by a small angle and released? Hz b. What is the frequency of oscillation if the mass of the disk is and then displaced by a small angle and released? Hzarrow_forwardWhich of the following mass-spring systems will have the highest frequency of vibration? Case A: A spring with a k=300 N/m and a mass of 200 g suspended from it.Case B: A spring with a k=400 N/m and a mass of 200 g suspended from it.arrow_forwardProblem 2: A block attached to a spring with unknown spring constant oscillates with a period of 3.3 s. Parts A to D are independent questions, each referring to the initial situation. a) What is the period if the mass is doubled? b) What is the period if the mass is halved? c) What is the period if the amplitude is doubled? d) What is the period if the spring constant is doubled? Answers: a) 4.7 s; b) 2.3 s; c) 3.3 s; d) 2.3 sarrow_forward
- 8.1arrow_forwardPart A The position of an object that is oscillating on an ideal spring is given by the equation z = (a) At time t =0.815 s, how fast is the object moving? (12.3 cm) cos[(1.26s-1)t]. cm/s Submit Request Answer Part B (b) At time t = 0.815 s, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the object? ΑΣφ cm/s2 Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardQuestion 2 ) = – 5 and y (0) = 5. An object is in simple harmonic motion with frequency 6. Suppose y(0) Find its displacement for t> 0. Also, find the amplitude of the oscillation and the sine and cosine of the initial phase angle o. Displacement: y(t) Amplitude sin(ø) cos(ø) =arrow_forward
- 3arrow_forwardProblem 2: Special sections of roadway are sometimes paved with “rumble strips” to alert inattentive drivers. In a particular case the grooves are spaced L = 0.26 m apart and the depth of each groove is d = 0.35 cm. As you drive over this rumble strip, the tires of your car oscillate about their equilibrium positions with a frequency of f = 68.6Hz. Refer to the figure, which is not drawn to scale. Part (b) Find the vertical position of the tire, in centimeters, at the time t = 1.85 s. Part (c) With your tire oscillating at a frequency of f = 68.6 Hz and the distance between grooves L = 0.26 m, what is the speed of your car, in kilometers per hour?arrow_forwardProblem 3: An object is undergoing simple harmonic motion along the x-axis. Its position is described as a function of time by x(t) = 1.7 cos(3.1t – 1.3), where x is in meters, the time, t, is in seconds, and the argument of the cosine is in radians. Part (a) Find the amplitude of the simple harmonic motion, in meters. Part (b) What is the value of the angular frequency, in radians per second? Part (c) Determine the position of the object, in meters, at the time t = 0. Part (d) What is the object's velocity, in meters per second, at time t = 0? Part (e) Calculate the object's acceleration, in meters per second squared, at time t = 0. Part (f) What is the magnitude of the object's maximum acceleration, in meters per second squared?arrow_forward
- Create a plot of the period vs. mass (exclude the steel bolt). Construct your plot on a computer program such as Microsoft Excel®.arrow_forwardAt an outdoor market, a bunch of bananas is set into oscillatory motion with an amplitude of 20.0 cm on a spring with a force constant of 16.0 N/m. It is observed that the maximum speed of the bunch of bananas is 43.0 cm/s. What is the weight of the bananas in newtons? Narrow_forwardA complete description of simple harmonic motion must take into account several physical quantities and various mathematical relations among them. This information is needed to solve oscillation Part A problems of this type. The position of a 40 g oscillating mass is given by x(t) = (2.0 cm) cos(10t), where t is in seconds. Determine the velocity at t = 0.40 s. Express your answer in meters per second to two significant figures. • View Available Hint(s) ? Vr = m/s Submit Part B 國 tarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios