
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Do all three solution approaches for simultaneous games work independently (not together)? If not, which do not?
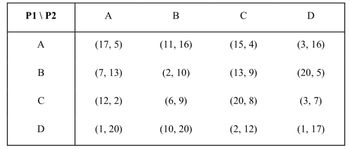
Transcribed Image Text:P1 \ P2
A
B
C
D
A
(17,5)
(7, 13)
(12, 2)
(1, 20)
B
(11, 16)
(2, 10)
(6,9)
(10, 20)
C
(15,4)
(13,9)
(20, 8)
(2, 12)
D
(3, 16)
(20, 5)
(3,7)
(1, 17)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- From a certain place K, 2000 people set off for work in the distant place S in the morning by car. Each of the drivers must decide whether to come to place S via point G or via point D (see the directed graph below). The travel time on segments G-S and K-D is not dependent on the number of drivers: each driver traverses the G-S segment in 60 minutes, and the K-D segment in 45 minutes, regardless of the number of drivers. However, the travel time on segments K-G and D-S depends on the number of drivers: if x drivers travel on the K-G segment, each driver on this segment consumes 0.005x minutes; if x drivers travel on the D-S segment, each driver on this segment consumes 0.01x minutes (see the directed graph below). Assume that all people start simultaneously and do not know the decisions of other people. Find all pure Nash equilibria of the game.arrow_forwardConsider the following three-player game represented in extensive form: Player 3 L Player 2 Player 1 R Player 2 U D Player 3 (0,2,0) U D U D (0, 1, 1) (0, 3, k) (0, 4, 3) (0,4,2) U D How many pure-strategy subgame-perfect Nash equilibria are there in this game if k > 1? 5 3 7 1 It depends on the value of k. (2,2, 0)arrow_forwardThis is a two-player, simultaneous one-move game represented as a game table (normal form). What is the pure strategy Nash equilibrium outcome if there is one? Is this a socially optimal outcome? If not, which outcome is preferred?arrow_forward
- Consider that there is one auctioneer who would like to sell one commodity and there are 2 individuals, 1 and 2. The auctioneer will apply the following tie-breaking rule: If there are multiple bidders who announce the highest bid, then select the bidder with the smallest index will be picked up as the winner. (For instance, let b(i) = b(j) . Then, i is the winner if and only if i < j.) Let each individual i's private value of the commodity, v(i), is given as: v(1) = $1600; v(2) = $2100. Considering a first-price auction, specify the set of Nash equilibria in this game.arrow_forwardA total of 10 players are each choosing a number from {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}. If a player's number equals exactly half of the average of the numbers submitted by the other nine players, then she is paid $100; otherwise, she is paid 0. Solve for the strategies that survive the IDSDS.arrow_forwardIn the normal form game below, the payoff matrix depends on the parameter a. 1 1 2 ABC a 0,2 6,4 -2,4 b 0, -24 -2a, 2a 8, 2 C 4,0 0,4 0, 14 Find the values of a, for which at least one pure strategy Nash equilibrium exists. Compute the value of a for which the expected payoff is the same for both players when the mixed strategy profile (01,02) = ((1/3,2/3,0), (0,1/4,3/4)) is played. Find the best response of player 1 (as a function of the parameter a) to player's 2 mixed strategy o2 = (1/2,1/2,0). Assuming a = 0 eliminate iteratively all dominated strategies and find a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium in this game.arrow_forward
- The Government of Malaca has decided to sell pollution permits that will allow people to discharge pollutants into its largest freshwater lake. Each permit represents the right to discharge one tonne of pollutants. Malaca has determined that the lake will tolerate a maximum of 10 tonnes of pollutants per year and has decided to sell the permits using a Dutch auction. This means that the auction starts at a very high price, which is reduced in steps until the price reaches a level that will result in all 10 tonnes of pollution permits being sold at the same price. The results of the bidding are shown in table below. Price per Pollution Bidder Bidder Bidder Bidder Bidder Permit A. B D $5, 500 1 5,000 4,500 4,000 1. 1. 1 2 2. 3 2 1 2 3,500 3,000 2,500 2,000 4 3 2 4 4 4 3 4 4 1,500 7 a. What will be the price of pollution permits as a result of this auction? Price: $ b. Suppose that Bidder E happened to be an environmental protection group. If this group had not participated in the…arrow_forwardExtend the Cournot model discussed in class to two firms with setup costs. Firm 2 chooses to produce q; at cost cq; where c> 0. The set up costs are denoted by K₁ < K2 respectively for firm 1 and 2. The selling price is P(Q) = (a - bQ) where Q = 91 + 92. What are the optimal production quantities for each firm? (Hint: A firm has the option of not producing at all with a cost of zero).arrow_forwardProblem 4: Consider an infinitely repeated game, where the base game is the following 2-person 2x2 game: A A 0,0 10, 10 S1: choose A always S2: choose B always B 10, 10 0,0 Assume both players discount the future at the same rate of r, 0 < r < 1. Limiting each player's strategies to the following six possibilities, S3: Choose A then mimic the other player's previous choice S4: Choose B, then mimic the other player's previous choice S5: Choose A, then choose the opposite of the other player's previous choice S6: Choose B, then choose the opposite of the other player's previous choice a. present the strategic form of this game, b. identify all pure-strategy Nash equilibria c. does repetition with these strategies "solve" the coordination dilemma that confronts the players in the single play of the above game.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education