
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Provide correct answer general accounting
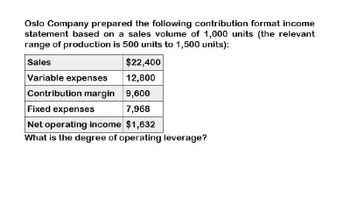
Transcribed Image Text:Oslo Company prepared the following contribution format income
statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant
range of production is 500 units to 1,500 units):
Sales
Variable expenses
$22,400
12,800
Contribution margin 9,600
Fixed expenses
7,968
Net operating income $1,632
What is the degree of operating leverage?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is the degree of operating leverage on these financial accounting question?arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Oslo Company prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant range of production is 500 units to 1,500 units): Sales $ 10,000 5,500 Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses 4,500 2,250 Net operating income $4 2,250 4. If sales increase to 1,001 units, what would be the increase in net operating income? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Increase in net operating incomearrow_forwardNeed answer the general accounting questionarrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Oslo Company prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant range of production is 500 units to 1,500 units): $ 45,000 31,500 13,500 Sales Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses 8,640 Net operating income $ 4,860 13. Using the degree of operating leverage, what is the estimated percent increase in net operating income of a 5% increase in unit sales? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 decimal places.) Increase in net operating income |%arrow_forwardOslo Company prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 Units (the relevant range of production is 500 units to 1,500 units): Sales Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses $ 15,000 9,000 6,000 3,120 Net operating income $2,880 4. If sales increase to 1,001 units, what would be the increase in net operating income? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Increase in net operating incomearrow_forwardWhat is the degree of operating leverage for general accounting?arrow_forward
- Required Information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below] Oslo Company prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant range of production is 500 units to 1,500 units): Sales Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses Net operating income $ 65,000 45,500 19,500 14,048 $5,460 13. Using the degree of operating leverage, what is the estimated percent increase in net operating income that would result from a 5% increase in unit sales? (Round your Intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 decimal places) increase in n openssting incomearrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Oslo Company prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant range of production is 500 units to 1,500 units): Sales Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses Net operating income $ 80,000 52,000 28,000 21,840 $ 6,160 Required: 4. If sales increase to 1,001 units, what would be the increase in net operating income? Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Increase in net operating incomearrow_forwardOslo Company prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant range of production is 500 units to 1,500 units): Sales Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses $ 15,000 9,000 6,000 3,120 $ 2,880 Net operating income 2. What is the contribution margin ratio? Contribution margin ratioarrow_forward
- Oslo Company prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant range of production is 500 units to 1,500 units): Sales$ 55,000Variable expenses33,000Contribution margin22,000Fixed expenses14,960Net operating income$ 7,04015. Assume that the amounts of the company’s total variable expenses and total fixed expenses were reversed. In other words, assume that the total variable expenses are $14,960 and the total fixed expenses are $33,000. Using the degree of operating leverage, what is the estimated percent increase in net operating income of a 5% increase in unit sales? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardOslo Company prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant range of production is 500 units to 1,500 units): Sales Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses $ 15,000 9,000 6,000 3,120 Net operating income $ 2,880 12. What is the degree of operating leverage? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Degree of operating leveragearrow_forwardOpereting leverage? General accountingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education