
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
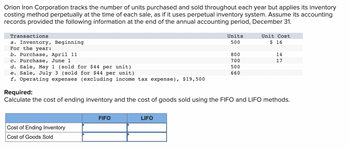
Transcribed Image Text:Orion Iron Corporation tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each year but applies its inventory
costing method perpetually at the time of each sale, as if it uses perpetual inventory system. Assume its accounting
records provided the following information at the end of the annual accounting period, December 31.
Transactions
Units
Unit Cost
a. Inventory, Beginning
500
$ 16
For the year:
b. Purchase, April 11
800
14
c. Purchase, June 1
17
700
500
d. Sale, May 1 (sold for $44 per unit)
e. Sale, July 3 (sold for $44 per unit)
660
f. Operating expenses (excluding income tax expense), $19,500
Required:
Calculate the cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the FIFO and LIFO methods.
FIFO
LIFO
Cost of Ending Inventory
Cost of Goods Sold
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Oahu Kiki tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each month, as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume Oahu Kiki's records show the following for the month of January. Sales totaled 280 units. Beginning Inventory Purchase Purchase Required: Date January 1 January 15 Units Unit Cost 120 $ 85 Total Cost $ 10,200 380 95 January 24 200 115 36,100 23,000 1. Calculate the number and cost of goods available for sale. 2. Calculate the number of units in ending inventory. 3. Calculate the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, and (c) weighted average cost methods. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Calculate the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, and (c) weighted average cost methods. Cost of Ending Cost of Goods Inventory Sold FIFO LIFO Weighted…arrow_forwardGladstone Company tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each period as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume its accounting records provided the following information at the end of the annual accounting period, December 31. Transactions Units Unit Cost Beginning inventory, January 1 3,200 $ 45 Transactions during the year: a. Purchase, January 30 4,550 55 b. Sale, March 14 ($100 each) (2,850 ) c. Purchase, May 1 3,250 75 d. Sale, August 31 ($100 each) (3,300 ) Assuming that for the Specific identification method (item 1d) the March 14 sale was selected two-fifths from the beginning inventory and three-fifths from the purchase of January 30. Assume that the sale of August 31 was selected from the remainder of the beginning inventory, with the balance from the purchase of May 1.arrow_forwardAt the end of January of the current year, the records of Donner Company showed the following for a particular item that sold at $15.20 per unit: Transactions Units Inventory, January 1 Purchase, January 12. 560 Amount $1,792 540 Purchase, January 26 140 2,808 1,008 Sale Sale (420) (200) Required: 1a. Assuming the use of a periodic inventory system, compute Cost of Goods Sold under each method of inventory: average cost, FIFO, LIFO, and specific identification. For specific identification, assume that the first sale was selected from the beginning inventory and the second sale was selected from the January 12 purchase. 1b. Assuming the use of a periodic inventory system, prepare a partial income statement under each method of inventory: (a) average cost, (b) FIFO, (c) LIFO, and (d) specific identification. For specific identification, assume that the first sale was selected from the beginning inventory and the second sale was selected from the January 12 purchase. 2a. Between FIFO and…arrow_forward
- i need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardAircard Corporation tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each period as if it uses a periodic inventory system. The following are the transactions for the month of July. Units Unit Cost July 1 Beginning Inventory 2,000 $ 35 July 5 Sold 1,000 July 13 Purchased 6,000 39 July 17 Sold 3,000 July 25 Purchased 8,000 41 July 27 Sold 5,000 Calculate the cost of goods available for sale, ending inventory, and cost of goods sold if Aircard uses (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, or (c) weighted average cost. (Round "Cost per Unit" to 2 decimal places.)\arrow_forwardanswer in text form please (without image)arrow_forward
- please all answerarrow_forwardPenultimate Company uses a perpetual inventory system and has a December 31 year-end. Its records show the following data for the current year: Inventory beginning of year per General Ledger - 36,450 Inventory end of year unadjusted per General Ledger - $35,000 Purchases during the year - $60,000 Physical inventory count end of year - 43,900 Accounts Payable invoices dated December for inventory purchases ordered but in transit at year end - $6,000 Trade terms with suppliers – Net 30 days, FOB destination Required 1: Assuming no other transaction happened, what value will show on Penultimate's year end balance sheet for inventory? $ Required 2: Assuming no other transaction happened, what value will show on Ultimate's Income Statement as the Cost of Goods Sold? $ Required 3: Assuming no other transaction happened, what was the amount of Merchandise Available For Sale? $arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
- The following purchase transactions occurred during the last few days of Whilczel Company's business year, which ends October 31, or in the first few days after that date. A periodic inventory system is used. · An invoice for P6,000, terms FOB shipping point, was received and entered November 1. The invoice shows that the material was shipped October 29, but the receiving report indicates receipt of goods on November 3. · An invoice for P2,700, terms FOB destination, was received and entered November 2. The receiving report indicates that the goods were received October 29. · An invoice for P3,150, terms, FOB shipping point, was received October 15, but never entered. Attached to it is a receiving report indicating that the goods were received October 18. Across the face of the receiving report is the following notation: "Merchandise not of the same quality as ordered - returned for credit October 19". · An invoice for P3,600 terms FOB shipping…arrow_forwardNeverstop Corporation sells item A as part of its product line. Information about the beginning inventory, purchases, and sales of item A are given in the following table for the first six months of the current year. The company uses a perpetual inventory system: Date January 1 (beginning inventory) January 24 February 8 March 16 June 11 Ending inventory Purchases Sales Number of Units Unit Cost Number of Units 570 $3.90 $4.00 $4.00 670 Gross profit 670 370 370 Sales Price Required: 1. Compute the cost of ending inventory by using the weighted-average costing method. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) $5.40 $5.40 2. Compute the gross profit for the first six months of the current year by using the FIFO costing method. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round the final answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardHaresharrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education