
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
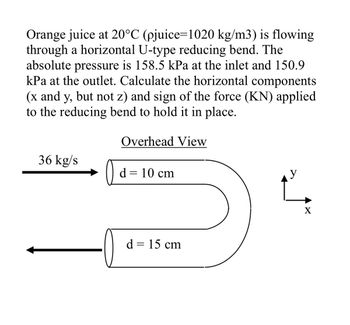
Transcribed Image Text:Orange juice at 20°C (pjuice=1020 kg/m3) is flowing
through a horizontal U-type reducing bend. The
absolute pressure is 158.5 kPa at the inlet and 150.9
kPa at the outlet. Calculate the horizontal components
(x and y, but not z) and sign of the force (KN) applied
to the reducing bend to hold it in place.
36 kg/s
Overhead View
d = 10 cm
-0
d = 15 cm
y
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A generator on a research aircraft requires 0.2 slugs per second of cooling air. A cooling air scoop for the generator is designed to be operated while the aircraft is cruising at 200 mph at 20,000 ft above sea level in standard atmospheric conditions. The scoop connects to an opening on the generator casing that has an area of 2 ft2 . Determine the required area of the inlet of the scoop. Also determine the air velocities and pressures at the scoop inlet and at the connection with the generator casing.arrow_forwardAir flows at 700 m/s through a long duct in a wind tunnel, where the temperature is 15°C and the absolute pressure is 90 kPa. The leading edge of a wing in the tunnel is represented by the 8° wedge. The angle of attack is set at a = 1.5°. (Figure 1) Figure 700 m/s 4° Ja 4° 1 of 1 Part A Determine the pressure created on its top surface. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. p= O D Submit Value μA Provide Feedback Request Answer 20 Units ? Next >arrow_forwardThe air in the reservoir has an absolute pressure of 500 kPakPa and a temperature of 30∘C∘C. The throat has a diameter of 50 mmmm. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 Part A Determine the greatest possible mass flow through the nozzle.arrow_forward
- A pipe bend has a cross sectional area of 0.01 m2 at inlet and 0.0025 m2 at outlet. It bends 900 from its initial direction. The velocity is 4 m/s at inlet with a pressure of 100 kPa gauge. The density is 1000 kg/m3. Calculate the forces acting parallel and perpendicular to the initial direction. V1 v2arrow_forwardThe gauge pressure of water at A is 150.5 kPa. Water flows through the pipe at A with a velocity of 18 m/s, and out the pipe at B and C with the same velocity v. Neglect the weight of water within the pipe and the weight of the pipe. The pipe has a diameter of 50 mm at A, and at B and C the diameter is 35 mm. Pw = 1000 kg/m³. (Figure 1) %D Determine the x component of force exerted on the elbow necessary to hold the pipe assembly in equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) HẢ ? Value Units %3D Submit Previous Answersarrow_forward1. A sphere of radius a is moving with velocity U along the axis of a tube with circular cross-section of radius a(1 + €) with a closed end. See Figure 1. Determine the force exerted by the fluid on the sphere if the Reynolds number and e are small.arrow_forward
- Oil flows through the 100-mm-diameter pipe with a velocity of 8 m/s (Figure 1). The flow occurs in the horizontal plane. Take p = 900 kg/m³. ▼ Part A If the pressure in the pipe at A and B is assumed to be 90 kPa, determine the component of force the flow exerts on the elbow. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ▾ View Available Hint(s) ▾ Hint 1. How to determine the component of force the flow exerts on the elbow Build a free body diagram of the control volume containing oil within the pipe and elbow between cross-sections at A and B. Then using the linear momentum equation determine the component of the force the flow exerts on the elbow. F₂ = Part B HÅ Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Value Fy = X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Submit Units If the pressure in the pipe at A and B is assumed to be 90 kPa, determine they component of force the flow exerts on the elbow. Express your answer to three significant figures and…arrow_forwardkg Water (p = 1000- -) flows through the elbow below. The diameter of both the inlet and outlet is 1.1 cm, and the velocity through the nozzle is V =4.5 m/s. The outlet m³ has an angle of 0 =15 degrees. The water is at a pressure of 29 kPa (gauge). Find the magnitude of the force on the elbow. 0 Varrow_forwardWater is flowing in a 90ο pipe with uniform cross section area of A=0.0083 m2. The velocity along the horizontal direction is v1=6.0 m/s. The pressure at the section 1 is p1=500kPa. Elevation difference and energy losses can be neglected. The density of water is ρ=1000kg/m3. An external force is needed to hold the pipe in equilibrium. (1) Select the correct expression of the external force component in the horizontal direction Rx_________ A. B. C. D.arrow_forward
- Problem 3 - The jet plane travels at M = 2.5 in still air at an altitude of 25 000 ft. If a shock forms at the air inlet of the engine, determine the stagnation pressure within the engine just before the shock and the stagnation pressure a short distance within %3D the chamber.arrow_forwardNeed help with this engineering problem. The answer needs to be in meters.arrow_forwardIn the figure below, the tank containing the water is very large and open to the air, and the pipe through which the water drains is very small. The pipe is not open to the air and the water can be treated as an ideal fluid. Find the speed at which the water is traveling in the pipe.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY