
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
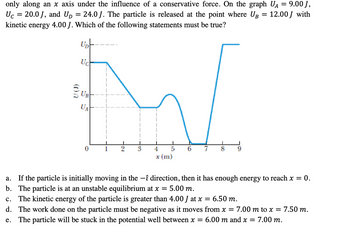
Transcribed Image Text:only along an x axis under the influence of a conservative force. On the graph UA 9.00 J,
Uc 20.0 J, and Up = 24.0 J. The particle is released at the point where UB = 12.00 J with
kinetic energy 4.00 J. Which of the following statements must be true?
=
tot
Uch
ŜUR
UA
0
6 7
a.
If the particle is initially moving in the −î direction, then it has enough energy to reach x = 0.
The particle is at an unstable equilibrium at x = 5.00 m.
b.
c. The kinetic energy of the particle is greater than 4.00 J at x = 6.50 m.
7.50 m.
d. The work done on the particle must be negative as it moves from x = 7.00 m to x =
e.
The particle will be stuck in the potential well between x = 6.00 m and x = 7.00 m.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure here shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of a 0.876 kg particle that can travel only along an x axis. (Nonconservative forces are not involved.) Three values are UA = 15.0 J, Ug = 35.0 J and Uc = 45.0 J. The particle is released at x = 4.50 m with an initial speed of 7.96 m/s, headed in the negative x direction. (a) If the particle can reach x = 1.00 m, what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the (b) magnitude and (c) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the left of x = 4.00 m? Suppose, instead, the particle is headed in the positive x direction when it is released at x = 4.50 m at speed 7.96 m/s. (d) If the particle can reach x = 7.00 m, what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the (e) magnitude and (f) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the right of x = 5.00 m? UcT UB 4 x (m) (a) Number i Unit (b) Number i Unit (c) (d) Number i…arrow_forwardIn the figure, a 2.8 kg block is accelerated from rest by a compressed spring of spring constant 620 N/m. The block leaves the spring at the spring's relaxed length and then travels over a horizontal floor with a coefficient of kinetic friction -0.241. The frictional force stops the block in distance D-8.2 m. What are (a) the increase in the thermal energy of the block-floor system, (b) the maximum kinetic energy of the block, and (c) the original compression distance of the spring? No frictionarrow_forwardThe figure here shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of a 0.898 kg particle that can travel only along an x axis. (Nonconservative forces are not involved.) Three values are UA = 15.0 J, UB = 35.0 J and Uc = 45.0 J. The particle is released at x = 4.50 m with an initial speed of 7.52 m/s, headed in the negative x direction. (a) If the particle can reach x = 1.00 m, what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the (b) magnitude and (c) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the left of x = 4.00 m? Suppose, instead, the particle is headed in the positive x direction when it is released at x = 4.50 m at speed 7.52 m/s. (d) If the particle can reach x = 7.00 m, what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the (e) magnitude and (f) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the right of x = 5.00 m? Uc UB UA 2 4 x (m) (a) Number i Unit (b) Number i Unit (c) (d)…arrow_forward
- Please asaparrow_forward. A pogo stick has a spring with a spring constant of 2.5×104N/m,, which can be compressed 12.0 cm. To what maximum height from the uncompressed spring can a child jump on the stick using only the energy in the spring, if the child and stick have a total mass of 40 kg?arrow_forwardThe figure here shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of a 0.878 kg particle that can travel only along an x axis. (Nonconservative forces are not involved.) Three values are UA-15.0J, Us - 35.0 J and Uc-45.0 J. The particle is released at x -4.50 m with an initial speed of 7.99 m/s, headed in the negative x direction. (a) If the particle can reach x -1.00 m, what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the (b) magnitude and (c) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the left of x- 4.00 m? Suppose, instead, the particle is headed in the positive x direction when it is released at x - 4.50 m at speed 7.99 m/s. (d) If the particle can reach x - 7.00 m, what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the (e) magnitude and (f) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the right of x-5.00 m? (0)2 Ucr UB UA 2 (a) Number (b) Number 10 4 x (m) (c) positive (+x) (e)…arrow_forward
- The figure here shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of a 0.877 kg particle that can travel only along an x axis. (Nonconservative forces are not involved.) Three values are UA = 15.0 J, Ug = 35.0 J and Uc = 45.0 J. The particle is released at x = 4.50 m with an initial speed of 7.39 m/s, headed in the negative x direction. (a) If the particle can reach x = 1.00 m, what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the (b) magnitude and (c) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the left of x = 4.00 m? Suppose, instead, the particle is headed in the positive x direction when it is released at x = 4.50 m at speed 7.39 m/s. (d) If the particle can reach x = 7.00 m, what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the (e) magnitude and (f) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the right of x = 5.00 m? Uc UB UA 4. x (m) (a) Number | Unit (b) Number Unit (c) (d) Number…arrow_forwardA child of mass m = 25 kg starts from rest and slides without friction from a height h along a slide next to a pool. She is launched from a height h/5 into the air over the pool. (a) Using conservation of energy, find the speed of the child at the end of the slide (b) Using your result of part (a) and equations related to a projectile, find ymax as shown in the picture, in terms of h and θ.arrow_forwardA particle is moving along the x axis under the influence of a conservative force given by F = [−(4.00 N/m)x + (9.00 N/m2)x2]î. If U(x) = 0 when x = 0, determine the following as the particle travels from xi = 2.70 m to xf = 6.10 m. (a) The potential energy function U(x). (Use the following as necessary: x. Do not enter units in your expression.)U(x) = (b) Change in potential energy of the particle. J(c) Change in kinetic energy of the particle. J(d) Work done on the particle by the force F. Jarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON