
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
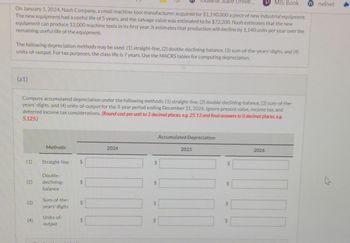
Transcribed Image Text:On January 1, 2024, Nash Company, a small machine-tool manufacturer, acquired for $1,190,000 a piece of new industrial equipment.
The new equipment had a useful life of 5 years, and the salvage value was estimated to be $72,200. Nash estimates that the new
equipment can produce 12,000 machine tools in its first year. It estimates that production will decline by 1,140 units per year over the
remaining useful life of the equipment.
(a1)
The following depreciation methods may be used: (1) straight-line, (2) double-declining-balance, (3) sum-of-the-years-digits, and (4)
units-of-output. For tax purposes, the class life is 7 years. Use the MACRS tables for computing depreciation.
(2)
Compute accumulated depreciation under the following methods: (1) straight-line, (2) double-declining-balance, (3) sum-of-the-
years'-digits, and (4) units-of-output for the 3-year period ending December 31, 2026. Ignore present value, income tax, and
deferred income tax considerations. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places, e.g. 25.12 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g.
5,125.)
(3)
(4)
Methods
Straight-line
Double-
declining-
balance
Sum-of-the-
years'-digits
Units-of-
output
$
$
$
$
2024
$
$
SA
na State Unive...
$
Accumulated Depreciation
2025
$
$
MIS Book
$
$
2026
nelnet
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Introduction to depreciation
VIEW Step 2: Calculation of depreciation under straight-line method
VIEW Step 3: Calculation of depreciation under double-declining balance method
VIEW Step 4: Calculation of depreciation under sum of years digits method
VIEW Step 5: Calculation of deprciation under units of output method
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calligraphy Pens is deciding when to replace its old machine. The machine's current salvage value is $2,400,000. Its current book value is $1.475,000. If not sold, the old machine will require maintenance costs of $645,000 at the end of the year for the next five years. Depreciation on the old machine is $295,000 per year. At the end of five years, it will have a salvage value of $90,000 and a book value of $0. A replacement machine costs $4,000,000 now and requires maintenance costs of $315,000 at the end of each year during its economic life of five years. At the end of the five years, the new machine will have a salvage value of $680,000. It will be fully depreciated by the straight-line method. In five years, a replacement machine will cost $3,000,000. The company will need to purchase this machine regardless of what choice it makes today. The corporate tax rate is 22 percent and the appropriate discount rate is 7 percent. The company is assumed to earn sufficient revenues to…arrow_forwardTech Manufacturing Corporation reports the following situations in 2020 with respect to its high-tech manufacturing equipment. Machine 1 was acquired at a cost of $872,000 in 2017. The machine was depreciated on a straight-line basis over its expected six-year life. At the end of 2020, management decided that this machine should have been depreciated over a total useful life of eight years. Salvage value, expected to be negligible, has not changed. Machine 2 was acquired at a cost of $448,500 in 2019. It was being depreciated on a declining-balance method using a rate of 40%. Salvage values were expected to be minimal. In 2020, management decided that, based on the usage patterns seen to date, unit-of-production would be a more appropriate method of depreciation. The machine is used sporadically and suffers from wear and tear only as used (i.e., obsolescence is not much of a factor in the loss of utility). Estimated units-of-production total 350,000 of which 75,000 units…arrow_forwardA local delivery company has purchased adelivery truck for $15,000. The truck will be depreciated under MACRS as five-year property. Thetruck’s market value (salvage value) is expectedto decrease by $2,500 per year. It is expected thatthe purchase of the truck will increase its revenueby $10,000 annually. The O&M costs are expectedto be $3,000 per year. The firm is in the 40% taxbracket, and its MARR is 15%. If the company plansto keep the truck for only two years, what would bethe equivalent present worth?arrow_forward
- Special Instrument company is considering replacing its machine with a new model that sells for $40,000, the cost of installation is $6,000. The old machine has been fully depreciated and has a $2500 salvage value. The new machine will be depreciated as a 3-year MACRS asset. Revenues are expected to increase $18,000 per year over the 5-year life of the new machine. At the end of 5 years the new machine is expected to have a $1500 salvage value. What is the NPV for this project if Special Instrument has a required rate of return of 12% and a marginal tax rate of 35%? Operating costs are not expected to increase from the current level of $8,000 per year. Briefly Discuss if you accept or reject the new machine and why.arrow_forwardUrmilabenarrow_forwardA small factory is considering replacing its existing coining press with a newer, more efficient one. The existing press was purchased five years ago at a cost of $200,000, and it is being depreciated according to a 7-year MACRs depreciation schedule and the first five years of depreciation have been taken (see below for MACRs chart). The CFO estimates that the existing press has 6 years of useful life remaining. The purchase price for the new press is $306,000. The installation of the new press would cost an additional $24,000, and this cost would be capitalized and added to the depreciable base rather than expensed immediately. The new press (if purchased) would be depreciated using the 7-year MACRs depreciation schedule. Interest expense associated with the purchase of the new press is estimated to be roughly $7,900 per year for the next 6 years. The appeal of the new press is that it is estimated to produce a pre-tax operating cost savings of $75,000 per year for the next 6 years,…arrow_forward
- A company has decided to replace its inspection machine with an advanced one. The advanced machine costs $15,000 and will have operating costs of $3,600 in the first year, increasing by $2,000 per year thereafter. The expected salvage value of the new machine is $6,000 at the end of the first year and will decline by 10% of the preceding S.V. each year. Find the missing values in the following table and determine the economic life of the new machine. Total Cost (8%) CR (8%) OC (8%) 3,600 1 10,200 13,800 2 ? ? ... .... .. 3 4332.36 5,495.82 ? 4 ? 6,406.46 ? .......... . 3086.31 7,293.42 10,379.73 OPTIMAL n = A+ta ch Ciloarrow_forwardreplace its current equipment with new high-tech equipment. The existing equipment was purchased 5 years ago at a cost of $121,000. At that time, the equipment had an expected life of 10 years, with no expected salvage value. The equipment is being depreciated on a straight-line basis. Currently, the market value of the old equipment is $42,900. The new equipment can be bought for $174,340, including installation. Over its 10-year life, it will reduce operating expenses from $190,000 to $145,400 for the first six years, and from $203,600 to $193,600 for the last four years. Net working capital requirements will also increase by $20,200 at the time of replacement. It is estimated that the company can sell the new equipment for $24,400 at the end of its life. Since the new equipment's cash flows are relatively certain, the project's cost of capital is set at 9%, compared with 15% for an average-risk project. The firm's maximum acceptable payback period is 5 years. Click here to view the…arrow_forwardChesterfield Constructions Ltd owns a crane which is used based on contract for many construction projects. The entity purchased the crane in April 2015 at a cost of $2,200,000. The manager estimates that the crane will work on average for 250 days each year for 10 years and then it would be sold at an estimated residual price of $200,000. By 30 June 2020 the crane had worked for 1,200 days.In July 2020 the motor of the crane started to shudder and lose power. An assessment of the crane’s motor resulted in repairs that were required to maintain the motor at its normal efficiency. The cost of $6,000 comprised labour of $4,000 and replacement parts of $2,000. The repairs were completed by the end of July 2020. The management decided that the cost would be regarded as a capital cost. At the same time management estimated that the crane would now be used for a total of 3,000 days with an estimated residual value of $90,000. In the remainder of the financial year to 2021 the crane worked…arrow_forward
- New Style Corporation is a company that manufactures and sells chairs. On 1/1/20, the company purchases a piece of manufacturing equipment for $3,100,000 cash. The expected residual value is $200,000 and the useful life is 5 years. The company expects to produce 5,000,000 chairs with the equipment – 1,200,000 chairs in 2020; 1,400,000 chairs in 2021; 1,000,000 chairs in 2022; and 600,000 chairs 2023; and 800,000 chairs in 2024. Show your work. Round per unit to the nearest cent. Assume that New Style Corporation uses the Units-of-Activity method of depreciation.arrow_forwardThe Darlington Equipment Company purchased a machine 5 years ago at a cost of $85,000. The machine had an expected life of 10 years at the time of purchase, and it is being depreciated by the straight-line method by $8,500 per year. If the machine is not replaced, it can be sold for $5,000 at the end of its useful life. A new machine can be purchased for $170,000, including installation costs. During its 5-year life, it will reduce cash operating expenses by $45,000 per year. Sales are not expected to change. At the end of its useful life, the machine is estimated to be worthless. The new machine is eligible for 100% bonus depreciation at the time of purchase. The old machine can be sold today for $50,000. The firm's tax rate is 25%. The appropriate WACC is 9%. If the new machine is purchased, what is the amount of the initial cash flow at Year 0 after bonus depreciation is considered? Cash outflow should be indicated by a minus sign. Round your answer to the nearest dollar.$…arrow_forwardThe Bigbee Bottling Company is contemplating the replacement of one of its bottling machines with a newer and more efficient one. The old machine has a book value of $550,000 and a remaining useful life of 5 years. The firm does not expect to realize any return from scrapping the old machine in 5 years, but it can sell it now to another firm in the industry for $250,000. The old machine is being depreciated by $110,000 per year, using the straight-line method. The new machine has a purchase price of $1,100,000, an estimated useful life and MACRS class life of 5 years, and an estimated salvage value of $160,000. The applicable depreciation rates are 20%, 32%, 19%, 12%, 11%, and 6%. It is expected to economize on electric power usage, labor, and repair costs, as well as to reduce the number of defective bottles. In total, an annual savings of $245,000 will be realized if the new machine is installed. The company's marginal tax rate is 35%, and it has a 12% WACC. a. What initial cash…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education