
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:On a diagram with quantity on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis, the short run per unit profit for a monopolist is
a. a vertical distance.
b. the area of a rectangle.
c. a horizontal distance.
d. area of a triangle.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
In a monopoly profit is maximized at the point where the marginal revenue curve intersects the marginal cost curve. And that quantity is the quantity produced by the monopoly.
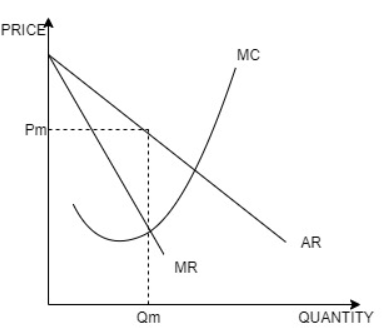
For monopoly, the profit is:
Profit=(Pm×Qm)-TC
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The graph below depicts the demand curve facing a monopolist. The monopoly has constant marginal costs of $5. On the graph: A). Use the straight line tool to draw the marginal revenue curve. B) use the straight line tool to draw the marginal cost curve up to 60 units of output C) use the point tool to plot the profit maximization point on the demand curve.arrow_forwardO Macmillan Learning (Figure: Determining Monopolist Profit) Based on the graph, the profit-maximizing price is at point Price and Cost h Of. O g. d. C MR Output MC ATCarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Figure 15-7 Price $20 15 10 ● 100 150 Figure 15-8 200 Marginal Cost Demand Quantity Refer to Figure 15-7. To maximize its profit, which outcome would a monopolist choose? Marginal Revenue a. 100 units of output and a price of $10 per unit * b. 100 units of output and a price of $20 per unit C. 150 units of output and a price of $15 per unit d. 200 units of output and a price of $10 per unit polist ?arrow_forwardHow do you graph this Consumer surplus and Deadweight Lossarrow_forwardQUESTION 12 The table below shows a monopolist's demand curve and the cost information for the production of its good. What will their profits equal? Quantity Price per UnitTotal Cost 10 $100 20 $80 $60 $40 $20 O 30 40 50 a. $600 O b. $1,200 O c. $1,600 O d. $1,000 $100 $400 $800 $1,400 $2,400arrow_forward
- If a monopolist with significant barriers to entry is making positive economic profit in the short run, what do we expect to happen as the market transitions to the long run? O The profit will increase since the monopolist has no competition, they can just raise the price to earn higher profits. O It will decrease as positive economic profit signals new firms to enter the market, increasing the market supply, and lowering the prevailing price. O It will increase, in the long run firms will drop out the market increasing the monopolists dominance in the marketplace. O The profit will stay the same, strong barriers to entry prevent new competition.arrow_forwardQUESTION 23 If the monopolist shown in the following figure could practice first-degree price discrimination, the producer surplus would be: Price (dollars) 50 40 30 20 10 $0. $225. $450. $900. O $1,200. 30 50 60 MR 100 MC Quantityarrow_forwardQuestion 30 Demand: P=120-Q Marginal Revenue: MR=120-2Q Total Cost: TC=Q² Marginal Cost: MC=2Q For this monopolist, the profit-maximizing price is and the profit-maximizing quantity is 90, 30 30, 90 40, 80 None of these answers O O Oarrow_forward
- 3. Suppose that a monopoly has the following demand curve and total costs: 오 P TR TC ATC MC MR Total Profit 50 40 1 45 50 2 40 72 - 3 35 95 - 4 30 125 - 25 165 6 20 225 a. Fill in the blanks in the preceding table. b. What output will maximize the monopolist's profit? c. What price will the monopolist choose?arrow_forwardIf a monopolist faces an inverse demand curve, p(y) = 100-2y and has constant marginal costs of $32 and zero fixed costs and if this monopolist is able to practice perfect price discrimination, its total profits will be O a. $1,156. O b. $17. O c. $578. O d. $1,734. O e. $289.arrow_forwardanswer quicklyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education