
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
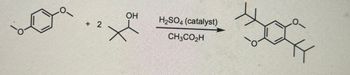
Transcribed Image Text:OH
H2SO4 (catalyst)
+ 2
CH3CO₂H
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Q) Drinking water may contain several unwanted ions such as phosphate ions. In order to remove the phosphate ions from the drinking water, a solution of calcium hydroxide can be added. As a result, a solid Ca5OH(PO4)3 is formed and isolated by filtration and a hydroxide ion are also formed. The reaction for this process is below: 5 Ca(OH)2 (aq) + PO43- (aq) → Ca5OH(PO4)3 (s) + OH- (aq) a) If 3.00 mL of 0.100 M calcium hydroxide is mixed with 4.00 mL of an aqueous solution of 0.0800 M phosphate ions (PO43-). What is the mass of Ca5OH(PO4)3 that can be isolated from the reaction? b) How many moles of the excess reactant remains unreacted? c) What is the concentration of the hydroxide ions in this solution? d) What is the mass of calcium (in grams) that can be recovered?arrow_forwardAspirin can be synthesized in the lab by combining salicylic acid (C,H,0,) and acetic anhydride (C,H,O,) to form aspirin ( C, H,O,) and acetic acid (C,H,O,). The balanced equation for this reaction is C,H,O, + C,H,O, → C,H¿O4 + C,H,O, A student started with 4.02 mL acetic anhydride (density of aspirin. = 1.08 g/mL) and 2.41 g salicylic acid. The student synthesized 2.41 g Select the limiting reactant. acetic anhydride (C,H,O,) salicylic acid (C,H,0,) O acetic acid (C,H,O,) aspirin (C,H¿O,) Calculate the theoretical yield of aspirin (C,H,O4). theoretical yield: g Calculate the percent yield for aspirin (C,H,O4). percent yield:arrow_forwardO • + 88 www-awu.aleks.com ALEKS - Anniston Stovall b My Questions | bartleby O CHEMICAL REACTIONS Anniston Solving for a reactant using a chemical equation 3/5 Wine goes bad soon after opening because the ethanol (CH,CH,OH) in it reacts with oxygen gas (0,) from the air to form water (H,O) and acetic acid (CH,COOH), the main ingredient of vinegar. What mass of ethanol is consumed by the reaction of 10. g of oxygen gas? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. olo g 18 x10 Ar Explanation Check © 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
- Gold(III)hydroxide is used for electroplating gold onto other metals. It can be made by the following reaction (note the equation is unbalanced) KAuCl4(aq) + NaɔCO3(aq) + 3H,O(1) - Au(OH);(aq) + NaCl(aq) + KCI(aq) + CO2(g) To prepare a fresh supply of Au(OH), a chemist at an electroplating plant has mixed 20.00g of KAUC1, with 25.00g of Na CO3 (both dissolved im excess water) a. How many grams of NaCO: will b'required to react with KAUCI4? (only 3 decimal places) g of NanCO b. what is the maximum number of grams of Au(OH); than can be formed? (only 2 decimal places) Activate Windows g of Au(OH); 11:04 Links 20°C 23-Nov- ch Ipcert | Deletearrow_forward2- 3C₂²- + 9:04 Write a balanced chemical equation based on the following description: solid barium carbonate decomposes into solid barium oxide and carbon dioxide gas when heated BaCO3(s) 1 2 3 4 (s) Cb Ba Question 5 of 20 Ox B Reset LO 5 Cr Be 6 7 G Tap here or pull up for additional resources ↑ Br 8 Ca 674 Submit 9 11 (aq) ( O x H₂Oarrow_forwardOne way in which the useful metal copper is produced is by dissolving the mineral azurite, which contains copper(II) carbonate, in concentrated sulfuric acid. The sulfuric acid reacts with the copper(II) carbonate to produce a blue solution of copper(II) sulfate. Scrap iron is then added to this solution, and pure copper metal precipitates out because of the following chemical reaction: Fe(s) + CUSO 4(aq) Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq) Suppose an industrial quality-control chemist analyzes a sample from a copper processing plant in the following way. He adds powdered iron to a 450. mL copper(II) sulfate sample from the plant until no more copper will precipitate. He then washes, dries, and weighs the precipitate, and finds that it has a mass of 147. mg. Calculate the original concentration of copper(II) sulfate in the sample. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. ?arrow_forward
- Dimethyl ether, a useful organic solvent, is prepared in two steps. In the first step, carbon dioxide and hydrogen react to form methanol and water: CO₂(g) + 3 H₂(g) CH₂OH(1) + H₂O(1) In the second step, methanol reacts to form dimethyl ether and water: 2 CH₂OH(1)→ CH₂OCH3(g) + H₂O(1) Calculate the net change in enthalpy for the formation of one mole of dimethyl ether from carbon dioxide and hydrogen from these reactions. Round your answer to the nearest kJ. เม kJ AH=-131. kJ Ś ΔΗ= 8. kJarrow_forward10 Ethylene (CH,CH,) is the starting point for a wide array of industrial chemical syntheses. For example, worldwide about 8.0 × 10º kg of polyethylene are made from ethylene each year, for use in everything from household plumbing to artificial joints. Natural sources of ethylene are entirely inadequate to meet world demand, so ethane (CH,CH,) from natural gas is "cracked" in refineries at high temperature in a kinetically complex reaction that produces ethylene gas and hydrogen gas. Suppose an engineer studying ethane cracking fills a 60.0 L reaction tank with 22.0 atm of ethane gas and raises the temperature to 500. °C. She believes K =0.050 at this temperature. Calculate the percent by mass of ethylene the engineer expects to find in the equilibrium gas mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Note for advanced students: the engineer may be mistaken about the correct value of K , and the mass percent of ethylene you calculate may not be what she actually observes. %arrow_forwardKOH(aq) + HBrO (aq) reaction CH₂ (CH₂)₂CH₂(g) + 80₂ (8) 5CO,(g) + 6H,O(g) 2 3 Ca (s) + F₂ (g) → K BrO (aq) + H₂O (1) NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → NaNO₂ (aq) + AgCl (s) CaF₂ (s) type of reaction (check all that apply) combination single replacement double replacement decomposition combination single replacement double replacement decomposition combination single replacement double replacement decomposition combination single replacement double replacement decomposition X 000 precipitation combustion acid-base precipitation combustion acid-base precipitation combustion acid-base precipitation combustion acid-base Śarrow_forward
- For each reaction in the table below, write the chemical formulae of any reactants that will be oxidized in the second column of the table. Write the chemical formulae of any reactants that will be reduced in the third column. reactants oxidized reactants reaction reduced Ni(s) + I, 6) Nil, (5) SCr(s) + S;(5) – 8Crs (s) Cr(s) + 2C1, (3) – CrCı, (;)arrow_forwardThe psychoactive drug methamphetamine ("speed"), which is sold as the prescription medication Desoxyn, C10H15N, under- goes a series of reactions in the body; the net result of these reac- tions is the oxidation of solid methamphetamine by oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide gas, liquid water, and an aqueous solution of urea, CH4N₂O. Write the balanced equation for this net reaction.arrow_forwardGive the correct standard line notation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY