
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
| A. |
Ogive
|
|
| B. |
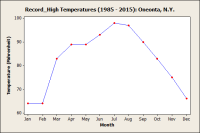
Time Series Chart |
|
| C. |
Frequency
|
|
| D. |
Pareto Chart |
|
| E. |
|
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Construct a frequency distribution of the data 2. Construct a frequency histogram of the data 3. Describe any patterns a. The classes with greatest frequency are 5 and 7. The class with the least frequency is class 1. b. The class the greatest frequency is class 6. The class with the least frequency is class 2. c. The class with the greatest frequency is class 1. The class with the least frequency is class 6. d. The class with the greatest frequency is class 1. The classes with the least frequency are classes 5 and 7.arrow_forwardDuring one shift, the express lane clerk recorded how many times customers violated the "10 items or less" rule for his lane. In particular, he recorded how many items over the limit each violator placed on the conveyor belt. This data is summarized in the histogram below. NOTE: The last class actually represents "7 or more items," not just 7 items. Frequency SHIFT 14- 12 10- 8- 6 CAPS 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 5.5 6.5 7.5 #items over 10 Q What is the frequency of times the limit was exceeded by at least 2 items? 38°F Clear 4 ans 2H TAB 61 Check Answer ESC ! F1 ! Q A Z BEBEEEE F2 X 2 W S F3 # * 3 Q Search X E F4 LA 4 F5 с % R 5 LLI F6 T V 6 HCO F7 1111 4+ 7 Y F8 G H * 00 с F9 J B Narrow_forwardIn a study conducted by some Statistics students, 73 people were randomly assigned to listen to rap music, music by Mozart, or no music while attempting to memorize objects pictured on a page. They were then asked to list all the objects they could remember. The summary statistics for each group are shown in the table. Complete parts a and b. HA: HM-HRU C. Ho: HM-HR <0 HA: HM-HR=0 ... Count Mean SD HA: HM-HRU D. Ho: HM-HR = 0 HA: HM-HR <0 Rap Mozart The 90% confidence interval for the negative difference in means is (.). (Round to three decimal places as needed.) 33 • 20 10.88 10.15. 3.71 3.04 No Music 20 13.29 4.88 Test the hypothesis. t = -0.78 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) P = 0.7799 (Round to four decimal places as needed.) State your conclusion. Use α = 0.05. Do not reject Ho. There is no evidence that the mean number of objects remembered by those who listen to Mozart is higher than the mean number of objects remembered by those who listen to rap music. b) Now compare…arrow_forward
- On the basis of a population survey, there were 84.4 million males and 98.2 million females 25 years old or older in a certain country. The educational attainment of the males and females is shown in the accompanying table. Complete parts (a) through (d) below.arrow_forwardConstruct a frequency distribution and a frequency histogram for the data set using the indicated number of classes. Describe any patterns. Number of classes: 8 Data set: Finishing timės (in seconds) of 20 male participants in a 5K race 1719 1634 1572 1475 2296 1446 1251 1803 1593 1778 1956 1525 1824 1617 1306 1822 2019 2082 1579 1478arrow_forward3. Complete the two-way frequency table below about the type of party your little sister's friends enjoy the most. Gender Male Female Total 2 Party Туре Bowling Skating Dancing 3 11 Total Part A: Determine P(Male). Part B: Determine P(Skating). Part C: Determine P(Male and Skating). Part D: Determine P(Male or Skating).arrow_forward
- Can you fill the table according to data? Thank you!arrow_forwardExhibit 1 gives a frequency distribution table of age of the individuals who are smokers. a) Using Exhibit 1 above, describe how you would find the age group which contains the median smokers. Specify the age group.arrow_forwardAfter recording the final grade (A, B, C, D, E) for each individual in a class of n = 26 students, the professor would like to display the grade distribution in a frequency distribution graph. What kind of graph should be used? Question 15 options: A bar graph A histogram A polygon Either a histogram or a polygonarrow_forward
- The given data represent the number of people from a town, aged 25-64, who subscribe to a certain print magazine. Construct a frequency polygon. Does the graph suggest that the distribution is skewed? If so, how? Age Реople 25-34 53 35-44 238 45-54 743 55-64 687 Construct a frequency polygon using the data. Choose the correct graph below. O A. В. D. Frequency Frequency Frequency Frequency 1000- 1000- 1000- 1000- 0- 25 0 25 65 19.5 69.5 19.5 69.5 65 Age Age Age Agearrow_forward5 TABLE 3.4 ATM Transaction Times (in Seconds) for 63 Withdrawals Time Transaction Time Transaction 12345849 6 7 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 FEB 2 000 F4 2 M M M M M M M 32 32 41 51 42 39 33 43 35 33 33 32 42 34 37 37 33 35 40 36 32 C ત્ર F5 8 25 232427MESSAG 34 32 34 35 3 42 46 2 36 37 32 39 35 41 32 33 34 38 32 35 33 hot 26 28 29 30 31 33 35 36 38 39 40 41 System Preferences D C F6 X 33 52 36 MacBook Air DS ATMTime Transaction F7 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 35,147 DII F8 8 F9 Time 37 32 33 33 40 35 33 39 34 34 33 38 41 34 35 35 37 39 44 40 39 F10arrow_forwarda) Construct a frequency distribution table. Take 20 as the lowest limit of the first class and 10 as the width of each class. b) Develop the relative frequency for the above data. c) Develop a cumulative frequency for the above data.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman