
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
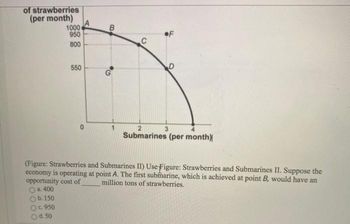
Transcribed Image Text:of strawberries
(per month)
1000
950
800
Oc950
O d. 50
550
A
B
G
C
2
3
Submarines (per month)
(Figure: Strawberries and Submarines II) Use Figure: Strawberries and Submarines II. Suppose the
economy is operating at point A. The first submarine, which is achieved at point B, would have an
opportunity cost of million tons of strawberries.
O a. 400
O b. 150
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 11 Figure 2-16 Gadgets 120- 110+ 100 90+ 80 + 70 + 60 8 50 2222 40+ 30 20 10 + A O 3. 8 D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Widgets Refer to Figure 2-16. Suppose this economy is producing at point B. Which of the following statements would bes explain this situation? a. The economy is getting all it can from the scarce resources available. b. The economy's available technology prevents it from producing more of either product. c. The economy does not have enough resources to produce more of either product. d. There is widespread unemployment in the economy.arrow_forward1. Suppose that the country of Greece has only one factor of production, labour, and can produce at most 1500 units of olives and at most 6000 units of cheese. (a) Draw the PPF of Greece, with cheese on the vertical axis. What is the oppor- tunity cost of producing cheese? What must be the relative price of olives for Greece to specialise in producing olives? To produce both goods? Pcarrow_forwardSuppose that Russia produces 10,000,000 barrels of oil and 1,000 bushels of wheat each week. Suppose that India produces 10657 barrels of oil and 10657 bushels of wheat each week. In autarky, what is the largest amount of wheat Russia can consume every week? amount of wheat per week: What does the term autarky refer to? O a major argument against globalization government policies meant to reduce international trade the process of negotiating terms of trade between two countries a situation where one country does not engage in trade with other countries bushelsarrow_forward
- Adjust the production possibilities frontier (PPF) to show the economy's new production possibilities after the deterioration of infrastructure. Note: Select either end of the curve on the graph to make the endpoints appear. Then drag one or both endpoints to the desired position. Points will snap into position, so if you try to move a point and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it a little farther. QUANTITY OF CARS (Millions) 24 16 0 0 O 5 OO PPF 10 QUANTITY OF COMPUTERS (Millions) 15 Suppose society faces a broad tradeoff between allocating resources to the production of investment goods (computers) and consumption goods (cars) before the deterioration of infrastructure described above. PPF Which of the following events would be most likely to lead to the deterioration of infrastructure you just illustrated? Increasing production of investment goods and decreasing production of consumption goods Decreasing production of investment and consumption goods Increasing…arrow_forward8 Introduction to Economics Please solve it very quickly ????arrow_forwardSuppose that United States produces 10,000,000 barrels of oil and 1,000 bushels of wheat each week. Suppose that China produces 14329 barrels 14329 barrels of oil and 14329 bushels 14329 bushels of wheat each week. In autarky, what is the largest amount of wheat United States can consume every week? amount of wheat per week:___________ bushels What does the term autarky refer to? a. a major argument against globalization b. a situation where one country does not engage in trade with other c. countries d. the process of negotiating terms of trade between two countries e. government policies meant to reduce international tradearrow_forward
- 2. Suppose that Happy Land produces only two goods-food and suntan oil. Its production possibilities are: Food (pounds per month) 300 200 100 0 Active Land also produces only food and suntan oil, and its production possibilities are: Food (pounds per month) 150 100 50 0 Draw the two PPFs Suntan oil (gallons per month) 0 50 100 150 Suntan oil (gallons per month) 0 100 2000 300 a. What are the opportunity costs of food and suntan oil in Happy Land? b. Why are the opportunity costs the same at each output level? c. What are the opportunity costs of food and suntan oil in Active Land? d. If each nation specialized where they have a comparative advantage; and then traded, find the acceptable ranges for trade. 1 pound of food would have to trade between which values of suntan oil? 1 pound of suntan oil would have to trade between which values of food? e. If each nation produces where they have a comparative advantage, and the terms of trade are 50 pounds of food for 75 gallons of suntan oil,…arrow_forward!arrow_forward2. Consider a simple exchange economy with two people: Bob and Jake. Bob and Jake both have ten hours of time available. They can use their time to do one of two things: make pancakes or make hamburgers. Bob can make two hamburgers in an hour or one pancake in an hour. Jake can make three pancakes in an hour or four hamburgers in an hour. a.) Draw Bob and Jake’s PPFs with hamburgers on the x-axis. Give equations for both PPFs in y=mx+b form. b.) Can Bob and Jake both benefit from trade if the terms of trade are three pancakes per hamburger? Why or why not?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education