
Aquaculture Science
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781133558347
Author: Parker
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please identify the curve shown below. What does this curve represent?
Please identify A, B, C, D, and E (the orange oval). What is occurring in these regions?
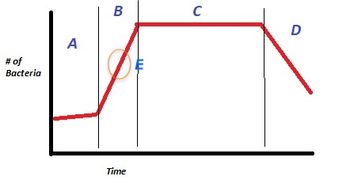
Transcribed Image Text:# of
Bacteria
A
B
C
D
Time
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Explain the statement that both types, bacteria and archaea, have the same basic structures, but built from different chemical components.arrow_forwardWhich of these statements is true? An antibiotic is any substance produced by a organism that is antagonistic to the growth of prokaryotes An antibiotic is any substance produced by a prokaryote that is antagonistic to the growth of other viruses An antibiotic is any substance produced by a prokaryote that is antagonistic to the growth of eukaryotic cells An antibiotic is any substance produced by a prokaryote that prevents growth of the same prokaryote.arrow_forwardFormation of a(n) ___ allows some soil bacteria to survive adverse conditions. a. pilus b. nucleoid c. endospore d. plasmidarrow_forward
- Bioremediation includes. the use of prokaryotes that can fix nitrogen the use of prokaryotes to clean up pollutants the use of prokaryotes as natural fertilizers All of the abovearrow_forwardAt the health center, a fecal sample was taken from a feverish student. Organisms with corkscrewlike flagella and no endomembranes but with cell walls that lack peptidoglycan were isolated as the cause for the illness. These organisms probably belong to the group: a. chlamydias. b. spirochetes. c. Euryarchacota. d. Cyanobacteria. e. Archaea.arrow_forwardMention three differences between bacteria and archaea.arrow_forward
- Describe briefly how you would detect the presence of a non-culturable prokaryote in an environmental sample.arrow_forwardWhich species does not cause human disease? a. Toxoplasma gondii b. Entamoeba histolytica c. Dictyostelium discoideum d. Trichomonas vaginalisarrow_forwardThe term _________________________________ means pertaining to a virus. viral virilearrow_forward
- There have been recurring cases of mad-cow disease in the United Kingdom since the mid-1990s. Mad-cow disease is caused by a prion, an infectious particle that consists only of protein. In 1986, the media began reporting that cows all over England were dying from a mysterious disease. Initially, there was little interest in determining whether humans could be affected. For 10 years, the British government maintained that this unusual disease could not be transmitted to humans. However, in March 1996, the government did an about-face and announced that bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), commonly known as mad-cow disease, can be transmitted to humans, where it is known as variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (VCJD). As in cows, this disease eats away at the nervous system, destroying the brain and essentially turning it into a spongelike structure filled with holes. Victims experience dementia; confusion; loss of speech, sight, and hearing; convulsions; coma; and finally death. Prion diseases are always fatal, and there is no treatment. Precautionary measures taken in Britain to prevent this disease in humans may have begun too late. Many of the victims contracted it over a decade earlier, when the BSE epidemic began, and the incubation period is long (VCJD has an incubation period of 10 to 40 years). A recent study concluded that 1 in 2,000 people in Great Britain carry the abnormally folded protein that causes VCJD. In spite of these numbers, the death rate from VCJD remains low. It is not clear whether this means that the incubation period for the disease is much longer than previously thought, or whether they may never develop the disease. How can a prion replicate itself without genetic material?arrow_forwardSynthetic compounds found in an organism but not normally produced or expected to be present in that organism are called _____________. pesticides bioi emediators recalcitrant compounds xenobioticsarrow_forwardProkaryotes stain as Gram-positive or Gram-negative because of differences in the_______. a. cell wall b. cytoplasm c. nucleus d. chromosomearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning  Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning


Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...
Nursing
ISBN:9781285244662
Author:White
Publisher:Cengage

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax


Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781305634350
Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. Schroeder
Publisher:Cengage Learning