
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The stress–strain diagram for an aluminum alloy specimen having an original diameter of 0.5 in. and a gauge length of 2 in. is given in the figure. Determine approximately the modulus of resilience and the modulus of toughness for the material.
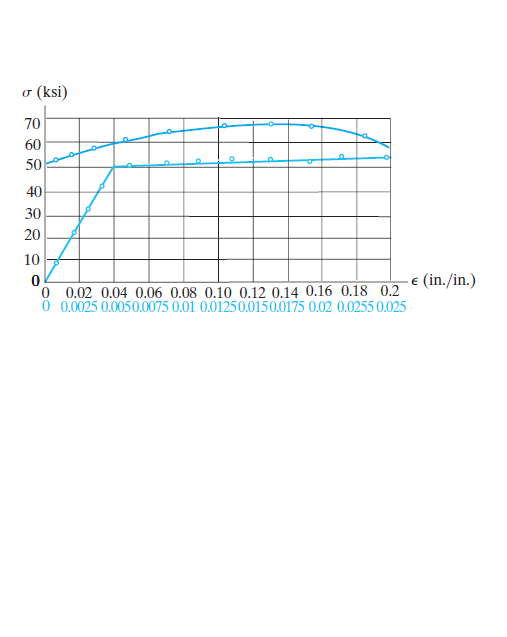
Transcribed Image Text:o (ksi)
70
50
40
30
20
10
e (in./in.)
0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.10 0.12 0.14 0.16 0.18 0.2
0 0.0025 0.0050.0075 0.01 0.01250.0150.0175 0.02 0.0255 0.025
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem F2 stress (ksi) 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0.000 0.025 0.050 0.075 0.100 0.125 0.150 0.175 strain (in/in) Above you will find the experimental stress-strain diagram of 1045 steel. Calculate the permanent set if a cylindrical specimen with a diameter of 2 in is loaded to the ultimate stress and then unloaded. Provide your answer in units of in/in with 3 significant figures after the decimal. The elastic modulus of 1045 steel is 29,000 ksi.arrow_forward3. For a steel alloy, the stress-strain behaviour is shown below. Determine the modulus of elasticity, proportional limit, yield strength at 0.002 and maximum allowable load. 600 500E 400- 500 300 400- 300아 200 200- 100- 100E 0.000 0.002 0.004 0.006 Strain 0.00 0.04 0.08 0.12 0.16 0.20 Strain Stress (MPa) Stress (MPa)arrow_forwardThe shear stress-strain diagram for an alloy is shown in the figure below (Figure 1). Take ✓ = 0.3 Figure 7 (ksi) и Ty 50 0.004 y (rad) < 1 of 2 Part A If a bolt having a diameter of 0.27 in. is made of this material and used in the lap joint, determine the modulus of elasticity E. (Figure 2) Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units. E 3.25x10 ksi Submit ✓ Correct Part B Previous Answers Determine the force P required to cause the material to yield. Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units. P= 5.73 X Incorrect Enter your Provide Feedback μA Submit Previou Answers Request Answer ksi ? Wronarrow_forward
- A square bar subjected to a tensile load of 100kN having a gauge length of 200mm extends to a length of 0.19mm . Given the tensile strength as 200 MPa , determine ( 1 ) Side of the bar ( express in mm ) Final length ( express in mm ) Modulus of elasticity ( express )arrow_forwardAn aluminum alloy [E = 70 GPa; v = 0.33; a = 23.0x10-6/°C] pipe is subjected to a tensile load P. The pipe has an outside diameter of D = 280 mm, a cross-sectional area of A = 7550 mm², and a length of L = 9.5 m. The initial longitudinal normal strain in the pipe is zero. After load P is applied and the temperature of the pipe has been increased by AT = 40°C, the longitudinal normal strain in the pipe is found to be 2260 με. Calculate the magnitude of load P. Answer: P = M. L kN D Parrow_forwardA steel rod with a cross-sectional area of 180 mm2 is stretched between two fixed points. The tensile load at 25°C is 3,600N. Assume thermal coefficient equal to 11.7 x 10-6 mm/ (mm°C) and E = 200 GPa. Which of the following most nearly gives the temperature at which the compressive stress will be 48 MPa? Which of the following most nearly gives the temperature at which the tensile stress will be 48 MPa? Which of the following most nearly gives the temperature at which the stress will be zero?arrow_forward
- 3. The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy is shown in the figure below. The specimen from which it was obtained had an original diameter of 13 mm and a gauge length of 50 mm. If a load of P = 20 kN is applied to the specimen, determine its diameter and gauge length. Take v = 0.4 σ (MPa) 400 0.002 e(mm/mm)arrow_forwardThe stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy specimen having an original diameter of 0.5 in. and a gauge length of 2 in. is given in the figure. If the specimen is loaded until it is stressed to 60 ksi, determine the approximate amount of elastic recovery and the increase in the gage length after it is unloaded.arrow_forwardThe principal plane stresses and associated strains in a 35 ksi, 02 = 15 ksi, plane at a point are 01 1 €1 = 1.02(10-3), 2 = 0.180(10-³). ▼ Determine the modulus of elasticity. Express your answer using three significant figures and include the appropriate units. E= Submit Part B V= μA Value Request Answer Submit Determine the Poisson's ratio. Express your answer using three significant figures. ΠΑΠΙ ΑΣΦ | Η VE Units Request Answer ? vec POSSIA space ?arrow_forward
- The stress–strain diagram for a steel alloy having an original diameter of 0.5 in. and a gage length of 2 in. is given in the figure. If the specimen is loaded until it is stressed to 70 ksi, determine the approximate amount of elasticrecovery and the increase in the gage length after it is unloaded.arrow_forwardA 45° strain gauge rosette placed on a stainless steel structure results in the following values being determined for the maximum and minimum principal strains: €1 = 1,625.9 ×10–6 and €2 = -753.4 x10-6. Assuming plane stess, determine the factor of safety against the Tresca criterion. For stainless steel, use Young's modulus E = 196 GPa, Poisson's ratio v = 0.29 and yield stress oy = 1120 M Pa. Give your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardDetermine the total strain energy and total potential energy in terms of the Prandtl stress function for torsion in a bar of length L and general cross-section A.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY