
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Now, suppose the economy is back in long-run equilibrium, and then the price of imported oil rises.
1. On the following graph, shift a curve or adjust the point to reflect the short-run effect of the increase in the price of oil. (Please use the image attached)
2. True or False: If the Fed undertakes expansionary monetary policy , it can return the economy to its original inflation rate but the unemployment rate will be higher.
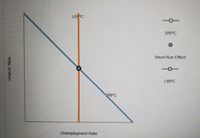
Transcribed Image Text:LRPC
SRPC
Short-Run Effect
LRPC
SRPC
Unemployment Rate
Inflation Rate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In 2013, Prussia's aggregate demand curve was determined by the equation M + 0 = 4%. A change in aggregate demand means that in 2014, Prussia's aggregate demand curve was determined by the equation M + U = 7%. Using this information, draw Prussia's old and new dynamic aggregate demand curves on the graph. Inflation rate 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 4 3 2 1 0 -4 -3 2-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 Real GDP growth rate AD 2013 AD 2014 6 7 8 9 10 Which of the factors could have resulted in the change in aggregate demand seen between 2013 and 2014? higher consumer confidence an improvement in technology O a decrease in oil prices an increase in importsarrow_forward6arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Suppose the economy is currently in equilibrium, with unemployment equal to the natural rate, and that people form expectations rationally. If the Federal Reserve announces that it is going to decrease the money supply, then: the economy will move to a lower price level but remain at potential GDP. the economy will permanently move to a higher level of output and a higher price level. the economy will permanently move to a lower level of output and a lower price level. the economy will move to a higher GDP level but remain at a constant price level.arrow_forwardGraph an economy which suffers a negative supply shock. How does this effect inflation (increase/decrease) and unemployment (increase/decrease)? What is the name for this situation? What is the relationship between unemployment and inflation as the economy heads into a recession normally? How about the relationship as the economy moves to the peak of the business cycle?arrow_forwardMA4. 13. If the equation for a country's Phillips curve is π = 0.05 – 0.8(u – 0.05), where π is the rate of inflation and u is the unemployment rate, what is the short-run inflation rate when unemployment is 3 percent (0.03)? A) .066 B) -.056 C) -.066 D) .056 11. The aggregate supply equation is Y = Y + α(P – EP). Assume that Y is 2,000, α = 200, P = 1.12 and EP = 1.00. What is the value of Y? A) 2,232 B) 2,024 C) 2,400 D) 2,012 9. If policymakers announce in advance how policy will respond to various situations but then renege on their announcements, this a problem of: A) policy by rule. B) policy by discretion. C) time inconsistency of policy. D) monetary policy. 10. According to the sticky-price model, output will be above the natural level if: A) firms expect a high price level and the demand for goods is high. B) the proportion of firms with flexible prices equals the proportion of firms with sticky prices. C) the price level is above the…arrow_forward
- part darrow_forwardExplain briefly three important reasons why firms have sticky prices in the short run. Given an example of a price that is sticky in the short run but flexible in the long run.arrow_forward“Members of Congress are interested in increasing the minimum wage from its current rate of $7.25 an hour to $15. What effect will this have on the unemployment rate for low-skilled workers? How is this likely to impact equilibrium output and the price level in the short run?"arrow_forward
- Assuming all else equal, the following happens in the economy. “Wages have grown more slowly than the economy in the wake of the 2008 crisis, and faster growth in recent months has been offset by rising inflation. The most recent available data, average hourly wages increased by 2.9 percent, but after adjusting for inflation, the increase was just 0.2 percent according to Department of Labor. … The Fed noted the turn toward nonwage compensation. The survey said that companies seeking workers, rather than baiting their hooks with wage increases, “were increasingly using benefits — such as vacation time, flexible schedules and bonuses — to attract and retain workers, as well as putting more resources into training. For the median worker, benefit compensation has increase 5 percent. With this change, labor costs in net increased compared to last year level.” What would happen in SR and LR equilibrium? Explain using aggregate demand and aggregate supply model.arrow_forwardtrue or false Suppose that the central bank lost credibility in the sense that people no longer believe its inflation target (that is, inflation expectations are not `anchored’). In this case, both short-run output and long-run output do not increase in response to a permanently higher inflation target.arrow_forwardSally, a resident of Scandia, goes to a salon for a haircut. The haircut, which usually costs $50, now costs $40. Sally is confused and curious to understand why she could get the haircut at a lower price despite the salon not offering any discounts. She also notices that the prices of all goods and services in Scandia have decreased. Which situation is occurring in the economy?Inflation Disinflation Deflation Stagflationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education