
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
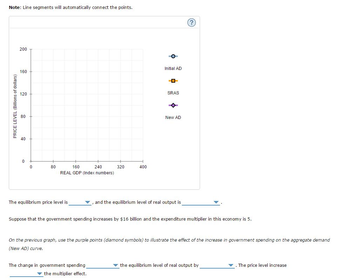
Transcribed Image Text:Note: Line segments will automatically connect the points.
PRICE LEVEL (Billions of dollars)
200
160
120
0
80
160
240
REAL GDP (Index numbers)
The equilibrium price level is
320
400
Initial AD
The change in government spending
the multiplier effect.
SRAS
New AD
✓, and the equilibrium level of real output is
Suppose that the government spending increases by $16 billion and the expenditure multiplier in this economy is 5.
On the previous graph, use the purple points (diamond symbols) to illustrate the effect of the increase in government spending on the aggregate demand
(New AD) curve.
the equilibrium level of real output by
. The price level increase
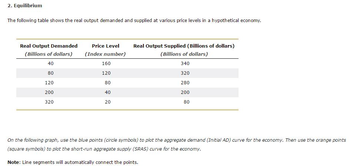
Transcribed Image Text:2. Equilibrium
The following table shows the real output demanded and supplied at various price levels in a hypothetical economy.
Real Output Demanded
(Billions of dollars)
40
80
120
200
320
Price Level
(Index number)
160
120
80
40
20
Real Output Supplied (Billions of dollars)
(Billions of dollars)
340
320
280
200
80
On the following graph, use the blue points (circle symbols) to plot the aggregate demand (Initial AD) curve for the economy. Then use the orange points
(square symbols) to plot the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve for the economy.
Note: Line segments will automatically connect the points.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In each of the following cases, calculate the values of MPC, MPW, and the spending multiplier. Enter your responses below rounded to 2 cecimal places. a. A $6 million increase in income leads to a $900,000 rise in consumption on domestic items. MPC is therefore and the spending multiplier is , MPW is b. A $8 million decrease in income results in a $0.8 million drop in consumption on domestic items. MPC is therefore and the spending multiplier is |. MPW is c. A $4 million decrease in income causes a $3.2 milion drop in withdrawals. MPC is therefore 1. MPW is and the spending multiplier isarrow_forwardIn each of the following cases, calculate the values of MPC, MPW, and the spending multiplier. Enter your responses below rounded to 2 decimal places. a. A $2 million increase in Income leads to a $700,000 rise in consumption on domestic items. MPC is therefore and the spending multiplier is b. A $10 million decrease in income results in a $3 million drop in consumption on domestic Items. MPC is therefore and the spending multiplier is c. A $10 million decrease in income causes a $9 million drop in withdrawals. MPC is therefore spending multiplier is MPW IS MPW IS MPW IS and thearrow_forwardYAS 1548 + 19P - 12Poil YAD = 412 – 33P+ 26G %3D Suppose initially, the Poil = $86 per barrel and government spending is equal to $780. Part (a): Calculate equilibrium GDP and the price level. Part (b): Determine the magnitude of the simple multiplier if oil prices exogenously rise by $1. Part (c): Determine the magnitude of the simple multiplier if government spending exogenously increases by $1.arrow_forward
- Suppose an economy is operating at point A on the graph showing aggregate demand. A decrease in the aggregate price level causes the economy to move to point B On the graph showing aggregate expenditures (AE), show the change caused by the movement from point A to point B on the aggregate demand curve. Aggregate price level Aggregate demand Aggregate output Aggregate expenditures Income (Y) Y-AE AEarrow_forward5. In an economy, the MPC is 0.5. The graph on the right depicts the economy's aggregate demand curve. Suppose the economy starts out at Point A on the aggregate demand curve. Draw the AE curve for this case. a. b. C. d. Suppose an increase in the price level causes the economy to move to Point B on the aggregate demand curve. Draw the new AE curve. Suppose government spending decreases by $0.2T. Draw the new AD curve. In place of the change in part (c), suppose net taxes decrease by $0.2T. Draw the new AD curve. Price Level (P) 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 AD 2.6 3.0 3.4 3.8 4.2 4.6 2.8 3.2 3.6 4.0 4.4 4.8 Y (T of $)arrow_forwardCan you answer this questionarrow_forward
- THE AGGREGATE EXPENDITURE MODEL (IN THE SHORT RUN)YOU MUST SHOW YOUR CALCULATIONS IN THE SPACE BELOWFOR THE NEXT PROBLEM USE THE FOLLOWING FORMULA:CHANGE IN GDP = [ 1 / (1-MPC) ] * CHANGE IN GInitially, the economy is producing $13 trillion in goods and services and the government is spending $2 trillion.Then the government decides to increase its spending to $2.7 trillion. What is the value of the spending multiplier?arrow_forwardI need help pleasearrow_forwardQuestion 3 of 16 Income and consumption changes for five people are shown in the table. Given this information, rank the marginal propensities to consume (MPC) for the five people from largest to smallest. Largest MPC Smallest MPC Answer Bank Bert Doug Eli Carter Al Name Income change Consumption change Al +$5,000+$5,000 +$3,000+$3,000 Bert +$2,500+$2,500 +$800+$800 Carter +$1,000+$1,000 +$800+$800 Doug −$2,500−$2,500 −$1,750−$1,750 Eli −$5,000−$5,000 −$2,000−$2,000arrow_forward
- Stiller 1. Suppose an economy is represented by the following equations. Consumption function C = 100 + 0.8Yd Planned investment I = 38 Government spending G = 75 Exports EX = 25 Imports IM= 0.05Yd Autonomous Taxes T = 40 Planned aggregate expenditure AE = C + I + G + (EX - IM) a. By using the above information calculate the equilibrium level of income for this economy, b. Calculate the value of expenditure multiplier. c. Suppose that government spending is increased by 5, what will happen to the equilibrium income level?arrow_forwardhi there is another picture as wellarrow_forwardHomework: Demand-Side Equilibrium: Unemployment or Inflation? The following graph shows the total expenditure line (TE) for an economy where current equilibrium output is $400 billion and potential output is $650 billion. REAL EXPENDITURE (Billions of dollars) § 2 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 0 100 45-degree ling 200 300 400 500 600 REAL GDP (Bilions of dollars) The economy is experiencing TE Potential GDP 700 800 TE equal to $ by billion. Thus, the value of the multiplier for this economy is billion. To close the output gap, government purchases could On the previous graph, shift the TE line to show the change in total expenditure necessary to close the output gap. Note: Select and drag the curve to the desired position. The curve will snap into position, so if you try to move a curve and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it a little farther.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education