
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
23rd Edition
ISBN: 9781337794756
Author: HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher: Cengage Learning,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Prepare journal entries
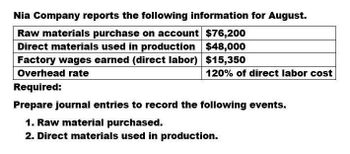
Transcribed Image Text:Nia Company reports the following information for August.
Raw materials purchase on account $76,200
Direct materials used in production $48,000
Factory wages earned (direct labor) $15,350
Overhead rate
Required:
120% of direct labor cost
Prepare journal entries to record the following events.
1. Raw material purchased.
2. Direct materials used in production.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- SCHEDULE OF COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED The following information is supplied for Sanchez Welding and Manufacturing Company. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the year ended December 31, 20--. Assume that all materials inventory items are direct materials. Work in process, January 1 20,500 Materials inventory, January 1 11,000 Materials purchases 12,000 Materials inventory, December 31 13,000 Direct labor 9,500 Overhead 5,500 Work in process, December 31 10,500arrow_forwardOReilly Manufacturing Co.s cost of goods sold for the month ended July 31 was 345,000. The ending work in process inventory was 90% of the beginning work in process inventory. Factory overhead was 50% of the direct labor cost. No indirect materials were used during the period. Other information pertaining to OReillys inventories and production for July is as follows: Required: 1. Prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured for the month of July. (Hint: Set up a statement of cost of goods manufactured, putting the given information in the appropriate spaces and solving for the unknown information. Start by using cost of goods sold to solve for the cost of goods manufactured.) 2. Prepare a schedule to compute the prime cost incurred during July. 3. Prepare a schedule to compute the conversion cost charged to Work in Process during July.arrow_forwardDuring the year, a company purchased raw materials of $77,321, and incurred direct labor costs of $125,900. Overhead is applied at the rate of 75% of the direct labor cost. These are the inventory balances: Compute the cost of materials used in production, the cost of goods manufactured, and the cost of goods sold.arrow_forward
- During the year, a company purchased raw materials of $77,321 and incurred direct labor costs of $125,900. Overhead Is applied at the rate of 75% of the direct labor cost. These are the inventory balances: Compute the cost of materials used in production, the cost of goods manufactured, and the cost of goods sold.arrow_forwardCost of Direct Materials, Cost of Goods Manufactured, Cost of Goods Sold Bisby Company manufactures fishing rods. At the beginning of July, the following information was supplied by its accountant: During July, the direct labor cost was 43,500, raw materials purchases were 64,000, and the total overhead cost was 108,750. The inventories at the end of July were: Required: 1. What is the cost of the direct materials used in production during July? 2. What is the cost of goods manufactured for July? 3. What is the cost of goods sold for July?arrow_forwardEllerson Company provided the following information for the last calendar year: During the year, direct materials purchases amounted to 278,000, direct labor cost was 189,000, and overhead cost was 523,000. During the year, 100,000 units were completed. Refer to Exercise 2.21. Last calendar year, Ellerson recognized revenue of 1,312,000 and had selling and administrative expenses of 204,600. Required: 1. What is the cost of goods sold for last year? 2. Prepare an income statement for Ellerson for last year.arrow_forward
- On December 1, Carmel Valley Production Inc. had a work in process inventory of 1,200 units that were complete as to materials and 50% complete as to labor and overhead. December 1 costs follow: During December the following transactions occurred: a. Purchased materials costing 50,000 on account. b. Placed direct materials costing 49,000 into production. c. Incurred production wages totaling 50,500. d. Incurred overhead costs for December: e. Applied overhead to work in process at a predetermined rate of 125% of direct labor cost. f. Completed and transferred 10,000 units to finished goods. (Hint: You should first compute equivalent units and unit costs. The unit cost should include applied, not actual, factory overhead.) Carmel Valley uses the weighted average cost method. The ending inventory of work in process consisted of 1,000 units that were completed as to materials and 25% complete as to labor and overhead. Required: Prepare the journal entries to record the above December transactions.arrow_forwardThe following data summarize the operations during the year. Prepare a journal entry for each transaction. A. Purchase of raw materials on account: $1,500 B. Raw materials used by Job 1: $400 C. Raw materials used as indirect materials: $50 D. Direct labor for Job 1: $200 E. Indirect labor Incurred for Job 1: $30 F. Factory utilities Incurred on account: $500 G. Adjusting entry for factory depreciation: $200 H. Manufacturing overhead applied as percent of direct labor: 100% I. Job 1 is transferred to finished goods J. Job 1 is sold: $1,000 K. Manufacturing overhead is under applied: $100arrow_forwardFactory overhead costs During May, Bergan Company incurred factory overhead costs as follows: indirect materials, 8,800; indirect labor, 6,600; utilities cost, 4,800; and factory depreciation, 9,000. Journalize the entry to record the factory overhead incurred during May.arrow_forward
- JOURNAL ENTRIES FOR MATERIAL, LABOR, AND OVERHEAD Eto Manufacturing had the following transactions during the month: (a) Purchased raw materials on account, 70,000. (b) Issued direct materials to Job No. 300, 25,000. (c) Issued indirect materials to production, 10,000. (d) Paid biweekly payroll and charged direct labor to Job No. 300, 8,000. (e) Paid biweekly payroll and charged indirect labor to production, 3,000. (f) Issued direct materials to Job No. 301, 20,000. (g) Issued indirect materials to production, 4,000. (h) Paid miscellaneous factory overhead charges, 6,000. (i) Paid biweekly payroll and charged direct labor to Job No. 301, 10,000. (j) Paid biweekly payroll and charged indirect labor to production, 2,000. REQUIRED Prepare general journal entries for transactions (a) through (j).arrow_forwardDuring March, the following costs were charged to the manufacturing department: $14886 for materials; $14,656 for labor; and $13,820 for manufacturing overhead. The records show that 30,680 units were completed and transferred, while 2,400 remained in ending inventory. There were 33,080 equivalent units of material and 31,640 of conversion costs. Using the weighted-average method, what is the cost of inventory transferred and the balance in work in process inventory?arrow_forwardSelected information concerning the operations of a company for the year ended December 31 is as follows: Work in process inventories at the beginning and end of the year were zero. Beginning inventory of finished goods was 9,650 (for 1,000 units). Cost of goods sold was 174,600. What was the companys finished goods inventory cost at December 31? a. 98,050 b. 29,100 c. 29,050 d. 40,600arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:9781337794756
Author:HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub