
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Of two possible structures A and B for the conjugate acid of guanidine, the more stable is the one that is better stabilized by electron delocalization. Which one is it? Write resonance structures showing this electron delocalization.
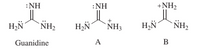
Transcribed Image Text::NH
: ΝΗ
+NH2
`NH2
NH3
H,Ñ
NH2
Guanidine
A
В
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. The following compounds or ions are aromatic. What is the Hückel number (n) for each one? Show your calculation. If more than one, give the larger n. H n = calculationarrow_forwardQUESTION 7 Which of the following is not true about anti-aromatic molecules? Anti-aromatic molecules must have 4N+2 pi electrons where N = 0, 1, 2, 3.... Anti-aromatic molecules must be cyclic Anti-aromatic molecules have to be planar Anti-Aromatic molecules are unstable compared to non-aromatic moleculesarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided resonance structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows to show the interconversion between resonance hybrid contributors. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :0: :N: Select to Add Arrows > ΚΘ KOarrow_forward
- (7) Heterolytic reactions involve A) Bond-breaking where each of the fragments retains one of the originally bonded electrons B) Bond-breaking where one of the fragments retains both of the originally bonded electrons C) Bond-making where each of the fragments retains one of the originally bonded electrons D) Bond-making where one of the fragments retains both of the originally bonded electronsarrow_forwardAn example of a conjugated system is two positively charged carbons separated by one single bond one negatively charged carbon adjacent to a л bond two negatively charged carbons separated by one single bond one positively charged carbon adjacent to a σ bondarrow_forwardWhich do you expect to have a more intense and concentrated “hot spot” of negative charge: methoxide ion or bicarbonate ion? Explain.arrow_forward
- Complete the following acid-base reaction . Show all valence electrons on the interacting atoms and show by the use of curved arrows the flow of electrons in each reaction.arrow_forwardOther than having 4n+ 2 pi electrons, which condition(s) must be met for a molecule to be aromatic? O The molecule must be planar. The molecule must be conjugated. O The molecule must be a ring. O All of the above.arrow_forward6. The structure originally proposed for Cordycepic acid, [a] = + 40.3°, has been shown to be in correct, suggest reason to be skeptical about the original structure, which is given below. CO2H HO Not OH HO OHarrow_forward
- For which of the following molecules are there two unique configurations about the double bond? Explain. (a) (CH3)2C=CHCI; (b) H2C=CHCH,CH3; (c) CIHC=CHBr; (d) HC=CCH=CHCIarrow_forwardDetermine α' and α for a molecule that experiences a Debye bond energy of -2 aJ being at a distance of 0.1 nm from a molecule of acetic acidarrow_forwardThe photo dimerization of benzophenone to benzopinacol is initiated by what type of electronic transition that then rapidly decomposes to a diradical since putting in electrons in anti bonds breaks bonds! The diradical then starts abstracting hydrogens from solution as pictured in the text? σ = electrons in sigma bonds n = electrons in non-bonding orbitals π electrons in pi bonds. anti bonds Hint: This process is very important because although the molecule responsible for human vision (retinal) is not a very long conjugated pi system, this transition allows retinal to absorb visible light. a. n to σ* b. σ to σ* C. π το π d. n to П e. σ to П* f. π to σ'arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY