
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
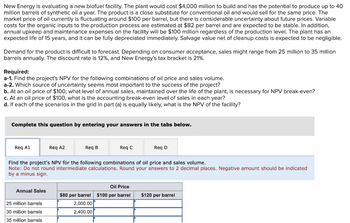
Transcribed Image Text:New Energy is evaluating a new biofuel facility. The plant would cost $4,000 million to build and has the potential to produce up to 40
million barrels of synthetic oil a year. The product is a close substitute for conventional oil and would sell for the same price. The
market price of oil currently is fluctuating around $100 per barrel, but there is considerable uncertainty about future prices. Variable
costs for the organic inputs to the production process are estimated at $82 per barrel and are expected to be stable. In addition,
annual upkeep and maintenance expenses on the facility will be $100 million regardless of the production level. The plant has an
expected life of 15 years, and it can be fully depreciated immediately. Salvage value net of cleanup costs is expected to be negligible.
Demand for the product is difficult to forecast. Depending on consumer acceptance, sales might range from 25 million to 35 million
barrels annually. The discount rate is 12%, and New Energy's tax bracket is 21%.
Required:
a-1. Find the project's NPV for the following combinations of oil price and sales volume.
a-2. Which source of uncertainty seems most important to the success of the project?
b. At an oil price of $100, what level of annual sales, maintained over the life of the plant, is necessary for NPV break-even?
c. At an oil price of $100, what is the accounting break-even level of sales in each year?
d. If each of the scenarios in the grid in part (a) is equally likely, what is the NPV of the facility?
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Req A1
Req A2
Req B
Req C
Req D
Find the project's NPV for the following combinations of oil price and sales volume.
Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. Negative amount should be indicated
by a minus sign.
Annual Sales
25 million barrels
30 million barrels
35 million barrels
Oil Price
$80 per barrel $100 per barrel $120 per barrel
2,000.00
2,400.00
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Hit or Miss Sports is introducing a new product this year. If its see-at-night soccer balls are a hit, the firm expects to be able to sell 42,700 units a year at a price of $64 each. If the new product is a bust, only 22,200 units can be sold at a price of $41. The variable cost of each ball is $27 and fixed costs are zero. The cost of the manufacturing equipment is $5.92 million, and the project life is estimated at 9 years. The firm will use straight-line depreciation over the 9-year life of the project. The firm's tax rate is 35% and the discount rate is 13%. Now suppose that Hit or Miss Sports can expand production if the project is successful. By paying its workers overtime, it can increase production by 20,100 units; the variable cost of each ball will be higher, equal to $32 per unit. By how much does this option to expand production increase the NPV of the project? Assume that the firm decides whether to expand production after it learns the first-year sales results. (Round…arrow_forwardA bicycle manufacturer currently produces 237,000 units a year and expects output levels to remain steady in the future. It buys chains from an outside supplier at a price of $2.20 a chain. The plant manager believes that it would be cheaper to make these chains rather than buy them. Direct in-house production costs are estimated to be only $1.60 per chain. The necessary machinery would cost $293,000 and would be obsolete after 10 years. This investment could be depreciated to zero for tax purposes using a 10-year straight-line depreciation schedule. The plant manager estimates that the operation would require $44,000 of inventory and other working capital upfront (year 0), but argues that this sum can be ignored since it is recoverable at the end of the 10 years. Expected proceeds from scrapping the machinery after 10 years are $21,975. If the company pays tax at a rate of 35% and the opportunity cost of capital is 15%, what is the net present value of the decision to produce the…arrow_forwardquick computing currently sells 7 million computer chips each year at a price of $12 per chip. It is about to introduce a new chip, and it forecasts annual sales of 22 million of these improved chips at a price of $15 each. However, demand for the old chip will decrease, and sales of the old chip are expected to fall to 1 million per year. The old chips cost $6 each to manufacture, and the new ones will cost $10 each. What is the proper cash flow to use to evaluate the present value of the introduction of the new chip?arrow_forward
- Given the soaring price of gasoline, Ford is considering introducing a new production line of gas-electric hybrid sedans. The expected annual unit sales of the hybrid cars is 26,000; the price is $21,000 per car. Variable costs of production are $11,000 per car. The fixed overhead including salary of top executives is $80 million per year. However, the introduction of the hybrid sedan will decrease Ford's sales of regular sedans b 9,000 cars per year; the regular sedans have a unit price of $20,000, a unit variable cost of $12,000, and fixed costs of $250,000 per year. Depreciation costs of the production plant are $49,000 per year. The marginal tax rate is 40 percent. What is the incremental annual cash flow from operations? Incremental annual cash flow from operations eTextbook and Media $arrow_forwardA bicycle manufacturer currently produces 391,000 units a year and expects output levels to remain steady in the future. It buys chains from an outside supplier at a price of $2.10 a chain. The plant manager believes that it would be cheaper to make these chains rather than buy them. Direct in-house production costs are estimated to be only $1.60 per chain. The necessary machinery would cost $292,000 and would be obsolete after ten years. This investment could be depreciated to zero for tax purposes using a ten-year straight-line depreciation schedule. The plant manager estimates that the operation would require $43,000 of inventory and other working capital upfront (year 0), but argues that this sum can be ignored since it is recoverable at the end of the ten years. Expected proceeds from scrapping the machinery after ten years are $21,900. If the company pays tax at a rate of 20% and the opportunity cost of capital is 15%, what is the net present value of the decision to produce the…arrow_forwardUnder pressure from its board of directors, management at Roadside is planning to enter the conventional battery-powered flashlight market. Roadside expects to sell this boring product to wholesalers for $18.12 per unit. Relevant fixed costs will total $334,573, and variable costs to make this product will be $14.57 per unit. Background research estimates the size of the market for conventional flashlights at 1.8 million units per year. If sales of this unit reach breakeven, what market share will Roadside have? Report your answer as a percent. Report 27.5%, for example, as "27.5". Rounding: tenth of a percent.arrow_forward
- A chemical company is planning to release a new brand of insecticide that will kill many insect pests but not harm useful pollinators. Buying new equipment to manufacture the product will cost $15 million. The equipment is expected to have a lifetime of nine years and will be depreciated by the straight-line method over its lifetime. The firm expects that they should be able to sell 1,400,000 gallons per year at a price of $65 per gallon. It will take $36 per gallon to manufacture and support the product. If the company's marginal tax rate is 40%, what are the incremental earnings after tax in year 3 of this project? $23.36 million $9.58 million $12.72 million $15.30 million $14.30 million $24.36 millionarrow_forwardThese are the values I was solving for, but I'm being told the $6,393,505.38 is incorrect. Not sure what I'm doing wrong. Thanks!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education