
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
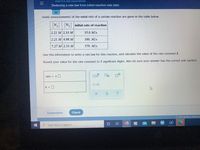
Transcribed Image Text:O KINETICS AND EQUILIBRIUM
Deducing a rate law from initial reaction rate data
Some measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below.
N2 H, initial rate of reaction
2.21 M 2.33 M
35.0 M/s
2.21 M 4.98M
160. M/s
7.27 M 2.33 M
379. M/s
Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k.
Round your value for the rate constant to 3 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol.
rate = k O
k = |
Explanation
Check
O 2021 McGraw-Hill Educ
P Type here to search
III
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Rate law: Rate law are the mathematical expression used to show concentration of reactant and product that changes with time.
It can be represented as: Rate = K [A]a [B]b here A nd B are reacting species, a and b are stoichiometry coefficient.
Rate constant (k): It is the proportionality constant used to show direct relation between rate of reaction and concentration of reactant.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Some measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. H2 12| initial rate of reaction 1.75 M 0.881M 0.347 M/s 0.320M 0.881M 0.0635 M/s 1.75 М | 2.22М 0.874 M/s Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 3 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k|| x10 k =arrow_forwardn=1 rate = k [A]arrow_forwardDetermine the rate law and the rate constant for this reaction. 13.125. The table contains reaction rate data for the reaction 2 NO(g) + Cl,(g)→ 2 NOCI(g) Initial Rate Experiment [NO], (M) [Cl_]o (M) (M/s) 1 0.20 0.10 0.63 0.20 О.30 5.70 0.80 0.10 2.58 0.40 0.20 Predict the initial rate of reaction in experiment 4. 13.126. An important reaction in the formation of photochemical smog is the reaction between ozone and NO: NO(g) + O3(g) → NO;(g) + O,(g) 2. 2. 3.arrow_forward
- Some measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. [N2] H2 initial rate of reaction 1.02M 1.73М 0.0437M/s 1.02M |6.60М 0.167 M/s 0.333 M 1.73М 0.00466M/s Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 3 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k k =arrow_forwardSome measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. [N₂] [H₂] initial rate of reaction 1.36M 2.01 M 0.639 M/s 1.36M 4.86M 3.74 M/s 0.400M 2.01 M 0.188 M/s Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k -0 - x10 Śarrow_forwardSome measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. [N₂] H₂ initial rate of reaction 0.945M 1.74M 1.00 × 106 M/s 0.945M 0.395M 0.458M 1.74M Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k -0 5.15 × 10 M/S 4.85 × 105 M/s k = x10 X Sarrow_forward
- Some measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. H2 12 initial rate of reaction 1.47M 1.17M 36.0M/s 1.47M 4.13M 127. M/s 0.591 M 1.17M 14.5 M/s Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 3 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k| x10 k = 0arrow_forwardSome measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. [₂] [H₂] initial rate of reaction 2.48M 1.13M 84.0 M/s 0.635M 1.13M 2.48M 0.211 M rate = k [] Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 2 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. k = 5.51 M/s 0 2.93 M/s x10 ■• X Śarrow_forwardGiven the equation: rate = k[H2O2]m[I-]n Which of the following statements is (are) true about the orders, m and n? a. m and n are equal to each other in all cases b. m and n are independent from the molar coefficients of the reactants in the balanced chemical equation c. m and n must be determined by experiment d. m and n are equal to the molar coefficients of H2O2 and I- in the balanced chemical reaction, respectivelyarrow_forward
- Some measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. alo N2| |H2 initial rate of reaction 0.875 M 1.32M 0.0545 M/s 0.875 M 0.342M 0.0141 M/s 3.25 M 1.32 M 0.752 M/s Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 3 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k O k = 0arrow_forwardInitial-rate data at a certain temperature is given in the table for the reaction SO₂Cl₂(g) → SO₂(g) + Cl₂ (g) [SO₂Cl₂], (M) k = 0.100 0.200 0.300 Initial rate (M/s) 2.40 x 10-6 4.80 x 10-6 7.20 x 10-6 Determine the value and units of the rate constant. units:arrow_forwardSome measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. [H] [1] initial rate of reaction 1.12M 2.03M 11.0M/s 1.12M 0.695M 3.77M/s 0.268M 2.0зм 2.63M/s Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 3 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k|| x10 k =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY