
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
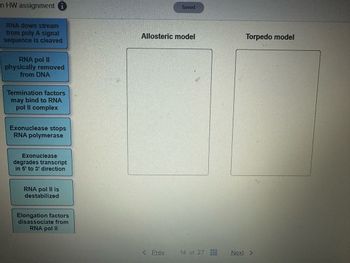
Place the labels in the correct column for Eukaryotic transcriptional termination
Transcribed Image Text:n HW assignment i
RNA down stream
from poly A signal
sequence is cleaved
RNA pol II
physically removed
from DNA
Termination factors
may bind to RNA
pol II complex
Exonuclease stops
RNA polymerase
Exonuclease
degrades transcript
in 5' to 3' direction
RNA pol II is
destabilized
Elongation factors
disassociate from
RNA pol II
Saved
Allosteric model
Torpedo model
< Prev.
14 of 27
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What type of RNA is involved in the post-transcriptional modification illustrated below? 5' in m 3' 5' 3' 5' AAAAGGGCUUUAACUUCA 9 AAAAGGGCUUUAACUUCA UUUUUUUGAAAUUGAAGU AAA AAAA A AAAUUUAUGUGUUGUCUUUUAACUUCA UUUAAAUAUAUAAUAGAAAAUUGAAGU AAAUUUAUGUGUUGUCUUUUAACUUCA 3' 3' 5' 3' 5' 3'arrow_forwardShown below is a schematic drawing of a gene, with the transcription unit divided into numbered regions. The arrows (;) indicate transcription initiation sites, "D" indicates a splice donor site, "A" indicates a splice acceptor site, and "An" indicates a polyadenylation signal. Give all the possible fully processed mRNAs that could be produced from transcripts of this gene (you don't need to draw anything, just list the regions that would be included in each mRNA by number).arrow_forwardIn a written paragraph, describe the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic TRANSCRIPTION. In your response, include the following: - differences in what structures (DNA, RNA, proteins etc...) are involved - differences in timing and location - DO NOT include any details on what happens after transcriptionarrow_forward
- The most common type of termination signal in E. Coli is a symmetrical inverted repeat of GC rich sequences followed by about 7 As that forms a stable stem-loop structure in the RNA, which disrupts its association with the DNA template and terminates transcription. true or falsearrow_forwardFor each of the following initiation factors, how would eukaryotic initiation of translation be affected if it were missing? A. eIF 2 B. eIF4 C. eIF5arrow_forwardExplain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription. In 3-4 sentencearrow_forward
- Describe the initiation step of bacterial transcription (make sure to include important enzymes, parts, and sequences in your answer) up to the beginning of elongation. What are three ways that transcription differs between bacteria and eukaryotes? (I'm not looking for types of RNA modification, just in terms of transcription)arrow_forwardWhich of the following sequences would most likely be the site of the initiation of transcription? ТАТАААТА GCTAGCTA GGCGGCCC Impossible to tellarrow_forwardA string of 8 adenine nucleotides in the mRNA is required for function of an intrinsic transcription terminator in bacteria. True Falsearrow_forward
- Although the genetic code is universal, a few organisms such as Paramecium have a slightly modified version in which UGA, a stop codon for most organisms, codes for tryptophan in Paramecium. Suppose that the researcher wanted to make an in vitro translation system using all of the components from Paramecium. Which of the components, if any, would she need to replace in order to have an in vitro system that was universal? Possible Answers: A. She would need to leave out the P site. B. She would need to leave out the termination factor proteins. C. She would need to leave out the tRNA that recognizes UGA. D. She would need to leave out the ubiquitinarrow_forwardIn eukaryotic transcription, which of the following is not included in the initiation of transcription? Group of answer choices RNA polymerase II TATA box Holoenzyme AAUAAA consensus sequencearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education