
Concept explainers
My hypothesis:
The Hyper-IgE syndrome, also known as Job’s syndrome, is an immunodeficiency disease resulting from the lack of function of a single gene (gene ‘X’). This Hyper IgE/Job's syndrome or STAT3 deficiency(HIES) is caused by STAT3 gene mutation. STAT3 is a gene involved in major signal transduction pathways including wound healing, angiogenesis, immune response, and allergies. This genetic mutation is autosomal dominant in nature. The above mentioned are the most likely immune function impaired in the Gene X-deficient patients including immunity with eczematous and non-immunologic system disorders.
Question:
In a lab, histological examination of tongue sections from Candida albicans infected mice were examined, and the numbers of infiltrating leukocytes (white blood cells) were quantified in each microscopic field of each section, and the results are shown in the figure below. Do these data support or refute my hypothesis stated above? Why or why not?
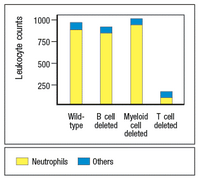
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- gamma:delta T-cell receptors are also generated by gene rearrangement. Some T cells express gamma:delta T-cell receptors rather than alpha:beta T-cell receptors. The organization of the a locus and the d locus helps to ensure that each T cell cannot express both types of T-cell receptors. The mechanism involved is that: The rearrangement of a T-cell receptor a gene deletes the d locus on that allele. The rearrangement of a T-cell receptor d gene deletes the a locus on that allele. The RAG recombinase enzymes are down-regulated immediately after the first T-cell receptor genes rearrange. The a:b T-cell receptor signals the T cell to delete the d locus. The g:d T-cell receptor signals the T cell to delete the a locus.arrow_forward. Mutants were isolated in which the constitutive phenotype of a missense lacI mutation was suppressed.That is, the operon was now inducible. These suppressor mutations mapped to the operon, not to the lacIgene. What could these mutations be?arrow_forwardcan you please explain the last part of step 2 further? Specifically this "The complementation does not occur in case of mutations are present in same gene. The complementation occurs between two mutations will suggests that mutations are present in different genes."arrow_forward
- Drug 2-Lumacaftor (VX-809): In people with the most common CF mutation, F508del, a series of problems prevents the CFTR protein from folding into the correct shape and reaching its proper place on the cell surface. The cell recognizes the protein as abnormal and targets it for degradation before it makes it to the cell surface. In order to treat this problem, two drugs are required - an agent to get the protein to the surface and then Ivacaftor to open the channel and increase chloride transport. The drug Lumacaftor has been identified as a treatment to help with the trafficking of the protein to the cell surface. When Lumacaftor is added to Ivacaftor, the protein gets to the surface and also increases chloride transport by increasing channel opening time. For which class(es) of mutations would Lumacaftor be most effective?arrow_forwardQ38. The ΔF508 mutation of the CFTR gene is the cause of most cases of cystic fibrosis (CF). One focus of research into a cure for CF is "gene therapy" — inserting normal copies of the CFTR gene into the cells of CF patients. Which of the following areas of CF research is most likely to improve symptoms for CF patients? A. Inserting extra copies of genes that code for the proteosome. B. Studying the chaperone proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). C. Improving the lung function of people who are carriers of the CF allele (Cc). D. Stabilizing the plasma membrane were the ΔF508 form of the protein accumulates.arrow_forwardshort answer please! thank you!arrow_forward
- Please help, doesn't it usually start before the promoter or after, please just give me a brief explanationarrow_forwardTrue or False. 1. a.) RNA polymerase decodes mRNA so the ribosome can make proteins. b.) Only coding RNA can interact with the ribosome. c.) The ribosome is composed of both protein and ncRNA. d.)The ncRNA components of the ribosome behave as a ribozyme. Pick one of the FALSE statements from the 4 previous questions and explain why it is incorrect.arrow_forward1. "Interferons (IFNs)‐α and ‐β are expressed in response to a virus infection and are released from the cell in which they are produced. IFNs induce an antiviral state in other neighboring cells. a. Which cellular process is inactivated when IFN‐treated cells are infected with a virus? b. One arm of the IFN‐induced antiviral state is the synthesis of 2′,5′‐oligoA in response to viral infection. In one sentence or a simple diagram, what is the effect of this on the cell? c. Another arm of the IFN‐induced antiviral state is activation of the protein kinase in response to viral infection. In one sentence or a simple diagram, what is the effect of this on the cell? d. All cells contain the genes for IFNs. IFN synthesis is stimulated by virus infection. Would you expect a cell that has been treated with IFN to synthesize IFN in response to a viral infection? Explain your answer."arrow_forward
- You are lovely little gene which makes the actin protein (the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton protein). You have just woken up to a transcription factor sitting down on your local TATA box. Tell me all your life events from beginning vou just saw the transcription factors) to end fyour protein death). Don't forget to mention WHERE you have lived during your life, how you have moved, what helped you along the way, and all the other proteins and other small molecules you havearrow_forwardYour identify a number of mutants and start to characterize the problems in their mismatch repair mechanisms. Based on the following initial results of your experiments, predict which mismatch repair protein(s) is mutated in each mutant. (Your experiments tells you what mismatches are being left unfixed.) Mutant 1: Still contains mismatches where G binds to T and T binds to G Mutant 2: Roughly one half of all mismatches remain. Mutant 3: All mutations remain, but you find that no mismatch repair proteins are non-functional. Mutant 4: All mutations remain, and you find increased MutL-MutS complexes bound to the DNA.arrow_forwardGENETICS - help me pleasearrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





