
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
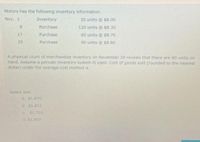
Transcribed Image Text:Motors has the following inventory information.
Nov. 1
Inventory
30 units @ s8.00
Purchase
120 units e $8.30
17
Purchase
60 units e $8.70
25
Purchase
90 units e $8.80
A physical count of merchandise inventory on November 30 reveals that there are 80 units on
hand. Assume a periodic inventory system is used. Cost of goods sold (rounded to the nearest
dollar) under the average-cost method is
Select one:
a $1.870.
b. $1.812
C 51.758
d. $1.859
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Crane Company uses a periodic inventory system. For October, when the company sold 1,690 units, the following information is available. Units Unit Cost Total Cost October 1 inventory 580 $ 22 $ 12,760 October 8 purchase 1,160 23 26,680 October 25 purchase 580 26 15,080 2,320 $ 54,520 Compute the October 31 inventory and the October cost of goods sold using the FIFO method. Ending inventory $ Cost of goods sold $ %24 %24arrow_forwardPharoah Company uses a periodic inventory system and reports the following for the month of June. Date June 1 12 23 30 Explanation Units Unit Cost Inventory $4 Purchase Purchase Inventory Cost of the ending inventory 112 Cost of goods sold 448 280 260 6 $ 8 (a) Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under (1) FIFO, (2) LIFO, and (3) average-cost. (For calculation purposes, round average cost per unit to 2 decimal places, e.g. 5.25. Round answers to O decimal places, e.g. 125.) Total Cost FIFO $448 2,688 2,240 $ GA $ LIFO $ GA $ LA Average-Costarrow_forwardVaiarrow_forward
- Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for an inventory item are as follows: Date Line Item Description Units and Cost Sep. 1 Beginning Inventory 24 units @ $15 5 Sale 17 units 17 Purchase 10 units @ $20 30 Sale 8 units Assuming a perpetual inventory system and the first-in, first-out method: a. Determine the cost of goods sold for the September 30 sale. fill in the blank 1 of 2$ b. Determine the inventory on September 30.arrow_forwardGiven the following data, calculate the cost of goods sold for the 04/15 sale using the weighted-average method for a perpetual inventory system, rounding to the nearest dollar. (Do not round in the process of your calculations, only round your final answer.) 1/1 3/5 Beginning inventory Purchases 4/15 Sale 5/30 Purchases 10/25 Purchases 11/15 Sale 12/31 Ending inventory O $280 O $600 $200 $230 50 units at $10 per unit 30 units at $14 per unit 20 units at $30 per unit 25 units at $15 per unit 20 units at $16 per unit 60 units at $32 per unit 45 unitsarrow_forwardSunland Co. began operations on July 1. It uses a perpetual inventory system. During July, the company had the following purchases and sales. Date July July 6 1 July 11 July 14 July 21 July 27 (a1) July 1 July 6 July 11 July 14 Units Unit Cost $150 5 6 Purchases 7 $ Calculate the average cost per unit at July 1, 6, 11, 14, 21 & 27. (Round intermediate calculations to O decimal places and final answers to 3 decimal places, e.g. $105.501.) ta ta $ $164 July 21 $ $175 Average cost for each unit July 27 $ Sales Units 3 5 5arrow_forward
- Wilkenson Inc. has the following information available for November: Date Units Cost per Unit Total Cost Nov 1 Beginning Inventory 70 $50 $3500 Nov 5 Purchase 30 $60 1800 Nov 14 Sale (60) Nov 25 Purchase 60 $52 3120 Nov 30 Sale (80) Total 20 $162 8420 Compute the cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory, respectively, assuming the perpetual weighted-average method. Description Perpetual-Weighted Average COGS Cost of Ending Inventoryarrow_forwardThe following units of a particular item were available for sale during the calendar year: Jan. 1 Inventory 4,100 units at $39 Apr. 19 2,500 units June 30 4,400 units at $45 Sept. 2 5,100 units Nov. 15 1,900 units at $48 Date Jan. 1 Apr. 19 The firm maintains a perpetual inventory system. Determine the cost of goods sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale, assuming the last-in, first-out method. Present the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 4. Under LIFO, if units are in inventory at two or more different costs, enter the units with the LOWER unit cost first in the Inventory Unit Cost column. June 30 Sept. 2 Nov. 15 Sale Dec. 31 Purchase Sale Purchase Quantity Balances Purchases Unit Cost Total Cost Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold LIFO Method Quantity Cost of Goods Sold Unit Cost Total Cost $ Quantity Inventory Unit Cost Total Cost $arrow_forwardSalmone Company reported the following purchases and sales of its only product. Salmone uses a perpetual inventory system. Determine the cost assigned to cost of goods sold using FIFO. Date Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail May 1 Beginning inventory 156 units @ $10 = $1,560 May 5 Purchase 226 units @$12 = $2,712 May 10 Sales 146 units @ $20 May 15 Purchase 106 units @$13 = $1,378 May 24 Sales 96 units @ $21arrow_forward
- Haynes Company uses the perpetual inventory system. The following information is available for the month the March. March 1 Beginning Inventory 10 units at $2 for $20, March 4 Sold 8 units, March 22 Purchased 50 units at $4 for $200, March 26 Sold 48 units. If Haynes Company uses the LIFO inventory costing method, what is the balance in Ending Inventory at March 31? A. $40 B. $16 C. $12 D. $8arrow_forwardWarnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Date March 1 March 5 March 91 March 18 March 25 March 29 Total Beginning inventory Purchases: March 5 March 18 March 25 Activities Beginning inventory Purchase Sales Purchase Purchase Sales Totals, Required: 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. Units Acquired at Cost 80 units @ $50.60 per unit 215 units @ $55.60 per unit # of units 75 units @ $60.60 per unit 130 units @ $62.60 per unit Cost per Unit 500 units Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Available. for Sale Units Sold at Retail 240 units @ $85.60 per unit 110 units @ $95.60 per unit 350 unitsarrow_forwardCullumber Co. began operations on July 1. It uses a perpetual inventory system. During July, the company had the following purchases and sales. Date July 1 July 6 July 11- July 14 July 21 July 27 (a1) Units Unit Cost July 1 Purchases July 5 6 July 21 7 July 27 July 6 $ July 11 $ $ Calculate the average cost per unit at July 1, 6, 11, 14, 21 & 27. (Round intermediate calculations to 0 decimal places and final answers to 3 decimal places, e.g. $105.501.) 14 $ SA $130 $ $144 Average cost for each unit $ $155 Sales Units 3 5 5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education