
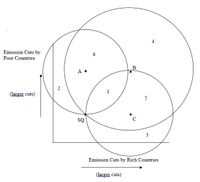
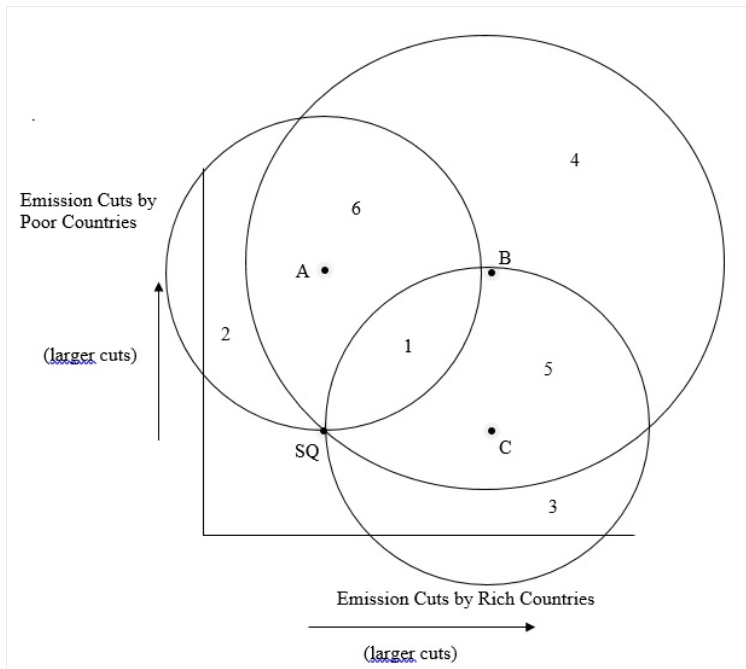
Most governments are concerned about climate change. They have thus sought to negotiate an agreement to reduce carbon emissions. These negotiations have been difficult because governments disagree about who should bear the burden of reducing emissions. Suppose governments have the following preferences: Poor countries such as China and India believe that poor countries should not have to make further emissions cuts, while rich countries should make large cuts. The US believes that rich countries should not have to make further cuts, but that poor countries should make large cuts. The European Union (EU) would like both groups of countries to make large cuts. These ideal points are depicted in the two-dimensional space below. “SQ” is the status quo, and represents the emissions cuts that governments have already agreed to in prior climate negotiations.
QUESTION:
In the figure, the numbers (1 through 6) refer to the regions demarcated by the various indifference
1.Does a win set exist that all of these actors (EU, US, China/India) prefer to the status quo? (Answer yes or no.)
2. If so, where is it? (Enter either the relevant number or NA.)
3.Given your answers, do you expect an agreement that moves policies away from the status quo? (Yes or No)
Given information
3 sets of the country
Rich country
Poor country
European Union
Rich country prefers larger emission cut by poor country
Poor country prefers larger emission cut by the rich country
European Union prefers to emission cut by both type of countries
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- Which is the best example of something which is nonrival in consumption? A) sharing a pizza with your family B) driving in a crowded city C) listening to public radio D) swimming in a public poolarrow_forwardParks confer many external benefits on society: open space, trees that reduce pollution, and so on. Therefore, the market equilibrium quantity of parks is not equal to the socially optimal quantity. The following graph shows the demand for parks (their private value), the supply of parks (the private cost of producing them), and the social value of parks, including both the private value and external benefits. Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the market equilibrium quantity. Next, use the purple point (diamond symbol) to indicate the socially optimal quantity.arrow_forwardSpring is here, and Manuel and his grandfather would like to go fishing for the weekend in Florida. Manuel could either go to the lake in town where anyone can fish without a permit, or he could drive up to a pond located on his family's property in the countryside to fish. Assume that, no matter where people fish, all of the fish that are caught would be kept (that is, there is no "catch and release" policy). The fish in the lake are considered and whereas the fish in the private pond are and . In other words, the fish in the lake are an example of , and the fish in the private pond are an example of . Fishing in the lake will likely lead to because of which of the following reasons? Nobody will enjoy fishing because of the lack of private contributions to the maintenance of the lake. Anyone can fish in the lake, and one person's fishing activity decreases the ability of someone else to fish with success. All fishermen will…arrow_forward
- One of the things that Theodore Roosevelt tried to do, both as a President, and later, as a presidential candidate, was to define the role of the federal government. A big piece of the puzzle was to determine the way that the federal government would relate to big business, particularly big business serving a public function. In Europe, many national governments chose to take ownership of some businesses, particularly railroads and public utilities. Roosevelt had a different take on the role of the federal government of the United States. What role did Roosevelt think was proper for the federal government, and why?arrow_forwardBriefly explain why the environmental protection efforts and public part beautification are unlikely to happen in a free market unless the government provides them.arrow_forward2. What Role for Government? In Naked Economics, Chapter 3 (in eReserves), Wheelan describes a number of ways in which the "government is your friend" in a well- functioning society and economy. List and explain two ways that, in your everyday lives, there is a need for an effective government role in an economy. Explain how this government role does or does not solve a market failure such as an externality.arrow_forward
- Suppose households do not care much for better environmental quality. Use the demand & supply model for urban labor to illustrate what happens to total employment (L) when a tax is imposed on firms to internalize the negative externalities of pollution. Briefly discuss.arrow_forwardWhich goods are sold in the markets? private goods public goods private goods and club goods private good, club goods, and common- resource goods all types of goodsarrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





